| A | B |
|---|
| The smaller structures inside the cell which have specific functions are called __. | organelles |
| Which cell structure is located only in animal cells and helps the cell to divide and reproduce? | centriole, 
|
| Which organelle stores the DNA of a cell? | nucleus |
| Which two cell structures are found in plant cells but not animal cells? | Cell wall and chloroplasts, 
|
| The dark structure located inside the nucleus that manufactures ribosomes is called ____. | the nucleolus, 
|
| What is located just inside the cell wall of plant cells? | the cell membrane |
| The ______ doesn't allow DNA to leave the nucleus. | nuclear envelope (a.k.a. nuclear membrane) |
| Which organelle do plants use for photosynthesis? | chloroplasts, 
|
| Long strands of DNA wrapped around proteins are known as ___. | chromosomes, 
|
| Which part of the cell regulates what enters or leaves the cell? | cell membrane |
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called ____ that helps capture the energy from the sun for the process of ___., 
| chlorophyll, photosynthesis, 
|
| Everything inside the cell membrane except for the nucleus is called ____. | the cytoplasm, 
|
| The network of tube-like protein filaments that help give cells shape and support and also help with movement is called the ___. | cytoskeleton, 
|
| The structure that modifies, sorts and moves complex molecules made in the endoplasmic reticulum to other parts of the cell (or even to the outside of the cell) is called the ____. | golgi |
| The organelle that specializes in transferring the chemical energy in food into molecules that the cell can more easily use for energy (ATP) is called the ___. | mitochondrion (plural is mitochondria), 
|
(true or false) Mitochondria are found only in animal cells., 
| False (plants need mitochondria also to break down the food they made during photosynthesis using the chloroplasts), 
|
| The organelle where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported (sent out of) the cell is called ____. | the endoplasmic reticulum, 
|
| The organelle that acts like a storage center is called ___. | a vacuole |
| The organelle that stores things and, in plant cells, also helps keep the cell from collapsing by storing large quantities of water, is called a(n) ____ . | vacuole |
| The small organelle that serves as the site where proteins are put together is called the ___. | ribosome, 
|
| The organelle that contains strong enzymes for breaking down food molecules and recycling old cell parts is called the __. | lysosome, 
|
| Which organelle stores the body's genetic information? | the nucleus |
The nucleolus manufactures the parts used to make __., 
| ribosomes, 
|
| The cell membrane is located just ___ of the cell wall in plants | inside |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | animal, cell membrane |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | plant, cell membrane |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | plant, cell wall |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______., 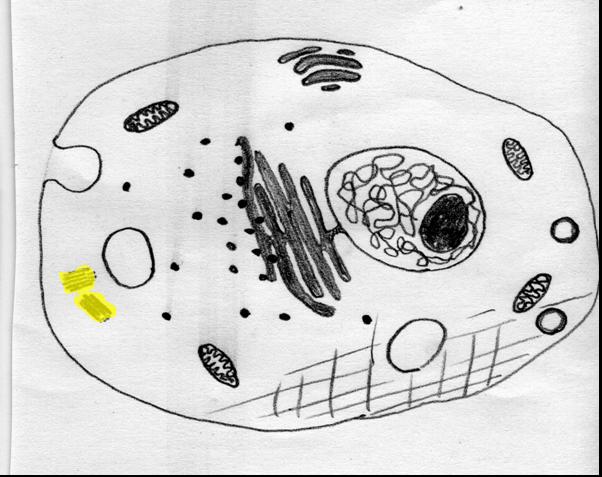 | animal, centrioles, 
|
The small green organelles in this picture are ___., 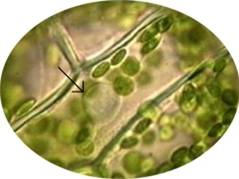 | chloroplasts, 
|
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | animal, endoplasmic reticulum, 
