| A | B |
|---|
| The vertebrate nervous system can be broken down into two parts. What are they? | Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS),  |
| The ______ consists of the brain and spinal cord. | central nervous system (CNS),  |
| The _____ consists of all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. | peripheral nervous system (PNS),  |
| The part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles is called the _____. | cell body,  |
| The extensions of the neuron that receive incoming messages are the _____. | dendrites,  |
| The extension of the neuron that transmits a signal to another cell is called the _____. | axon,  |
| What are the three types of neurons? | sensory, motor, and interneuron (associated neuron) |
| What's another name for interneurons? | associate neurons |
| Where are interneurons found? | spinal cord |
| Interneurons receive ________ and transfer the information directly to a(n) ______ or the _______. | sensory stimuli, motor neuron or the brain. |
| A neuron can have hundreds of _____ but only one _____. | dendrites, axon,  |
| The peripheral nervous system can be broken into which two categories? | sensory and motor |
| The motor category of the peripheral nervous system can be broken into which two categories? | Somatic and Autonomic,  |
| The autonomic system can be broken into which two categories? | sympathetic and parasympathetic,  |
What is "A" referring to in the diagram below?, 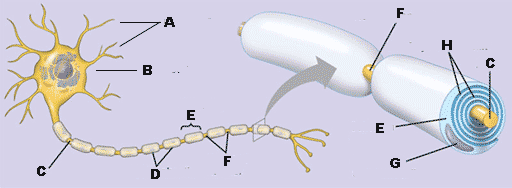 | dendrites,  |
What is "B" referring to in the diagram below?,  | cell body,  |
What is "C" referring to in the diagram below?,  | axon (it extends from the cell body to the end of the neuron),  |
What is "D" referring to in the diagram below?,  | myelin sheath,  |
What is "E" referring to in the diagram below?,  | Schwann cell,  |
What is "F" referring to in the diagram below?,  | nodes of ranvier,  |
What is "G" referring to in the diagram below?,  | nucleus of Schwann cell,  |
What is "H" referring to in the diagram below?,  | layers of myelin,  |
| The sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system is associated with ________. | the "fight or flight" response to danger (In response to danger the sympathetic nervous system increases heart and breathing rate, converts glycogen in the liver to glucose and releases it into the bloodstream, dilate blood vessels in lungs to increase gas exchange, and releases adrenalin) |
| The parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system is associated with ________. | calming the body by opposing the sympathetic system (heart/breathing rate decreases, enhances digestion by sending more blood to the digestive organs) |
| The simplest nerve response is the _____ because it doesn't involve the brain. | reflex arc (because the sensory signals don't have to travel all the way to the brain to affect a motor response, the reflex arc is a much quicker way to react to a dangerous stimulus, like touching a stove,  |
| _____ cells are supporting cells that are essential for the normal functioning of the neuron. | Glial cells (one type of glial cell is the Schwann cells that make up the myelin sheath in the PNS and oligodendrocytes that make up the myelin sheath in the CNS) |
| ______ cells are glial cells that form the myelin sheath around the axons of neurons in the peripheral nervous system, speeding the passage of impulses. | Schwann cells (Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheet around neurons of the CNS),  |
| Which type of cells form the myelin sheath in the central nervous system? | oligodendrocytes (in the peripheral nervous system, its the Schwann cells that form myelin) |
