MACROECONOMICS
THE FOLLOWING WEBSITE WILL PROVIDE YOU WITH MOST OF WHAT YOU WILL NEED TO FULLY UNDERSTAND FOR THE MACRO UNITS
http://whitenova.com/thinkEconomics/simul.html
http://whitenova.com/thinkEconomics/adas.html
http://whitenova.com/thinkEconomics/policy.html
MACROECONOMIC DATA RELEASE DATES (copy/paste link)---->
http://biz.yahoo.com/c/e.html
MICROECONOMICS
PRACTICE QUIZ - PRICE DETERMINATION (supply/demand) (copy link)--->
http://www.quia.com/quiz/1158732.html
MORE PRACTICE FOR GENERAL MICROECONOMICS (copy link)--->
http://www.quia.com/rr/94221.html?AP_rand=373643148&playHTML=1
COMPETITIVE MARKET STRUCTURES ACTIVITY (copy/paste link)--->
APPLY WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNED: SCENARIOS THAT EFFECT SUPPLY & DEMAND
MODELS/GRAPHS: Create supply and demand models that reflect changes in the breakfast cereal industry (BELOW). One shift will occur in each model.
1. New regulations require cereal box packaging to include tamper resistant, and evidence of tampering seals.
2. Consumers can now purchase breakfast cereals tax free.
3. Muffins, bagels, oatmeal, and fruit bars producers all lower their prices by 40%
4. Following the lead of auto workers and the UAW, employees of Post, Kelloggs, and General Mills join the newly formed BCP Union (Breakfast Cereal Producers Union).
5. Wheat, oat and barley farmers experience record ‘bumper crops.’
6. News reports on a recent study that shows Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT), a phenolic chemical compound used to keep cereal from changing flavor, odor, and color, has been found to cause tumors in lab animals.
7. Dairy output has increased dramatically, resulting in significantly lower milk prices.
8. Europe’s largest cereal company, “Euro-Flakes,” begins selling its products in the U.S.
9. The breakfast cereal oligopolists switch from using cane sugar to using cheaper high fructose corn sugar (HFCS) as the means of sweetening their products.
10. Popular diet books advocate skipping breakfast as a proven, safe method to lose weight and keep it off.
Chapter 4: "DEMAND"
1.Describe the nature of demand.
2.Interpret a demand schedule and graph
3.List six reasons for changes in demand.
4.Describe the principle of diminishing marginal utility.
5.Define the law of demand
6.Describe the two types of demand elasticity
7.Explain how demand elasticity is used to set a price
SOME ONLINE PRACTICE>>>>>>
PRACTICE QUIZ FOR DEMAND (copy/past link)--->
http://go.hrw.com/activities/frameset.html?main=7607.html
PRACTICE QUIZ FOR DEMAND ELASTICITY (copy/paste link)--->
http://go.hrw.com/activities/frameset.html?main=7631.html
PRACTICE QUIZ CHAPTER 4 ALL (copy/paste link)--->
http://www.glencoe.com/qe/qe50nat2005.php?qi=1249&state=&chapter=4
Chapter 5: "SUPPLY"
1.Define the law of supply
2.Interpret a supply schedule and graph
3.Identify the reasons for changes in supply
4.Describe the two types of supply elasticity
5.Define the law of variable proportions
6.Explain the stages of variable proportions in productivity
7.Describe the four (4) key measures of cost
8.Formulate the "Break-even Point"
9.Use marginal analysis to determine optimum production levels
Chapter 6: "PRICING SYSTEM"
1.Define equilibrium relative to surplus and shortage
2.Interpret equilibrium price on a graph
3.Determine shortages and surpluses at various price levels
4.Illustrate cause/effect scenarios using supply & demand models
5.Illustrate the effects of government manipulation of the “invisible hand”
DEMAND ELASTICITY ENRICHMENT
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): What does it mean?
=1: unit elastic >1: elastic <1: inelastic
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (copy/cut/paste)--->
http://www.tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/elasticity/elastic.htm
MARKET DEMAND (copy/cut/paste)--->
http://www.tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/demandsupply/market_demand.htm
Chapter 7: "Competitive Markets"
1.Compare and contrast the 4 main types of competitive markets based on 4 characteristics.
2.Give examples of each type of competitive market.
3.Explain why the Sherman Antitrust Act and Clayton Antitrust Act are important to competition.
