| A | B |
|---|
| Simple animals like sponges, cnidarians, flatworms, and earthworms accomplish gas exchange through ___________. | their skin |
| Insects accomplish gas exchange through holes called ____ that lead to ______. | spiracles, tracheal tubes,  |
| In arthropods and some mollusks, there is a type of blood called _____ that uses a molecule called ______ instead of hemoglobin to bind oxygen and this molecule uses _______ instead of iron as its core atom. | hemolymph, hemocyanin, copper |
| _______ is an oxygen carrying molecule with iron as its oxygen binding atom. | hemoglobin,  |
| The principle of running water across gills in the opposite direction that blood flows in the gills in order to maximize diffusion is called _______. | Countercurrent exchange,  |
| Trace the path of air as it travels through the nose to the parts of the lung where diffusion occurs | pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, broncheoles, alveoli,  |
| Plants with leaves respire through holes in the leaf called ______. | stomata,  |
| The microscopic air sacs where diffusion of gases occur in the lungs are called _______. | alveoli |
| Air is drawn into lungs by _____ pressure. | negative pressure (As the diaphragm contracts and the muscles of the rib cage cause the chest cavity to expand, the pressure decreases as the volume of the chest cavity increases. This reduces the pressure on the lungs causing it to be less than air pressure from outside. Air is drawn into the lungs due to this "negative" pressure., 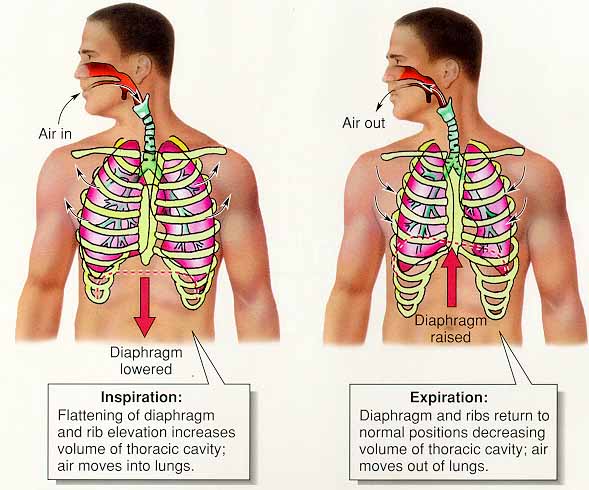 |
| Which muscle forms the bottom wall of the chest cavity and is partially responsible for causing inhalation when it contracts? | diaphragm,  |
| Which part of the brain controls breathing? | The medulla (it senses changes in pH caused by changing carbon dioxide levels in the blood and adjusts the breathing rate accordingly) |
| The medulla senses changes in _____ caused by changing ________ levels in the blood and adjusts the breathing rate accordingly. | pH, carbon dioxide |
| Blood pH lower than 7.4 causes a(n) ______ in breathing rate. | increase (pH is lowered by carbon dioxide being released by cells to form carbonic acid in blood. If cells are undergoing heavy cellular respiration, they are giving off a lot of carbon dioxide, lowering the pH of blood, which signals the medulla to increase the breathing rate to facilitate the high rate of cellular respiration) |
| Blood pH greater than 7.4 causes a(n) ______ in breathing rate. | decrease |
| A drop in pH _____ the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. | lowers (blood pH is lowest around cells giving off a lot of carbon dioxide due to cellular respiration. These cells need oxygen. Hemoglobin will drop off its oxygen in the area of these cells because its affinity for oxygen has been lowered) |
| The Bohr shift describes the phenomena of ______. | hemoglobins reduced affinity for oxygen at lower pH's.,  |
| Whose hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen, a pregnant woman's or her fetus' ? | The fetus' hemoglobin has to have a higher affinity for oxygen or else it wouldn't be able to pry the oxygen away from the mother's blood.,  |
| Which substance dissolved in blood acts as a buffer against rising pH? | carbon dioxide (notice in the bottom equation how carbon dioxide removes hydroxide ions which would otherwise cause pH to rise),  |
| Which substance dissolved in blood acts as a buffer against increasing acidity? | The bicarbonate ion (notice in the top equation how an increase in the hydrogen ion equation will cause a reaction that will produce more carbonic acid as it combines with the bicarbonate ion. This prevents large increases in the acidity that the hydrogen ion would otherwise cause),  |
