Early Flight Navigation - Pilot's Sectional Project
________________________________________________________________________________
INTRODUCTION - Were you aware that mail pilots during the Golden Age of aviation use to fly using a sectional chart? A sectional is a navigation map designed for visual flight of slow or medium speed aircraft. Mail pilots used landmarks such as railroad tracks, water towers, rivers and lakes to fly from town to town, some only having a compass and a chart to navigate.
Pilots also used compass headings to navigate. COMPASS HEADINGS are directions you would follow (north, south, east, and west) using a compass reading from 0 degrees (due North) to 180 degrees (due south) to 90 degrees (due east) to 270 degrees (due west). DECLANATION LINES adjust for the error in the magnetic compass and they are also called variation lines. ROTATING BEACONS helped mail pilots fly at night. Airports would have light beacons that appeared to flash on and off and the pilots would follow the beacons to the airport.
An AERONAUTICAL SECTIONAL CHART is designed for visual navigation for slow or medium speed aircraft. Topographical information on these charts feature a portrayal of relief and a selection of visual checkpoints for visual navigation. The aeronautical information on these charts includes airports, restricted areas (WPAFB), and obstructions. These maps are called "SECTIONALS" because the FAA divides air space into sections or divisions. The Dayton area is located on the Cincinnati sectional. People who live north of us are on the Detroit Sectional.
________________________________________________________________________________
PROJECT - USING MICROSOFT PAINT, CREATE A SECTIONAL OF YOUR HOMETOWN GIVING DIRECTIONS FROM 10 TO 20 MILES OUT TO YOUR HOUSE - On an 8 1/2 x 11 sheet of paper create a sectional of your town. You can draw it by hand or it can be computer generated. Your sectional will be graded using the numbered checklist below. Use GoogleEarth loaded on the desktop of your computer to create the chart.
________________________________________________________________________________
GRADING CHECKLIST - Project is worth 50 Assessment Points
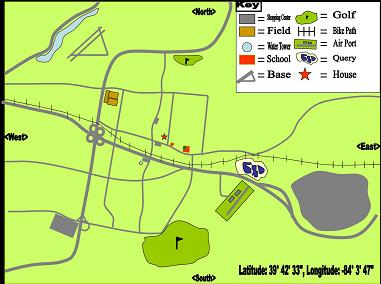
1. Ten landmarks are included which are visible from 1,000 to 1,500 feet in the air. They include WPAFB, railroad tracks, bike path, bridges, rivers, towers, cell towers, highways, water towers, race tracks, school athletic fields, malls, golf courses, large schools, private aircraft runways, or any location easily visible from the air.
2. Sectional represents a 10 to 20 mile radius from the student's house. If you live in the country it may be a 20 mile radius because there are few visible landmarks.
3. Correct longitude and latitude along with altitude are included. Longitude and latitude can be found on Google Earth. Altitude is measured from sea level (MSL). The area in which we live is approximately 900 - 1,000 above sea level.
4. Sectional includes a Key or Legend and the Sectional is IN COLOR. Directs (North, South, East, and West) are included.
5. It is obvious that a great deal of time, effort and thought was put into the Sectional.
________________________________________________________________________________
Day 1
AIM Compare and Contrast Golden Age navigation technology to today's navigation technology
AGENDA
1. Lecture - How to use a pilot's sectional
ASSESSMENT I can explain how Golden Age pilots used sectionals navigate.
________________________________________________________________________________
Days 1 and 2
AIM using Spatial Thinking and Skills, use geographic representations to create a pilot's sectional
AGENDA
1. Activity in class - How to give directions using compass readings
2. Explore Google Earth in class - locate your home
3. Using GoogleEarth, locate 3 or 4 easily visible landmarks around your home from about 1,000 - 2,000 feet.
4. Create a rough draft of your sectional map on a piece of paper and show it to Mrs. Tiffany.
ASSESSMENT Using GoogleEarth I can locate my home and point out significant identifiable structures or "natural" structures within a 20 mile radius of my home.
________________________________________________________________________________
Days 3 and 4
AIM create a pilot's sectional so that Mrs. Tiffany can locate your house from the air.
AGENDA
1. On a sheet of paper, record the landmarks in the center of the paper with your house in the center of the paper. The landmarks should include major roads (I-675, I-70, SRs 35, 42, 68), water towers, bike paths, airports, ball fields, WPAFB, silos, lakes, golf courses
2. Using Google Earth, locate 6 or 7 more visible landmarks that are visible from about 10,000 to 15,000 feet. Record them on your sheet of paper.
3. Create a legend using icons for the locations on your sectional; for example, a school could be signified as a bell.
4. Also record
a. directions (North, South, East, West)
b. longitude and latitude readings (available at the bottom of the map on Google Earth)
c. Elevation (approximately how far above sea level is your house)
5. Show your hand drawn map to Mrs. Tiffany. It will be counted as a "Rough Draft."
AGENDA - I can transfer visible landmarks from GoogeEarth onto a piece of paper to create a rough draft sectional.
________________________________________________________________________________
Day 5
AIM Using a digital program create a sectional map from your rough draft.
AGENDA
1. Transfer your sectional map using Microsoft Paint or Photoshop. In addition to your 10 landmarks, don't forget to include
a. longitude/latitude reading.
b. North, South East, West directions
c. altitude (distance in feet above sea level)
d. Map Key
2. Post Sectional Map in Schoology
ASSESSMENT I can create a digital sectional map with directions to my home
___________________________________________________________________
Academic Content Standards
Theme - World Geography
Spacial Thinking and Skills
Content Statements 1 & 2 - Properties and functions of geographic representations affect how they can be used to represent, analyze and interpret geographic patterns and processes. Geospatial technologies are used to investigate, analyze and communicate the results of geographic problem solving.
|
|