| A | B |
|---|
What does "A" in this graph represent?,  | Energy of activation without an enzyme present,  |
What does "B" in this graph represent?,  | The lowered energy of activation due to an enzyme being present,  |
What does "C" in this graph represent?,  | The change in free energy (∆G) for this reaction, which would be negative, indicating an exergonic reaction,  |
What is the green molecule called?, 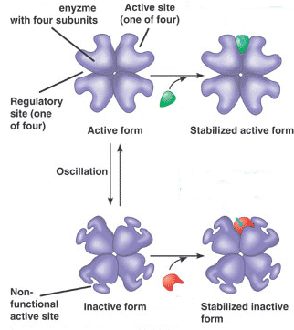 | an allosteric activator,  |
What is the red molecule called?,  | an allosteric inhibitor,  |
What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "A" represent?,  | "A" represents the three phosphate groups in ATP,  |
* What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "B" represent?,  | "B" represents the ribose sugar in ATP,  |
* What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "C" represent?,  | "C" represents the adenine (a nitrogenous base) in ATP,  |
What concept is this diagram showing and what does the blue molecule represent?,  | competitive inhibition, competitive inhibitor,  |
* What concept is being shown in this diagram?, 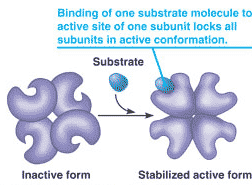 | cooperativity,  |
* The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | endergonic (notice the positive ∆G),  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction.,  | endergonic,  |
The change in free energy is ____ for this reaction.,  | positive,  |
The letter "A" represents a(n) ____.,  | active site,  |
The letter "B" represents a(n) ____.,  | enzyme,  |
The letter "C" represents a(n) ____.,  | substrate,  |
The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | exergonic (notice the negative ∆G),  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction., 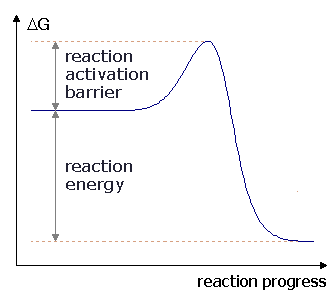 | exergonic,  |
The change in free energy is ____ for this reaction.,  | negative,  |
The molecules labeled "A" are known as the _____.,  | reactants,  |
The molecules labeled "B" are in the _____ state.,  | transition state,  |
The molecules labeled "C" are known as the _____.,  | products,  |
The arrow labeled "D" shows the ______.,  | change in free energy (∆G) for the reaction (which is negative indicating an exergonic reaction),  |
The difference in free energy between A and B is called the ____.,  | energy of activation,  |
This diagram shows a type of metabolic regulation called _____.,  | feedback inhibition,  |
Which molecule acts as the inhibitor in this diagram and what kind of inhibitor is it?,  | isoleucine acts as an allosteric inhibitor,  |
This diagram represents the concept of a _______., 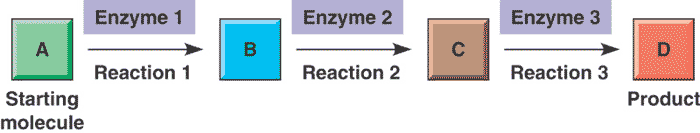 | metabolic pathway (Involves multistep processes to go from the reactant to the final product. Each step is regulated by a different enzyme. "B" and "C" are intermediary products),  |
This diagram shows _____ inhibition. The red molecule is a(n) _______ inhibitor.,  | non-competitive inhibition, allosteric inhibitor,  |
| A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics is called a(n) ______. | competitive inhibitor |
| Any non-protein molecule or ion that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme is called a(n) _____. | cofactor |
| The reactant on which an enzyme works is called the _____. | substrate |
| ______ energy is energy stored by matter as a result of location or spatial arrangement. | Potential energy |
| A protein serving as a catalyst is called a(n) ____. | enzyme |
| Any substance, organic or inorganic, that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction is called a(n) _____. | catalyst |
| Another word for thermal energy is ____. | heat |
| Another word for heat is ____. | thermal energy |
| An organic cofactor is called a(n) _____. | coenzyme |
| Most vitamins serve as ____ in important metabolic reactions. | coenzymes |
| The specific portion of an enzyme that attaches to the substrate by means of weak chemical bonds is called _____. | the active site |
| A metabolic pathway that synthesizes a complex molecule from simpler compounds is called a(n) ______ pathway. | anabolic |
| A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule (anabolic pathway) or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler molecules (catabolic pathway) is called a(n) _______ | metabolic pathway |
| The change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate is referred to as _____. | induced fit |
| A metabolic pathway that releases energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds is called a(n) _____. | catabolic pathway |
| An interaction of the constituent subunits of a protein whereby a conformational change in one subunit is transmitted to all the others. | cooperativity |
| The study of energy transformations is called ____. | thermodynamics |
| A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate is called a(n) ____. | non-competitive (or allosteric) inhibitor |
| An adenine-containing nucleoside triphosphate that releases free energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed. This energy is used to drive endergonic reactions in cells. | ATP (adenosine triphosphate) |
| A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s). | enzyme-substrate complex |
| The amount of energy that reactants must absorb before a chemical reaction will start. | Energy of activation (or activation energy) |
| A type of regulation that involves the binding of a molecule to a protein that affects the function of the protein at a different site. | allosteric regulation |
| A spontaneous chemical reaction, in which there is a net release of free energy. | exergonic reaction |
| The energy of motion, which is exponentially related to the speed of that motion is called ____ energy. Moving matter does work by imparting motion to other matter. | kinetic |
| A quantitative measure of disorder or randomness is called ____. | entropy |
| The symbol for entropy is ___. | S |
| The principle of conservation of energy which states that energy can be transferred and transformed, but it can't be created or destroyed. | first law of thermodynamics |
| Energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules; a form of potential energy. | chemical energy |
| A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway. | feedback inhibition |
| The principle whereby every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe. Ordered forms of energy are at least partly converted to heat, and in spontaneous reactions, the free energy of the system also decreases. | second law of thermodynamics |
| In cellular metabolism, the use of energy released from an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction | energy coupling (the reactions would be called coupled reactions) |
| A non-spontaneous chemical reaction, in which free energy is absorbed from the surrounding. | endergonic reaction |
| The total amount of kinetic energy due to molecular motion in a body of matter. | heat |
| The average kinetic energy of a body of matter. | temperature |
| A molecule that has been the recipient of a phospate group is said to have been ____. | phosphorylated |
| The portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system is called ___. | free energy |
| To calculate whether a reaction will be spontaneous or not, you need to calculate the ______ using the equation ______ | The potential change in Gibb's free energy using the equation ∆G= ∆H- T∆S where ∆H is the change in enthalpy, T is temperature in degrees Kelvin and ∆S is the change in entropy |
| A positive ∆H means that a reaction will be ____. | endothermic |
| A negative ∆H means that a reaction will be ____. | exothermic |
| A positive ∆G means that a reaction will be ____. | endergonic and non-spontaneous |
| A negative ∆G means that a reaction will be ____. | exergonic and spontaneous |
| A positive ∆S means that ____. | The products of the reaction are more disordered (have higher entropy) than the reactants |
| A negative ∆S means that ____. | The products of the reaction are more ordered (have lower entropy) than the reactants. |