| A | B |
|---|
| ______ produce their organic molecules from carbon dioxide and other organic raw materials obtained from the environment. | Autotrophs p184 |
| _______ are autotrophs that use light as a source of energy to synthesize organic substances. | Photoautotrophs p184 |
| What are three types of organisms that are photoautotrophs? | All plants, some Protists and some Prokaryotes p184 |
| Photosynthesis converts _____ energy to the ______ energy of food. | light, chemical p184 |
| _____ are the major sites of photosynthesis in most plants. | Leaves p186 |
What is "A" referring to?, 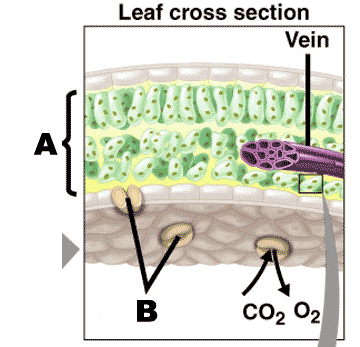 | The mesophyll layer of a leaf (The root word "meso" means middle) p186,  |
What is "B" referring to?,  | stomata p186,  |
What is #1 pointing to?,  | a thylakoid p186,  |
What is #2 pointing to?,  | A granum (a stack of thylakoids) p186,  |
What is #3 pointing to?,  | The stroma p186,  |
| How many molecules of water are "actually" used and produced to make one molecule of glucose during photosynthesis? | 12 used, 6 produced p187 |
| What is the net chemical equation for photosynthesis? | The equation below shows the net usage and production of molecules in photosynthesis. In reality, 12 water molecules are used as reactants and 6 water molecules are produced. p187,  |
| Energy from the sun is used to produce the high energy molecules NADPH and ATP during the ______ reactions of photosynthesis. | light p188,  |
| Energy from the sun is used to produce the high energy molecules ______ and ______ during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | NADPH and ATP p188,  |
| Electrons are stripped from water, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules during the ______ reaction of photosynthesis. | light p188,  |
| Electrons are stripped from _____, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | water p188 |
| _______ are stripped from water, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | electrons p188,  |
| Electrons are stripped from water, producing _________ and ________ molecules during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules p188,  |
| The _____ reaction of photosynthesis takes place on the thylakoid membrane. | light p189,  |
| The light reaction of photosynthesis takes place on the _________. | thylakoid p189,  |
| The _______ cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. | Calvin p189 |
| The Calvin Cycle takes place in the ______ of the chloroplast. | stroma p189 |
Which molecule belongs in the "A" spot?,  | water p188, 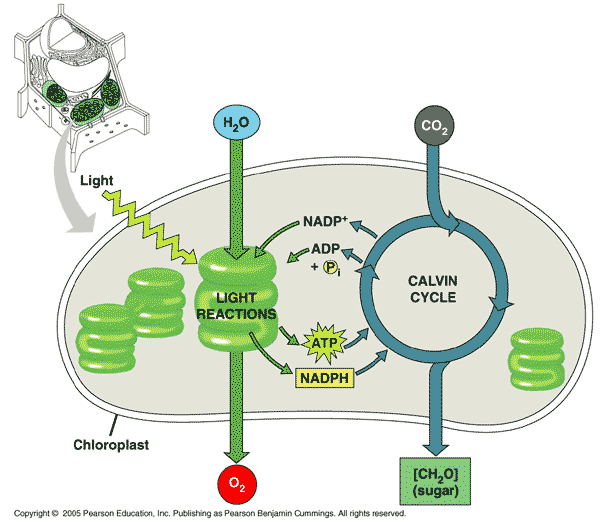 |
Which molecule belongs in the "B" spot?,  | oxygen p188,  |
Which molecule belongs in the "C" spot?,  | carbon dioxide p188,  |
Which molecule belongs in the "D" spot?,  | [CH2O] This is the generic formula for a carbohydrate. The actual carb that exits the Calvin cycle is a triose sugar called Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P). This molecule can be linked to form glucose, sucrose, or starch. Or it can be used as raw material to make amino acids and lipids. p188,  |
Which molecules belongs in the "E" spot?,  | NADP+ and ADP and P p188,  |
Which molecules belong in the "F" spot?,  | NADPH and ATP p188,  |
What is "A" pointing to?,  | photosystem I (a.k.a. P700) p197,  |
What is "B" pointing to?,  | NADP+ reductase p197,  |
What is "C" pointing to?,  | NADP+ (NADPH) p197,  |
