Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
What is the bond angle in a bent molecule, such as water?
A | 90° | B | 104.5° | C | 107.3° | D | 109.5° | E | 120° |
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the bond angle in a trigonal planar molecule?
A | 90° | B | 104.5° | C | 107.3° | D | 109.5° | E | 120° |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following statements about ionic bonding is
INCORRECT.
A | The force of attraction between oppositely charged ions (cations and anions)
consitutes an ionic bond. | B | Ionic bonding occurs between atoms of elements
that have large differences in electronegativity. | C | The units of ionic compounds can be seperated
easily by direct heating of the crystal salt. | D | The ions that make up the ionic solid are
arranged in a specific array of repeating units. | E | The ions that make up the ionic solid are
arranged in a rigid lattice structure so that the cations and anions are arranged so that the system
has the minimum possible energy. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which one of the following statements about covalent bonding is
CORRECT.
A | Covalent bonding involves a balance between the forces of attraction and replusion
that act between the nuclei and electrons of two or more atoms. | B | There is an optimum
seperation between the individual atoms involved in a covalent bond at which the nucleus-electron
repulsions, nucleus-nuclues attractions, and electron-electron attractions acheive a
balance. | C | Lithium Sulfide is an example of a molecule with covalent bonds. | D | A covalent bond
involves the formation a new orbital, caused by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. The new
orbital has energy levels that are higher than those of the original atomic
orbitals. | E | In many cases, electron sharing enables each atom in a covalent bond to acquire full
d orbital. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following statements about the following structure and molecular
polarity diagrams is INCORRECT. 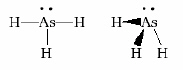 A | AsH3 has the VSEPR notation AX3E | B | The molecular shape
would be classificed as trigonal pyramidal. | C | The difference in electronegativity for As and H
is basically zero. | D | The molecule would not have a overall
dipole. | E | none of the above are incorrect |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following statements is CORRECT for two bonded atoms that
have very different electronegativities.
A | The atom with the higher electronegativity attracts the shared electrons more
strongly than the atom with the lower electronegativity. | B | The atom with the
lower electronegativity attracts the shared electrons more strongly than the atom with the higher
electronegativity. | C | If the DEN is greater
than 0.4 and less than 1.7 the bond is considered polar. | D | both A and C are
correct | E | only A is correct |
|
|
|
7.
|
An expanded valence energy level can be defined as
A | an atom is 8 electons forming around a bonded atom | B | an atom with more
than 8 electrons forming around a bonded atom | C | an atom with a maximum of 2 bond
| D | an atom following the octect rule | E | none of the
above |
|
|
|
8.
|
The term that is used to refer to the ways in which groups of valence electrons
are positioned around the central atom of a molecule.
A | molecular shape | D | bond energy | B | electron group arrangement | E | resonance structures | C | polar
bonds |
|
|
|
9.
|
Electron dot diagrams are used to represent the Lewis model of the arrangement
of electrons in atoms. Which of the following statements regarding electron dot diagrams is
INCORRECT?
A | It is made up of the chemical symbol and dots indicating the number of electrons in
the valence energy level. | B | They can help us represent both atoms or their
ions | C | They illustrate the theory that ionic bonds tend to produce full outer orbits of
electrons: a configuration exactly the same as that of the noble gases. | D | Four valence orbitals
are represented by the four sides of the element symbol. | E | Pairs of dots around
the symbol represent the bonding capacity of the atom. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Binary ionic compounds
A | contain two ions with charges of 2+ and 2– | B | are formed from the
combination of two nonmetal ions | C | are composed of only two kinds of monatomic
ions | D | contain a transition metal cation | E | contain double
bonds |
|
|
|
11.
|
A student records the following evidence in a lab book. Unknown Substance | Pure State | Solubility in Water | Solution Conductivity | I | solid | high | low | II | solid | low | low | III | solid | high | none | IV | solid | high | high | | | | |
Which of the substances shown in the table above is most likely an
ionic compound? A | I | D | IV | B | II | E | none of the above | C | III |
|
|
|
12.
|
The number of valence electrons in a fluorine atom is
|
|
|
13.
|
According to the Lewis model of the atom, the number of bonding electrons in a
nitrogen atom is
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following atoms is believed to contain three lone pairs of
electrons?
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following formulas does NOT represent a molecular
compound?
A | CO2(g) | B | CoCl2(s) | C | SO2(g) | D | PCl5(g) | E | HCl(g) |
|
|
|
16.
|
The concept of multiple covalent bonds is used to explain the molecular formula
of
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is the proper electron dot diagram for NaCl?
|
|
|
18.
|
If XF2 is the correct formula for a metallic fluoride, then the
formula for the oxide of X is
|
|
|
19.
|
A metallic element X forms a carbonate with the formula
X(CO3)2. The corresponding fluoride compound of element X would have the
formula
|
|
|
20.
|
When both electrons that make up a bond are provided by the same atom, the bond
is called a _________________________ bond.
A | polar covalent | C | co-ordinate covalent | B | ionic bond | D | molecular |
|