|
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | plant, endoplasmic reticulum, 
|
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______., 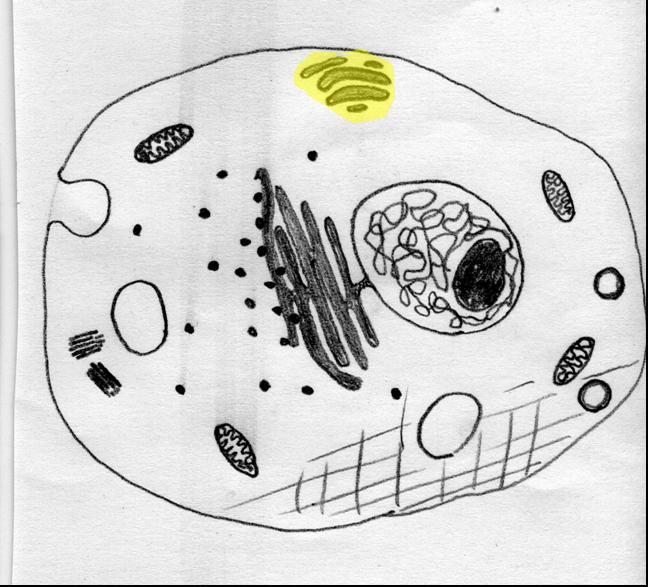 | animal, golgi |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______., 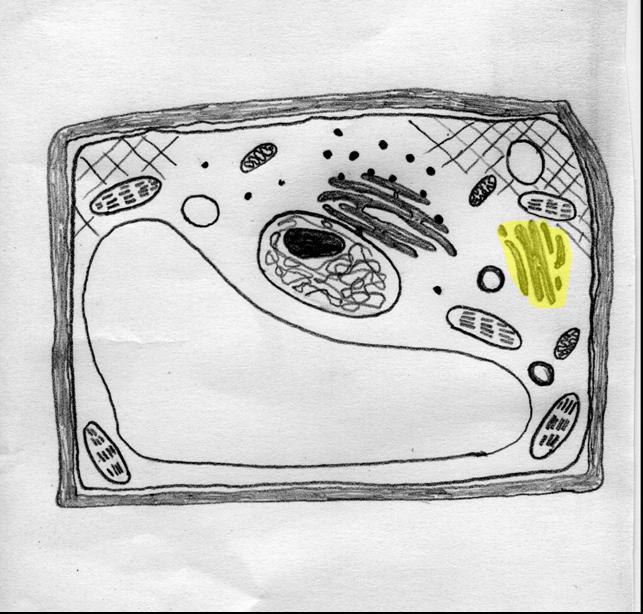 | plant, golgi |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______., 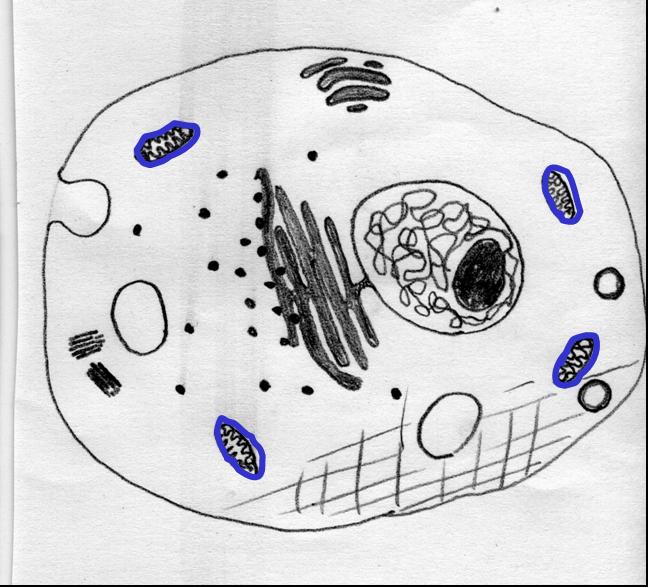 | animal, mitochondria, 
|
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | plant, mitochondria, 
|
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | animal, nucleus |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | plant, nucleus |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | animal, ribosomes, 
|
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | plant, ribosomes, 
|
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | animal, vacuole |
The highlighted portion of this _____ cell is called a ______.,  | plant, vacuole |
The short hair-like structures that help some single-celled organisms (like the one pictured below) swim, and that are also found on cells lining our throats, are called ___,  | cilia, 
|
The longer tail-like structures that help some single-celled organisms (like the one pictured below) swim are called ___,  | flagella, 
|
| Who was the first to discover and name "cells"? | Robert Hooke (in 1665) |
| What type of cells were the first cells to be seen under a microscope? | Cork cells (by Robert Hooke in 1665) |
| What was Anton van Leeuwnhoek's contribution to the cell theory? | He was the first person to see living cells under a microscope. He looked at pond water in 1675 and saw a bunch of single cell organisms swimming around. He called them "animalcules." |
| Who coined the phrase "All plants are made of cells," in 1838? | Schleiden |
| Who coined the phrase "All animals are made of cells," in 1839? | Schwann |
| Who was the first to state that "All cells come from pre-existing cells." in 1858? | Virchow |
| What is the first statement of the modern cell theory? | All living things are made of cells. |
| What is the second statement of the modern cell theory? | Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. |
| What is the third statement of the modern cell theory? | All cells come from pre-existing cells. |
| What do all cells have in common? | A cell membrane and DNA for at least part of their life. |
| All cells can be divided into these two categories based on whether they have a nucleus or not. | Prokaryotic (no nucleus, includes all types of bacteria) and Eukaryotic (all other types of life except the two kingdoms of bacteria) |
Which type of electron microscope produces 2 dimensional images like the one below?,  | transmission electron microscope (TEM) |
Which type of electron microscope produces three dimensional images like the one below?,  | scanning electron microscope |
Which type of microscope can produce an image of something as small as the molecules of DNA below?,  | Scanning probe microscope |
What type of microscope is pictured below?,  | Compound Light Microscope |
| What is the difference between magnification and resolution? | Magnification is how many times bigger the image in a microscope appears while resolution is how detailed you can see things. High magnification without good resolution is worthless. |