CASE STUDIES PROVIDE AN ILLUSTRATION OF THE PRINCIPLES IN PRACTICE
1. Short term and long run effects of "rent controls" in NYC
2. Agricultural price support programs
3. Dairy farmer strikes of 1930’s
4. Wheat surplus of the 20th century
5. Coke Cola's cost cutting strategy
6. Wages in various labor markets (Traditional Theory of Wage Determination)
BY THE CONCLUSION OF MCROECONOMICS UNIT, YOU MUST:
1: Define the term microeconomics and lists elements in the microeconomy (e.g., consumers, households, and businesses).
2: Identify how supply and demand determine prices.
- interpret schedule and graphs
- interpret and create supply/demand models
- impact of price floors and price ceilings
- compute shortages, surpluses, revenue, costs, profit
- elasticity
- utility
- production schedules
- economies of scale
3: Illustrate the economic relationship among households, businesses and governments by using a diagram of the circular flow of resources, goods, services and money payments through markets.
4: Compare and contrast the various forms of business organizations, the advantages and disadvantages of each and the sources of funding for these various enterprises.
- sole proprietorship
- partnership
- corporations
5: Identify, characterize, and give examples of various types of competitive market structures.
- pure (perfect)competition
- monopolistic competition
- monopoly
- oligopoly
WELCOME TO THE SUPPLY AND DEMAND TUTORIAL!
This series of step-by-step approaches looks at the concepts of supply and demand and the working of the market. The activity will take you through the market process to develop understanding of how markets work in the real world and how so called 'market forces' cause changes in resource allocation.
MARKET DEMAND (copy/cut/paste)--->
http://www.tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/demandsupply/market_demand.htm
READ AND COMPLETE, SLOWLY... STEP BY STEP... (copy/paste link)--->
http://www.bized.ac.uk/learn/economics/markets/mechanism/interactive/part3.htm
APPLY WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNED: SCENARIOS THAT EFFECT SUPPLY & DEMAND
Directions: Create supply and demand models that reflect changes in the breakfast cereal industry. One shift will occur in each model.
1. New regulations require cereal box packaging to include tamper resistant, and evidence of tampering seals.
2. Consumers can now purchase breakfast cereals tax free.
3. Muffins, bagels, oatmeal, and fruit bars producers all lower their prices by 40%
4. Following the lead of auto workers and the UAW, employees of Post, Kelloggs, and General Mills join the newly formed BCP Union (Breakfast Cereal Producers Union).
5. Wheat, oat and barley farmers experience record ‘bumper crops.’
6. News reports on a recent study that shows Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT), a phenolic chemical compound used to keep cereal from changing flavor, odor, and color, has been found to cause tumors in lab animals.
7. Dairy output has increased dramatically, resulting in significantly lower milk prices.
8. Europe’s largest cereal company, “Euro-Flakes,” begins selling its products in the U.S.
9. The breakfast cereal oligopolists switch from using cane sugar to using HFCS as the means of sweetening their products.
10. Popular diet books advocate skipping breakfast as a proven, safe method to lose weight and keep it off.
CHAPTER 2: ECONOMIC SYSTEMS / SOCIO-ECONOMIC GOALS
Economic systems help societies provide for the wants and needs of their people. This chapter deals with the main types of economic systems, the way in which the performance of economic systems can be evaluated, along with the nature of capitalism and free enterprise.
SECTION 1
Introduces the three systems—traditional, command, and market economies—that have evolved over the years. In the traditional economy, the WHAT, HOW, and FOR WHOM questions are answered by tradition, customs, and even habits handed down from generation to generation. In a command economy, a central authority answers the three basic questions. In a market economy, decision making is decentralized with consumers and entrepreneurs playing a central role.
SECTION 2
Examines seven major economic and social goals—economic freedom, economic efficiency, economic equity, economic security, full employment, price stability, and economic growth—on which most people seem to agree. These goals are important, because they can be used to evaluate the performance of an economic system. If the system does not perform as people would like, people can lobby for laws to achieve their goals. One example would be the Social Security program that was enacted to achieve the goal of economic security.
SECTION 3
Deals with capitalism and economic freedom. Free enterprise, another term used to describe the American economy, refers to the competition that is allowed to flourish with a minimum of government interference. The key to the market economy is the economic freedom and voluntary exchange that takes place in a way that makes everyone better off. The entrepreneur is the risk-taking individual in the economy that starts new businesses and undertakes new ways of doing things in search of profits. The consumer is sometimes thought of as being "king" or sovereign of the market, and government is involved in the economy primarily because people want it to be involved. Because of the government involvement, the American economy can also be described as a mixed economy, or a modified private enterprise economy.