| What is the final electron receptor in the light reaction of photosynthesis? | NADP+ (In cellular respiration, it is oxygen. However, whereas the electrons at the end of the electron transport chain of cellular respiration contain very little potential energy, the electrons that end up in NADP+ to form NADPH still contain a significant amount of potential energy, so NADPH, unlike water, is an energy carrier and will be used in the next phase, the Calvin Cycle, to drive endergonic reactions that build up carbohydrates) p195 |
| What supplies electrons to the electron transport chain of photosynthesis? | Water (when it is split) p194 |
| Where do hydrogen ions end up when they are moved by active transport during the light reaction of photosynthesis? | inside the thylakoid space p196,  |
| In which direction do protons (aka - hydrogen ions) flow through ATP synthase in the light reaction of photosynthesis? | From the thylakoid space out to the stroma of the chloroplast. p196,  |
What is "D" pointing to?,  | Photosystem II (a.k.a. P680) p197,  |
What is "E" pointing to?,  | Electron transport chain of photosynthesis p197,  |
What is "F" pointing to?,  | thylakoid space (also known as the thylakoid lumen) p197,  |
What is "G" pointing to?,  | thylakoid membrane p197,  |
What is "H" pointing to?,  | ATP synthase p197,  |
What is "I" pointing to?,  | stroma of the chloroplast p197,  |
| How is water split during photosynthesis? | With a Chuck Norris roundhouse kick (Actually, it's split by coming in contact with an enzyme in close proximity to a P680 that has lost an electron to the primary electron acceptor of photosystem II after having it's electron boosted to an excited state by light. This oxidized form of P680, now known as P680+ is the strongest biological oxidizing agent known, with an extremely high electronegativity, so it strips electrons from water with the help of the enzyme. But it's really Chuck Norris, because Chuck told me so) p194,  |
What is this graph showing?, 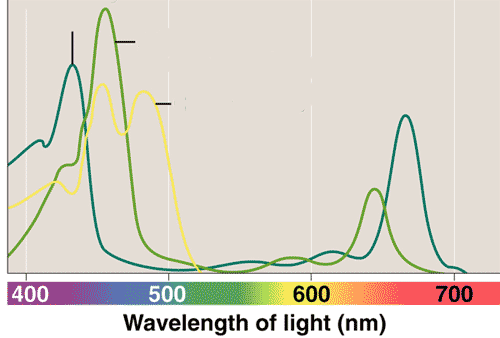 | The absorption spectra of chlorophyl a and b plus carotenoids p191,  |
The yellow line shows the absorption spectrum of ____.,  | carotenoids (carotene is one of the pigments classified as a carotenioid) p191,  |
The green line shows the absorption spectrum of ____.,  | chlorophyll b p191,  |
The blue-green line shows the absorption spectrum of ____.,  | chlorophyll a p191,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "A" spot?,  | gamma rays p189,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "B" spot?,  | X-rays p189,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "C" spot?,  | UV rays p189,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "D" spot?,  | visible light p189,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "E" spot?,  | infrared p189,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "F" spot?,  | microwaves p189,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "G" spot?,  | radiowaves p189,  |
Visible light has a wavelength range between ______ at the violet end and _____ at the red end.,  | 380 nanometers (violet end), 750 nm at the red end p189,  |
Violet light has ____ energy, _____ wavelength and ______ frequency compared to red light.,  | violet light has greater energy, shorter wavelength and higher frequency compared to red light p189,  |
| The frequency of electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional to ______ but directly proportional to _____. | frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength but directly proportional to the energy of the ray. p189 |
| Where do the ATP and NADPH that are produced during the light reaction head next? | the Calvin Cycle pp198&199 |
| What are two other names for the Calvin Cycle? | Dark reactions, light independent reactions p189 |
