Eye Receptors

The human eye is an organ that reacts with light and dark. Rod and cone cells are photoreceptors in the retina, allowing humans to see color and adjust to darkness. Cone cells enable humans to see up to 10 million different colors. Once light comes through the eye, the image from the right eye crosses with the image from the left and goes to the optic nerve and produces the final image in which you see.
Sensory receptors are found everywhere in the body. Each receptor has different impulses that allow the body to react to touch, pain, pressure, et cetera. Some examples of sensory receptors are:
-Mechanoreceptors: pressure, touch, stretch, motion, and sound
-Chemoreceptors: taste and smell
-Electromagnetic: photoreceptors
-Thermoreceptors: body surface and core temperature
-Pain: stimulus becomes translated into a negative reaction
-Light Receptors: provide info about light intensity
-Exteroreceptors: outside world
-Interoreceptors: internal environment
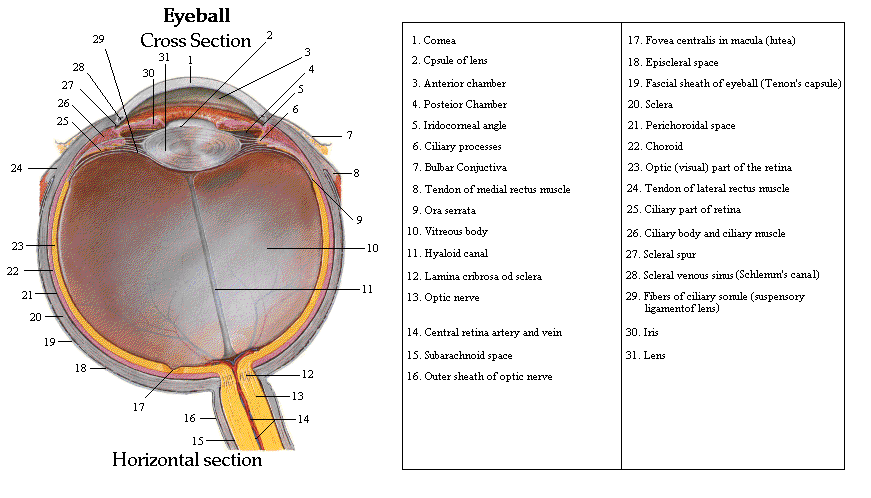
The eye has many parts that help us see. First, the eyes have to process the light. the light then passes through the cornea and then the lens. Both of those images combine to produce a clear image on a sheet of photoreceptors called the retina. Photo receptors gather information by taking in light and then sending electrical signals to other neurons. The signals are then sent to other parts of the brain via the optic nerce. Which our brain is the ultimate location that processes the image and allows us to see.
Works Cited
Vision: It all starts with light. (2012, April 1). Retrieved from http://www.brain.org
Regulation of synaptic. (2012, October 22). Retrieved from http://jp.physoc.org
(2011). This is a mammalian imaging forming eye. (2011). [Web Photo]. Retrieved from http://carolguze.com/text/102-25-ReceptorsNervousSystem.shtml
Novartis, F. (Artist). (2011). Basic anatomy. [Web Photo]. Retrieved from http://www.ivo.gr/en/patient/information-eye/information-eye.html

The human eye is an organ that reacts with light and dark. Rod and cone cells are photoreceptors in the retina, allowing humans to see color and adjust to darkness. Cone cells enable humans to see up to 10 million different colors. Once light comes through the eye, the image from the right eye crosses with the image from the left and goes to the optic nerve and produces the final image in which you see.
Sensory receptors are found everywhere in the body. Each receptor has different impulses that allow the body to react to touch, pain, pressure, et cetera. Some examples of sensory receptors are:
-Mechanoreceptors: pressure, touch, stretch, motion, and sound
-Chemoreceptors: taste and smell
-Electromagnetic: photoreceptors
-Thermoreceptors: body surface and core temperature
-Pain: stimulus becomes translated into a negative reaction
-Light Receptors: provide info about light intensity
-Exteroreceptors: outside world
-Interoreceptors: internal environment
The eye has many parts that help us see. First, the eyes have to process the light. the light then passes through the cornea and then the lens. Both of those images combine to produce a clear image on a sheet of photoreceptors called the retina. Photo receptors gather information by taking in light and then sending electrical signals to other neurons. The signals are then sent to other parts of the brain via the optic nerce. Which our brain is the ultimate location that processes the image and allows us to see.

Works Cited
Vision: It all starts with light. (2012, April 1). Retrieved from http://www.brain.org
Regulation of synaptic. (2012, October 22). Retrieved from http://jp.physoc.org
(2011). This is a mammalian imaging forming eye. (2011). [Web Photo]. Retrieved from http://carolguze.com/text/102-25-ReceptorsNervousSystem.shtml
Novartis, F. (Artist). (2011). Basic anatomy. [Web Photo]. Retrieved from http://www.ivo.gr/en/patient/information-eye/information-eye.html