This Picture Below Portrays The Basic Features Of Neurons And Each Feature’s Different Function In The Cell.
Picture obtained from enchantedlearning.com/thebrain
The Cell Body
-where the nucleus is located in the neuron.
The Nucleus
-where the genetic material of the cell is located.
Myelin Sheath
-surrounds and protects the nerve fibers.
Node
-gaps between the myelin sheath (where action-potential occurs).
-carries the nerve impulses.
-produce myelin.
-send impulse across synapse to dendrites.
-attached to the cell body, receive the impulse.
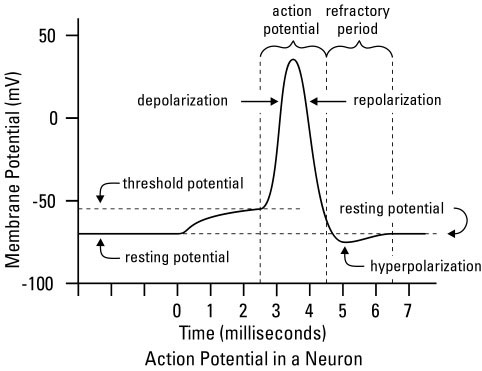
This picture was obtained from media.wiley.com
1. Resting Potiental when the charge of the nueron is -70mv.
2. Threshold Potentail is when the charge of the nueron is -55mv.
3. Depolarization occurs when the charge if the nueron moves toward 0mv.
4. Action Potiental breaks threshold and the impluse is sent.
5. Refractory Period is when the charge of the nueron is below -70mv; this makes it difficult to stimulate the nueron.
6. Repolarization is when the charge of the nueron moves back to -70mv known as resting potential.
7. Resting Potential when the charge of the nueron is -70mv.
8. Hyperpolarization when the charge drops below -70mv.