| What does the myelin sheath do to nerve impulses? | speed them up (the action potential jumps from one node of ranvier to the next, speeding up the impulse over what it would have been if the depolarization had to occur along the whole length of the axon. This jumping impulse is called saltatory conduction),  |
| Membrane potential is caused by a difference in _____ between the cytoplasm and the extracellular fluid surrounding the cell. | charge,  |
| _______ is caused by a difference in charge between the cytoplasm and the extracellular fluid surrounding the cell. | Membrane potential,  |
| A neuron in its unstimulated or polarized state (at resting potential) has a membrane potential of about ____mV. | -70 mV (the negative sign indicates that the inside of the cell is negatively charged compared to the extracellular fluid), 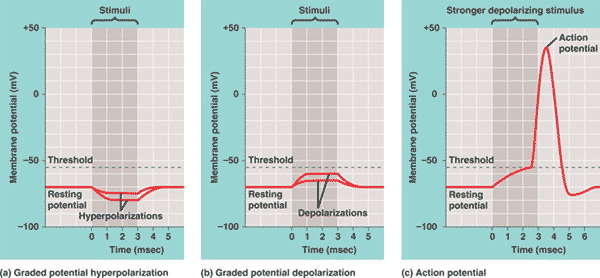 |
| A neuron at a membrane potential of -70 mV is at its _____ potential. | resting,  |
| If the membrane potential of a neuron reaches _____ mV, it is said to have reached its threshhold potential, at which point, voltage-gated ______ channels will open up causing the neuron to become depolarized. | -55 mV, sodium channels open up,  |
| In order to maintain the high concentration of ______ ions outside the neuron and the high concentration of _____ ions inside the neuron when the neuron is at "rest," energy must be used to power the _____ pump. | sodium (outside), potassium (inside), sodium-potassium pump, 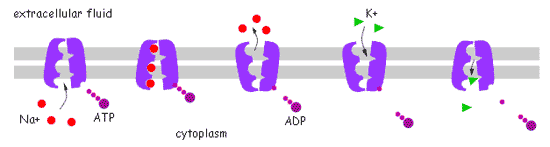 |
| If an axon is stimulated, sodium channels will briefly open to allow the neuron to become slightly _______. If the stimulation is great enough, the membrane potential will exceed the threshold potential (-55 mV) to initiate the _______ potential | depolarized, action potential,  |
| As an action potential propagates down an axon, ____ channels open first followed by _____ channels. | sodium, potassium,  |
| At the completion of the action potential, the _____ restores the concentration of sodium ions on the ____ of the membrane and _____ on the inside of the membrane in order to re-establish the _____ potential | sodium-potassium pump, sodium --> outside, potassium --> inside; resting potential (the part of the graph labeled D is where this all occurs), 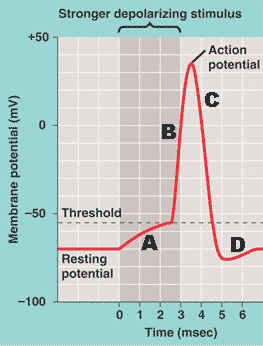 |
What is causing the change in the membrane potential seen around the letter A in the figure below?,  | A stimulus that is causing some sodium channels to open.,  |
What is causing the change in the membrane potential seen around the letter B in the figure below?,  | The opening of sodium channels (caused by crossing the threshold potential) and the rushing in of positively charged sodium ions.,  |
What is causing the change in the membrane potential seen around the letter C in the figure below?,  | The opening of potassium channels (caused by the depolarization of the membrane) which is allowing positively charged potassium ions to flow out of the cell (The K+ channels actually start to open up at -55mV, just like the Na+ channels, but the voltage-gated K+ channels open up more slowly, and also close more slowly, than the voltage-gated Na+ channels. Na+ also rushes in much faster than K+ rushes out because of the initial negative membrane potential inside the neuron attracts Na+),  |
What is causing the change in the membrane potential seen around the letter D in the figure below?,  | Toward the end of the action potential, some of the K+ gates start to close, causing a slow down in the leakage of K+ out of the neuron. The drop in membrane potential below the resting potential at the end of the action potential is called the "overshoot" and is caused by more K+ channels being opened than there are normally during the resting potential. As these gates close, more K+ stays inside and moves the inside of the neuron to the more positive average of -70mV compared to the -80mV during the overshoot.,  |