| The light reactions convert light energy to the chemical energy of ____ and _____. | ATP and NADPH p188 |
| When electromagnetic energy hits matter, it can either be _____, _____, or _____ depending on the wavelength of energy and type of matter. | absorbed, reflected, or transmitted p190 |
| When electromagnetic energy hits matter, it can either be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted depending on the _______ and _____. | wavelength of energy and the type of matter p190 |
What is "A" pointing to?, 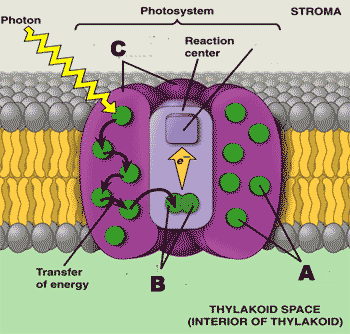 | Pigment molecules p193,  |
What is "B" pointing to?,  | special chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center p193,  |
What is "C" pointing to?,  | Light-harvesting complexes p193,  |
The red arrow signifies ______., 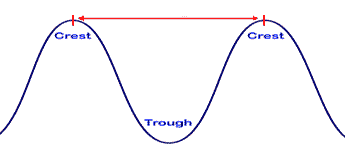 | The wavelength of this wave p189,  |
| Another word for electromagnetic energy is ______. | electromagnetic radiation p189 |
| The Calvin Cycle uses _____ and _____ to convert ______ to sugar. | ATP, NADPH, carbon dioxide p198 |
| The Calvin cycle for most plants occurs during the ____. | day p189 |
| Which enzyme helps fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in the Calvin cycle? | Rubisco pp.198&199 |
What is the name of molecule A?, 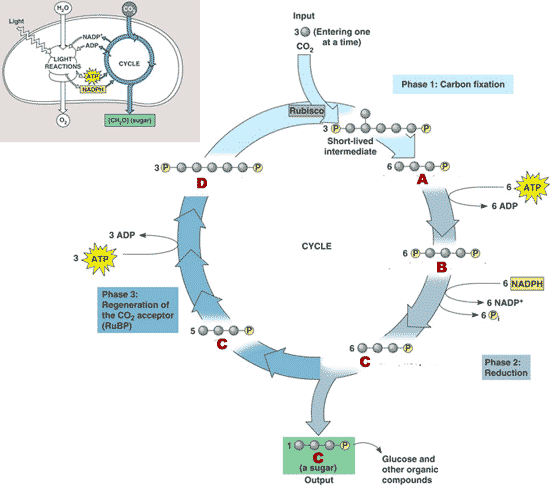 | 3-phosphoglycerate (This molecule is sometimes abbreviated as 3-PGA, but this book does not do that) pp.198&199,  |
What is the name of molecule B?,  | 1,3-biphosphoglycerate pp.198&199,  |
What is the name of molecule C?,  | G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate) ** This molecule is also commonly called PGAL, as it is in the cellular respiration tutorial. The PGAL stands for phosphoglyceraldehyde, which is just another, older name for glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. It is one of the molecules that is formed when glucose is split in cellular respiration. pp.198&199,  |
What is the name of molecule D?,  | RuBP (Ribulose biphosphate) pp.198&199,  |
| What is the full name of RuBP? | Ribulose biphosphate pp.198&199 |
| What is the full name of G3P? | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate (An older but still commonly used naming system refers to this molecule as phosphoglyceraldehyde, abbreviated PGAL) pp198&199 |
| What is the name of the 5-carbon starting molecule of the Calvin cycle? | RuBP (Ribulose Biphosphate) pp198&199,  |
| What is the name of the molecule that exits the Calvin cycle and is used as raw material to build other organic molecules? | G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate) pp198&199,  |
What is the name of the first phase of the Calvin cycle?,  | carbon fixation p199,  |
What is the name of the second phase of the Calvin cycle?,  | reduction phase p199,  |
What is the name of the third phase of the Calvin cycle?,  | Regeneration of the carbon dioxide acceptor RuBP p199,  |
| When the ________ are open to take in carbon dioxide during the day, the plant becomes vulnerable to water loss through _________. | stomata, transpiration p199 |
| When oxygen concentrations inside a plant leaf increase, the enzyme ______ may bind oxygen instead of carbon dioxide in an inefficient process called _____. | rubisco, photorespiration pp199&200 |
| In the C4 pathway, carbon dioxide is fixed by an enzyme in the outer mesophyll cells called _______ that has no affinity for molecular oxygen. | PEP carboxylase p200, 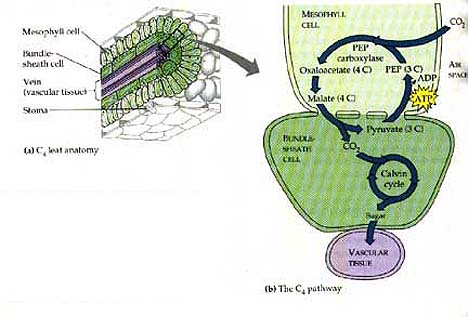 |
