| A | B |
|---|
Brown black pigment seen here is:, 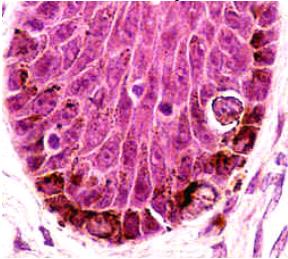 | melanin |
Identify the black granules shown here:, 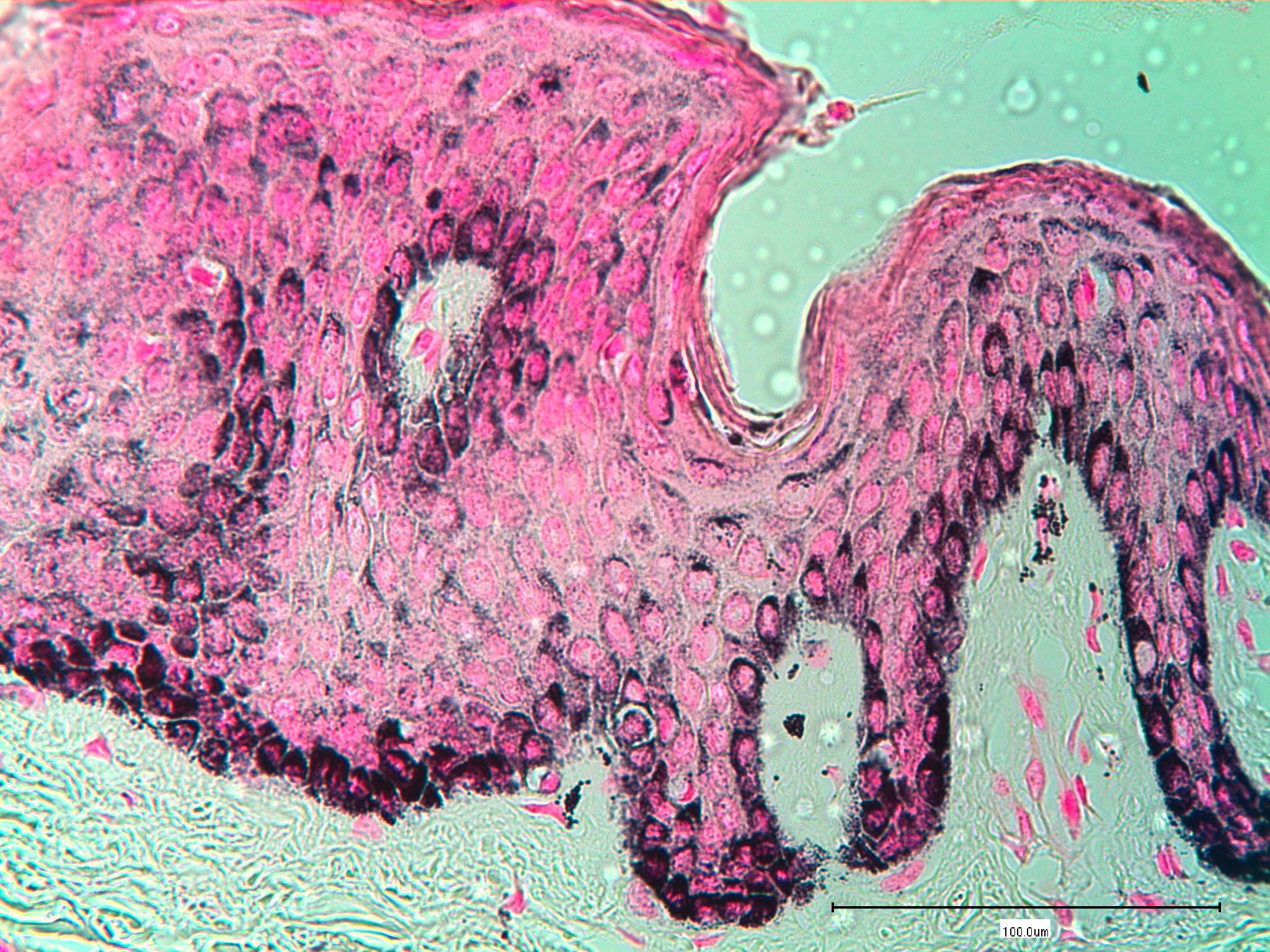 | argentaffin granules |
| A method specific for melanin pigment | ferrous ion uptake |
| Pigment that cannot be bleached, dissolved out of tissue, or demonstrated with special strains | carbon |
Identify this staining technique:, 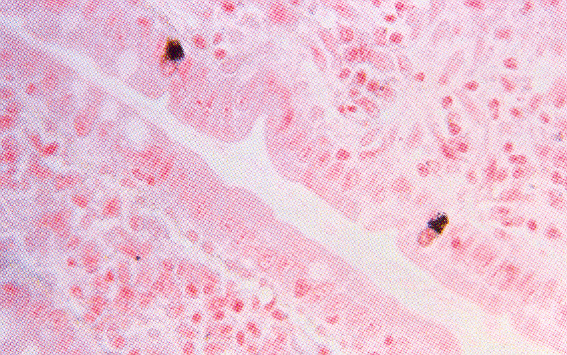 | Fontana-Masson |
| Tumor associated with exposure to asbestos | mesothelioma |
| Hemosiderin-laden machrophages in the lungs are caused by | cardiac failure |
The red structures seen here are stained by:,  | NFR |
| Demonstrates with the argentaffin reaction | melanin |
| The Schmorl method will stain reducing substances | blue |
The tissue seen here is:, 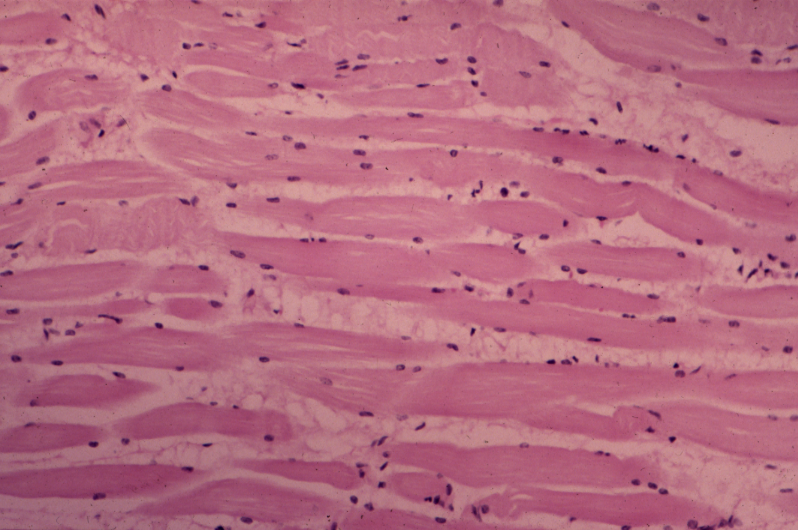 | skeletal muscle |
| Melanin is insoluble in | acetone |
| Melanoma may be confirmed by using | DOPA osidase |
| Fixation pigment caused by not rinsing in water | chrome |
| Calcium is demonstrated by | Von Kossa |
| Urate crystals are demonstrated by | GMS |
| Iron and copper are demonstrated by | Mallory's |
| A malignant neoplasm of connective tissue | sarcoma |
| Pigment present in portal area of liver with billiary cirrhosis | copper |
| Disorder of excess iron in tissues which causes tissue damage | hemochromatosis |
| Calcium oxalate is best demonstrated by | pizzolato |
| ATPase demonstrates enzyme activity in | muscle fibers |
| Skeletal muscle biopsies used for enzymes should be | prechilled in isopentane |
| A monoclonal antibody for demonstration of melanoms | HMB-45 |
| A monoclonal antibody used to demonstrate neuritic plaques | beta amyloid protein |
The substance staining emerald-green seen here is:,  | bilirubin |
| Microincineration involves | temperatures around 650 degrees Celsius and the use of paraffin embedded tissue |
| An increase in aluminum | Alzheimer's disease |
| Silica | anthracotic pigment |
The pigment seen here may be bleached with:,  | potassium permanganate |