The period of time where the sodium-potassium pump is working to restore the membrane's resting potential (seen in the part of the graph labeled D below) is called the _______ period and during this time, the neuron can't ______,  | relative refractory period, neuron can't respond to another stimulus as easily (takes more stimulus to start another action potential because a lot of the sodium channels and potassium channels haven't reset themselves to the point where they can be opened again). Parts B and C of this graph are in the absolute refractory period because none of the channels are capable of opening again, because they haven't reset themselves.,  |
| If an axon is ______, the action potential (impulse) moves down the axon even faster because it leaps from node to node in ______ (jumping) fashion. | myelinated, saltatory,  |
| The body distinguishes between a strong outside stimulus and a weak one by the _____ of the action potentials. | frequency |
| The small space between the terminal axon branch of one neuron and the dendrite of the post-synaptic cell is called a(n) _____. | synapse, 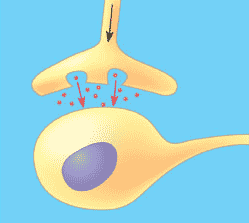 |
| The cytoplasm at the end of an axon contains many small vesicles. What's in those vesicles? | neurotransmitters,  |
| The entrance of _____ through gated channels in the presynaptic membrane stimulates vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane, releasing neurotransmitters into the synapse. | calcium ions (Ca++),  |
| What opens the calcium channels in the presynaptic membrane of the axon terminus? | Depolarization of the membrane caused by an arriving action potential (the calcium channels are voltage-gated channels),  |
| Once in the synapse, neurotransmitters bond with ______ embedded in the postsynaptic membrane. | receptors (usually a ligand gated channel that allows ions to flow into the postsynaptic neuron and stimulate an action potential),  |
| Neurotransmitters exit the presynaptic neuron by the process of ____. | exocytosis,  |
| Neurotransmitters in the synapse are either destroyed by _____ or taken back into the presynaptic neuron (reuptake) by active transport | enzymes,  |
| The most common neurotransmitter is ______. Others include seratonin, dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine (also used as hormones in the bloodstream) and GABA. | acetycholine,  |
| A gas that is used as both a neurotransmitter between neurons and a local regulator between other types of cells is ____. | NO (nitric oxide) |
The highlighted part of this human brain is called the ______.,  | cerebrum (which is composed of two cerebral hemispheres),  |
Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "A" pointing to?, 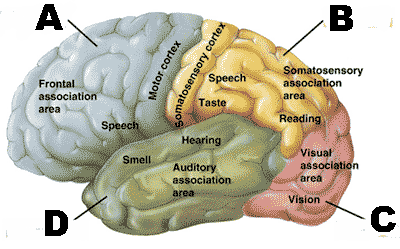 | Frontal Lobe,  |
Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "B" pointing to?,  | Parietal lobe,  |
Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "C" pointing to?,  | Occipital lobe,  |
Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "D" pointing to?,  | Temporal lobe,  |
| The thick band of axons that allows communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _____. | corpus callosum, 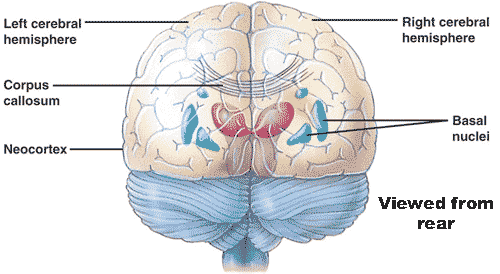 |
The cerebral cortex controls ______ and ______.,  | cognitive function and voluntary movement,  |
| The lymbic system is your _____ control center. | emotional,  |
The portion of the brain highlighted below is called the _____ and consists of the medulla oblongata, ponsk, and midbrain. It functions in homeostasis, coordination of movement, and conduction of information to higher brain centers., 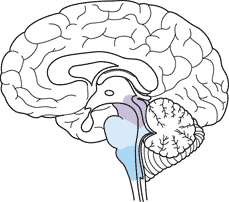 | brainstem (this is an older part of the brain in evolutionary terms and is sometimes called the reptilian brain),  |