PRACTICE ACTIVITY FOR CHAPTER 2 (copy/paste link to new window)--->
http://www.glencoe.com/sec/socialstudies/tutor/economics/econprinciples2005/puzzles/epp2005_02.html
VOABULARY FLASHCARDS ACTIVITY (copy/paste link to new window)--->
http://www.glencoe.com/qe/efcwin.php?qi=12525
PRACTICE QUIZ FOR CHAPTER 2 (copy/paste link to new window)--->
http://www.glencoe.com/qe/qe50nat2005.php?qi=1247&state=&chapter=2
STUDY GUIDE FOR UNIT #2 EXAM --->
What is the purpose of government in a command economy?
Identify several examples of market economies in the world.
Define and describe US economic and social goals.
Which group ultimately determines the products that a free enterprise economy produces?
The United States economy can be described using different terms. What are they?
What are some advantages of communism from the worker’s point-of-view?
Describe the characteristics of a market economy.
The minimum wage is an example of a federal law that supports what goal?
Explain the concept of voluntary exchange.
What is the government's roles in a mixed economy?
According to Adam Smith, what directs the choices business people make?
What social/economic goal is addressed by Medicare?
What social/economic goal is addressed by Affirmative Action laws.
Describe some advantages of socialism.
How did Joseph Stalin demonstrate the main advantage of a command system?
What challenges do countries face when trying to change from a command economy to a market economy?
What are the qualities and characteristics of Socialism?
What caused the economic failure of the Soviet Union?
What is meant by the term capital-intensive economy?
Describe some characteristic of a market economy.
Describe some characteristics of a command economy.
Describe some characteristics of a traditional economy.
What type of economy recently collapsed in the communist bloc countries of Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union?
Describe some examples of economic growth.
Why is economic growth an important goal of the United States?
Describe some examples of a trade-off among social and economic goals?
Describe some characteristics of capitalism.
What is another term for a modified private enterprise economy?
Why are entrepreneurs important in a free enterprise economy?
How do consumers exercise their power in the American economy?
Who plays the roles of protector, consumer, regulator, and promoter of economic goals in the United States? Give examples.
List several reasons for income inequality in the US
How does an economist distinguish whether or not an individual is living in poverty?
About how many Americans are currently living in poverty? How many are children?
How are poverty thresholds determined?
What is the ‘glass ceiling’?
What is the Lorenz curve? What does it express? What does the shape of the curve tell us?
In the US, why has the income gap between the lowest and highest quintile widened since 1980?
What is a major advantage of socialism?
In which respects did the economy of the Soviet Union differ from that of the United States?
The basic philosophy of communism was the work of ___________________ who wrote__________________________.
Students should explain three of the following problems faced by former communist countries: (1) privatizing industries that were formerly state owned; (2) finding new political leadership; (3) adapting to the discipline of a capitalist system; (4) learning how to respond to the new kinds of incentives offered by capitalism.
Though the socialist party was defeated in 1976, Sweden still adheres to many socialist principals, especially on the question of FOR WHOM to produce. To support generous maternity, education, disability, and old-age benefits, Sweden has much higher taxes than the United States. Both countries allow private enterprise to determine the question of WHAT to produce, and the basic industries owned by Sweden are scheduled to be privatized in the future. Both countries have suffered from massive government deficits. Sweden's real per capita GNP is about two-thirds that of the United States.
Marx viewed history as a class struggle between capitalists or “bourgeois” (the owners of the factors of production) and the workers. According to Marx, capitalists (“the few”) “exploited” or used unfairly the workers (“the many”) by selling the goods the workers made and keeping the profit. He felt that the profit rightly belonged to the workers who made the products.