| In what two forms is carbon dioxide carried through the circulatory system? | Carbon dioxide reacts to form carbonic acid and the bicarbonate ion, both of which are highly soluble in blood plasma. Carbon dioxide itself is a gas that would create bubbles in your bloodstream (not good),  |
| Trace the path of blood through the heart (including the trip to the lungs and the names of the semilunar and atrioventricular valves). | 1. Inferior (a.k.a. - posterior) / superior (a.k.a. - anterior) vena cavas 2. Right atrium 3. Tricuspid valve 4. Right ventricle 5. Pulmonary valve 6. Pulmonary artery 7. Lung capillaries 8. Pulmonary vein 9. Left atrium 10. Mitral valve 11. Left ventricle 12. Aortic valve 13. Aorta,  |
| The __________, located on the wall of the right atrium, sets the timing of the contractions of the heart and is often referred to as the pacemaker of the heart. | sinoatrial node (SA node) |
| The average heart pumps about _____ of blood per minute at a rate of ___ beats per minute. | 5 L, 70 beats/min |
| Electrical impulses from the heart can be detected by a(n) _______. | Electrocardiogram (EKG) |
| The average blood pressure for an adult is 120/80. 120 is the _____ pressure measured when the ventricles contract. 80 is the _____ pressure measured when the heart relaxes. | systolic, diastolic,  |
| The liquid portion of blood that contains dissolved clotting factors, hormones, antibodies, gases, nutrients and waste is called ______. | plasma, 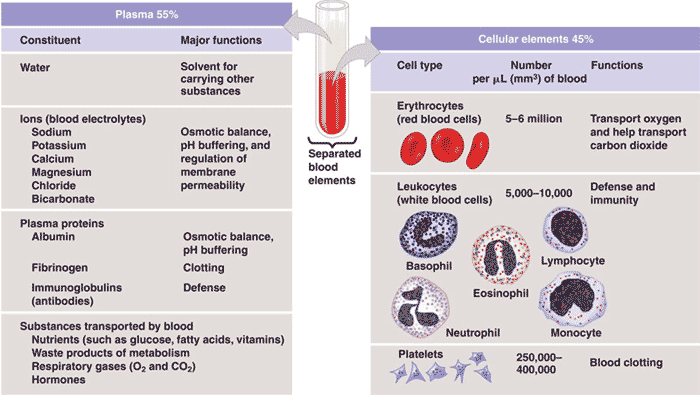 |
| The scientifc name for red blood cells is ________. | erythrocyte,  |
| The scientifc name for white blood cells is ________. | leukocyte,  |
| The scientific name for platelets is ________. | thrombocyte,  |
| Fragments of cells that are involved with blood clotting are called ____. | platelets (a.k.a. thrombocytes),  |
| Neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes are types of _____. | white blood cells (leukocytes),  |
| Red blood cells are unique in that they don't carry a(n) _____. | nucleus |
| A circulatory system in which blood travels through vessels to and from the heart in a circuit is called a(n) _________. | closed circulatory system (examples of organisms with a closed circulatory system include earthworms and humans) |
| A circulatory system in which blood only travels through vessels for part of its journey is called a(n) __________. | open circulatory system (examples of organisms with an open circulatory system include crustaceans and mollusks) |
| Blood clotting begins with the release of _____ from platelets and damaged tissue. | clotting factors |
| Another word for a blood clot is a(n) ____. | thrombus |
| The inactive plasma protein called _______ is activated by a complex set of reactions initiated by the release of clotting factors that cause ______ to turn into its active form called ______ | fibrinogen (inactive form) --> fibrin (active form that forms a mesh, trapping materials to form a clot) |
| The heart is made of a type of muscle called _____ muscle. | cardiac (the other two types of muscles are the smooth (involuntary) and the striated (voluntary). |
| Blood pressure is ______ in the arteries and ______ in the veins. | highest, lowest,  |
| How many chambers would a fish's heart have? | 2,  |
| How many chambers would an amphibian's heart have? | 3,  |
| How many chambers would a reptiles heart have? | 3 (but notice there is partial separation of the ventricles, so it could be argued that they have three-and-a-half chambers),  |
| How many chambers would a bird's heart have? | 4,  |
| How many chambers would a mammal's heart have? | 4,  |
| What type of animal has a zero chambered heart? | Chuck Norris, who doesn't have a heart. Just ask his victims,  |
| What is the advantage of having a 4 chambered heart? | Allows for the complete separation of oxygenated blood coming from the lungs from deoxygenated blood entering from the right atrium,  |