The highlighted portion of the brain in the picture below is the ______., 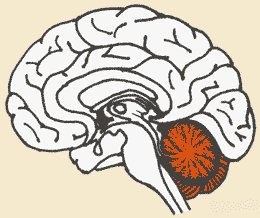 | cerebellum (The cerebellum is responsible for coordinating movement, planning, motor activities, learning and remembering of physical skills and for some cognitive abilities),  |
| Which part of the brain is associated with coordination and the memorization of physical skills (like skiing). | the cerebellum,  |
What is the system of neurons in the brainstem called that filters sensory input, passing on important information to the cerebral cortex?,  | reticular formation,  |
| Which lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is responsible for hearing and smell? | temporal lobe,  |
| Which lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is responsible for speech, reading, and taste? | parietal lobe,  |
| Which lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is responsible for vision? | occipital lobe,  |
| Which lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is most responsible for critical thinking, learning, and maturity? | frontal lobe,  |
| The part of the brain that is a bridge between the nervous and endocrine system is the _____. | hypothalamus |
| The three types of muscles are ____, ____, and ____. | smooth, cardiac and skeletal (striated) |
| Smooth muscles can also be called _____ muscles. | involuntary |
| Smooth (involuntary) muscles line the walls of the _____ and the _____. | blood vessels, digestive tract |
| Smooth muscles are under the control of the _____. | autonomic nervous system (smooth muscles are also called involuntary muscles because they are controlled by a part of the nervous system that is not under the direct control of conscious thought) |
| Which type of muscle is found in the heart? | cardiac |
| The _____ is modified plasma membrane that surrounds each muscle fiber and can propagate an action potential. | sarcolema |
| The _______ is modified ER that contains sacs of Ca++ ions necessary for normal muscle contraction. | sarcoplasmic reticulum,  |
| The _____ is the functional unit of the muscle fiber (cell). The boundaries are the _____, which give skeletal muscle its characteristic striated appearance. | sarcomere, Z-line, 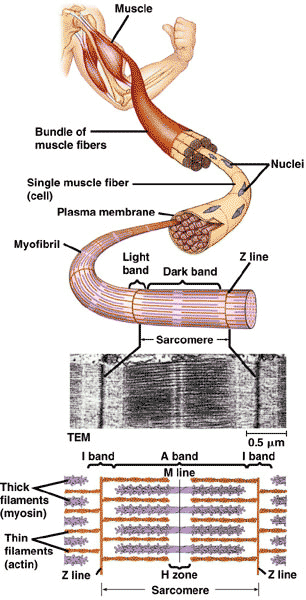 |
| Within the cytoplasm of each muscle cell are thousands of fibers called ______ that run parallel to the length of the cell. | myofibrils |
| Myofibrils consist of ______. | thick and thin filaments,  |
| Thin filaments consist of two chains of ____ wound around each other. | actin proteins,  |
| Each thick filament is composed of two chains of _____, each with a globular head at one end. | myosin molecules,  |
| Muscles contract as ____ and ____ slide over each other. | thick and thin filaments,  |
Which ion allows thick and thin filaments to develop cross bridges so they can interact?,  | calcium ions (Ca++),  |
| The axon of a motor neuron synapses on a skeletal muscle at the _________. | neuromuscular junction |
| Which neurotransmitter stimulates muscle contraction? | acetylcholine (Ach), 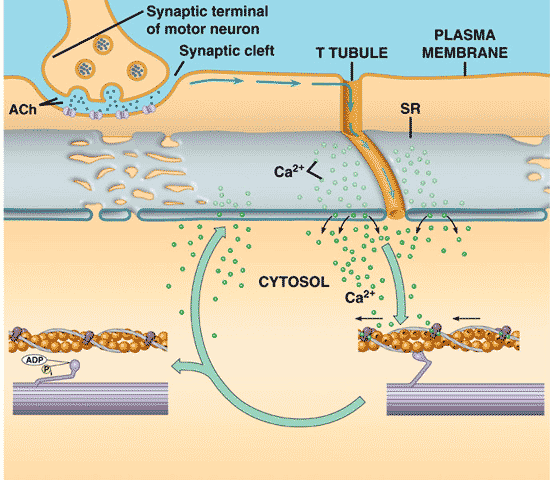 |
| Acetylcholine released into the neuromuscular synapse binds to receptors on the _____, depolarizing the muscle cell membrane to set up an action potential. | sarcolema,  |
| The ______ is a system of tubules that connects the sarcoplasmic reticulum to the extracellular fluid | T system,  |
| _____ connects muscle to bone. | Tendons (ligaments connect bone to bone), 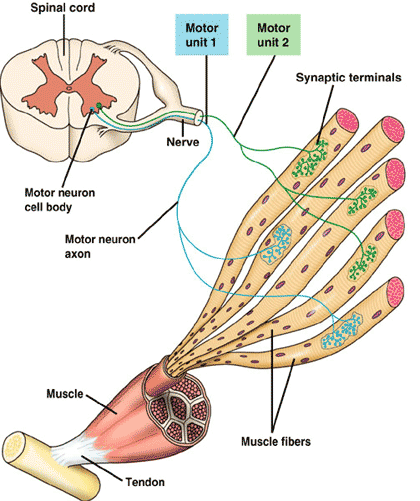 |
| A ____ consists of a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls. | motor unit,  |
What does "A" refer to?, 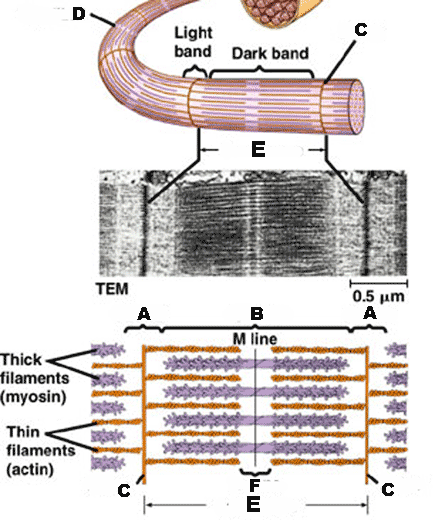 | I - band, 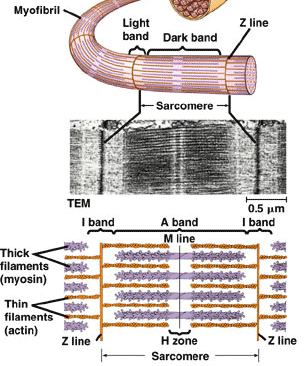 |
What does "B" refer to?,  | A - band,  |
What does "C" refer to?,  | Z - line,  |
What does "D" refer to?,  | myofibril,  |
What does "E" refer to?,  | sarcomere,  |
What does "F" refer to?,  | H-zone,  |