UNIT 1 - BASIC ECONOMIC CONCEPTS
THESE ARE PRODUCTION POSSIBILITIES FRONTIER (PPF) DIAGRAMS
Simple PPF (linear trade-off)
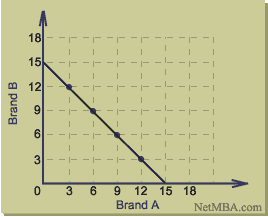
1. What is the Maximum Output Potential of Brand A? Brand B?
2. TRUE or FALSE > This Country is Producing Efficiently.
Classic PPF Model
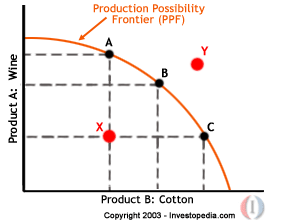
3. What Can You Say About Points A? B? C? X? Y?
4. What is The Opportunity Cost of Going From A to C? B to A?
PPF Model Illustrates a Shift
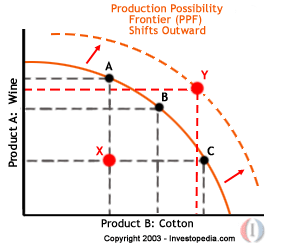
5. What Causes a PPF to Shift Out?
6. What Events Can Cause a PPF to Shift Inward?
PPF's Can Shift For Only 1 Product
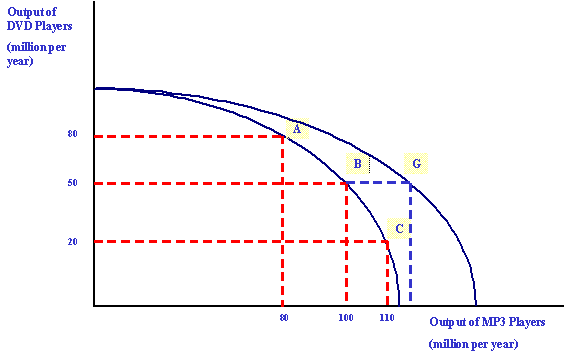
7. Describe a Scenario that Could Cause such a Shift?
8. Before the PPF Shift, What is the Opportunity Cost of Going from Point A to Point B?
9. After the Shift, Can This Country Produce 105 MP3 Players AND Slightly More than 20 DVD Players?
10. Let's Say Point G Represents an Output of 50 DVD Players and 105 MP3 Players.
If This Country Was Producing at Point G, What Would Be the Opportunity Cost of Re-Allocating Resources in a Way That Resulted in Producing 20 Dvd Players and 80 MP3 Players?
PPF's ARE EXPLAINED HERE (copy links to new window)--->
http://www.tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/introduction/ppfs.htm
http://www.tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/introduction/shifts_in_ppf.htm
PPF's INTERACTIVE QUIZ (skip #1, answer #2-7)--->
http://www.tutor2u.net/quiz/economics/jbc_econ_ppf_1.htm
WHAT IS ECONOMICS?
Economics is a social science, that deals with the fundamental economic problem of scarcity—a condition caused by the combination of seemingly unlimited wants and limited resources. Because of this, choices and decision making are the central focus of Chapter 1.
Chapter 1, Section 1 introduces the concepts of needs such as food, clothing, and shelter—and wants, which are ways of expressing needs. The notion of TINSTAAFL, which stands for There Is No Such Thing As A Free Lunch, is often used to remind us that resources are scarce and that we must make careful economic decisions regarding WHAT, HOW, and FOR WHOM to produce. Other concepts relevant to economics, such as the four factors of production-land, capital, labor, and entrepreneurs—along with the meaning and scope of economics, are also examined.
Chapter 1, Section 2 introduces a number of key economic concepts, including utility, value, and wealth. The concepts of goods, services, consumers, markets, factor markets, product markets, productivity, economic growth, and economic interdependence are explained and are linked in the circular flow diagram. Productivity is necessary for economic growth, and growth takes place when specialization and the division of labor are present. Human capital, the sum of our skills, abilities, health, and motivations, is another important component of growth.
Chapter 1, Section 3 deals with the way economists think about choices. Choices are explained in terms of trade-offs, or alternatives that are available whenever a decision is made. The cost of every decision is measured in terms of its opportunity cost, which is the cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another. Trade-offs can be analyzed with a decision-making matrix, or illustrated with a production possibilities frontier. The production possibilities frontier, the decision-making matrix, and the circular flow diagram are some of the more useful "tools" used by economists.