| Which alternate method of carbon fixation reduces photorespiration by separating carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle spatially? | C4 (Carbon fixation takes place in the outer mesophyll cells and is then funneled into the inner bundle-sheath cells where the Calvin Cycle takes place. This keeps the carbon dioxide concentrations high for rubisco) p200,  |
| Which alternate method of carbon fixation reduces photorespiration by separating carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle temporally? | CAM (CAM plants fix carbon dioxide at night and store the carbon in organic acids until daytime when the carbon is funneled into the Calvin Cycle. Separating something temporally means separating something by time, in this case, day versus night ) pp201&202, 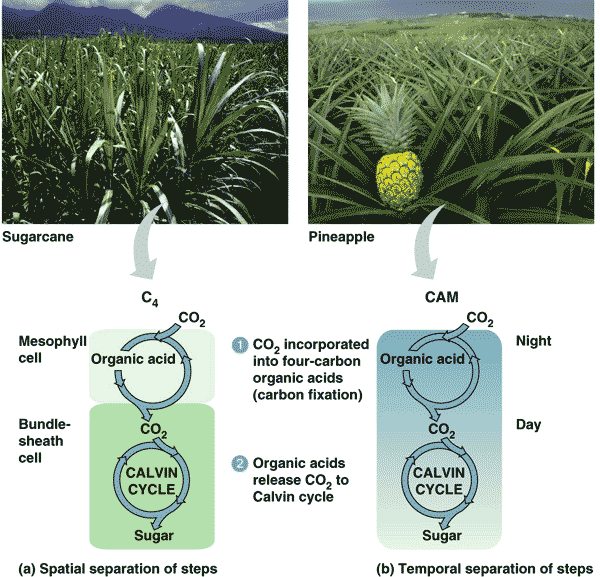 |
| Sugarcane and corn are examples of _____ plants (named for their mode of carbon fixation) | C4 p200,  |
| Pineapples and most cacti are _____ plants (named for their mode of carbon fixation) | CAM p201,  |
| Most plants, including rice, wheat, and soybeans are ____ plants (named for their mode of carbon fixation). | C3 (They are called C3 plants because the first product after carbon fixation is the 3 carbon molecule 3-phosphoglycerate) p200 |
| Many plants that evolved in ____, ____ climates have evolved alternate modes of carbon fixation such as C4 and CAM to reduce photorespiration. | hot, arid (arid means "dry") p200,  |
| Cyclic electron flow in the light reaction produces _____. | ATP only (Chloroplasts will switch to cyclic flow because they need more ATP for the Calvin cycle than they do NADPH. In addition, C4 plants use only cyclic flow in their bundle-sheath cells in the inner part of the leaf because they only have PSI, not the PSII which splits water and releases oxygen. This keeps oxygen levels low in the bundle-sheath cells which use rubisco to fix carbon dioxide that is being shuffled in by the outer mesophyll cells that fix carbon dioxide using PEP carboxylase (which, unlike rubisco, has no affinity for oxygen) to incorporate carbon dioxide into an organic molecule that then breaks off carbon dioxide after being shuttled into the inner bundle-sheath cells. This concentrates carbon dioxide in the bundle sheath cells without building up oxygen, so that rubisco won't photorespirate even though the stomata are partially closed during the hot daytime and oxygen levels are building up in the outer mesophyll cells. The C4 pathway also needs extra ATP provided by cyclic electron flow because ATP is needed to regenerate the organic molecule called PEP that is used in the outer mesophyll cells to bind carbon dioxide) pp195&200,  |
| Linear electron flow (also known as non-cyclic electron flow) in the light reaction produces _____. | Both ATP and NADPH (It is linear/non-cyclic because the electrons start off in water molecules and end up in NADPH after going through both PSII and PSI) pp193&194 |
| Which method of carbon fixation keeps stomata closed during the hot daytime hours and opens them up at night to fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules that will be broken down during the day to provide carbon dioxide to the Calvin Cycle? | CAM pp201&202,  |
| About how much of the organic material made by plants is consumed as fuel for cellular respiration in the mitochondria of the plant cells? | 50% (The rest helps the plant grow, much of it being converted to cellulose) p203 |
| What does the root word "meso-" mean? | middle (mesophyll cells are cells in the middle of C4 plant leaves while bundle-sheath cells are the innermost cells that surround the vein of the leaf),  |