CHAPTER 1 VOCABULARY ACTIVITY (copy/paste link to new window)--->
www.glencoe.com/qe/efcwin.php?qi=12354
CHAPTER 1 CROSSWORD PUZZLE (copy/paste link to new window)--->
http://www.glencoe.com/sec/socialstudies/tutor/economics/econprinciples2005/puzzles/epp2005_01.html
CHAPTER 1 SELF-CHECK QUIZ (copy/paste link to new window)--->
http://www.glencoe.com/qe/qe50nat2005.php?qi=1246&state=&chapter=1
STUDY GUIDE FOR QUIZ #2
• Scarcity is the basic economic problem in which resources are limited and wants are limited
• Productive resources are the inputs required to produce a good or service
• Land is the input referring to natural resources
• Labor is the input referring to human resources
• Capital is the input referring to tools, factories, and equipment
• Entrepreneurship is the input referring to the risk taker in search of profits
• Resource allocation strategies
• Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best alternative when a choice is made (it’s what is given up)
• The PPF diagram represents maximum output potential when resources are fully & efficiently employed
• Trade-offs are the alternatives that must be given up when one choice is selected rather than another
• Marginal benefit is the extra benefit derived from making one choice over another
• Marginal cost is the extra cost incurred from making one choice rather than another
• Specialization occurs when inputs perform tasks they can do more efficiently than others
• Voluntary exchange is the act of buyers and sellers freely engaging in market activities
• Explain how rational decision-making influences your purchases of goods and services
CAN YOU ANSWER THESE QUESTION???? IF NOT, YOU BETTER STUDY!!!
What is the fundamental problem of Economics?
What is the condition that arises because society does not have enough resources to produce all the things that people would like to have?
The academic study of economics includes analysis and __________________________.
Specialization and division of labor in a free market economy will typically lead to _______________.
The factor of production that involves risk-takers in search of profits is/are __________________.
The factor of production that includes the tools, equipment, and factories used in the production of goods and services is/are ______________________________________.
What tool that can be used to help a consumer (let’s call him Jesse) make an economic decision by identifying alternatives and criteria to evaluate the alternatives?
The three basic economic questions are ________________________________________.
What are the four factors of production? (give examples)
What term is used to describe the “next best alternative choice”?
A diagram representing various combinations of goods and/or services an economy can produce when all productive resources are fully employed is the _________________ .
What diagram shows the economic interdependence that occurs in an economic system which encourages voluntary exchange and free flow of goods, services, and factors of production based on profit motive and self-interest?
A shortage of money does not cause scarcity. Why?
CAN YOU EXPLAIN THE FOLLOWING? YOU NEED TO FOR EXAM #1 !!!
1: Define and apply the concepts of scarcity, decision-making, choice, and opportunity cost to problem situations.
- production possibilites frontier (PPF's)
2: Explain how the four factors of production are utilized in the production process: land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship.
3: Relate specialization to efficient use of resources, and to domestic economic growth.
4: Explain how specialization, savings, investment in capital goods (technology) and investment in human capital (know how) influence productivity and economic growth/development.
5: Identify the three questions facing every economic system and analyzes how our society has organized to answer these questions.
- What will be produced?
- How will it be produced?
- For whom will it be produced?
6: Illustrate the economic relationship among households, businesses and governments by using a diagram of the circular flow of resources, goods, services and money payments through markets.
7: Explain why countries trade and how economic specialization promotes interdependence among nations.
8. If a person has a limited amount of income, how does utility influence purchasing decisions?
9. Interpret PPF models.
10. Interpret PPF Models with intersecting PPFs
11. Interpret PPF Table of data.
12. Interpret a Production Table
13. Interpret a quote “It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or the baker that we expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own interest.” ~Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations
14. Interpret a Production Table w/ marginal output and total output data.
15. Define and exemplify division of labor and specialization.
MORE EXAM #1 PREP....
DO THE QUIA ACTIVITIES AT THE BOTTOM OF THIS WEB PAGE!!!
ECONOMICS EOCT PREP SITES
http://www.gadoe.org/ci_testing.aspx?PageReq=CI_TESTING_EOCT
Scroll Down to (along right side)>>>
STUDENT GUIDES
>>>Economics/Business/Free Enterprise (GPS)
9th Grade Literature and Composition Part A (GPS)
9th Grade Literature and Composition Part B (GPS)
American Literature and Composition Part A (GPS)
American Literature and Composition Part B (GPS)
EOCT RELEASED TESTS
Algebra
American Literature
Biology
>>> Economics
Geometry
Ninth Grade Literature
Physical Science
U.S. History
Answer Key
MORE EOCT PRACTICE AT>>>
www.usatestprep.com
CLICK Member login (upper right part of screen)
username: centennial
student password: newton31
CLICK “I Agree”
CLICK Social Studies tab located near top of page
CLICK GA Economics EOCT - GPS (upper left, just above the pie chart)
|
|