| How do you calculate the total magnification of a compound light microscope? | Total magnification = magnification of the objective lens X the magnification of the ocular |
| Cells with a nucleus are called __. | Eukaryotic cells, 
|
| Cells without a nucleus are called ___. | Prokaryotic cells, 
|
| The movement of water molecules across a cell membrane (from areas of high water concentration to areas of low water concentration) is called ___. | osmosis |
| In a salt water solution, the salt is known as the ___. | solute |
| If a cell membrane allows glucose to pass through it, then the cell membrane is said to be ____ to glucose. | permeable, 
|
| In a salt water solution, the water is known as the ____. | solvent |
| The movement of particles across a cell membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration is known as ____. | diffusion |
| The cell membrane is said to be _______ permeable to substances because it lets some pass through but not others. | selectively |
| The type of substances that can most easily diffuse across a cell membrane are ____ substances. | small |
| The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a __________ with ____ proteins | phospholipid bilayer, embedded, 
|
| Larger molecules, polar molecules, and charged particles (ions) usually pass through _____ to get into or out of a cell. | transport proteins |
| Cells will shrink if placed into a _____ solution. | hypertonic |
| When energy is needed to force molecules across a cell membrane, _______ is taking place. | active transport |
| Cells will grow bigger if placed in a ____ solution. | hypotonic |
When osmotic pressure increases in plant cells, why don't the cells usually burst?, 
| Plant cells have a tough cell wall that keeps the cell from expanding enough to burst. |
| If a solution is 6% solutes, it will be ____ % water. | 94 |
| If a solution is 90% water, it will have ___ % solutes. | 10 |
| A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the interior of a cell is known to be ____. | isotonic |
| Active transport requires _____. | energy |
| If a substance is crossing a cell membrane due to active transport, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ____ concentration. | low, high |
| If a substance is diffusing across a cell membrane, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ___ concentration. | high, low |
| The four types of proteins found in cell membranes are: | transport, receptor, marker, and pumps |
When osmotic pressure decreases in a plant, the ______ shrink and the plant ____., 
| vacuoles, wilts |
| When osmotic pressure increases in plants, the ______ gets bigger and the plant ___. | vacuole, gets stiff |
| The type of cell membrane protein that allows larger molecules and ions to pass through by facilitated diffusion is called a ____. | channel protein |
| The type of protein that a hormone could attach to on the outside of a cell membrane is called a ____. | receptor protein |
| The type of cell membrane protein that allows your body to recognize your own cells is called a ____ . | marker protein |
The elodea cells in this picture are surrounded by a ______ solution.,  | hypotonic |
The process pictured below is called ____., 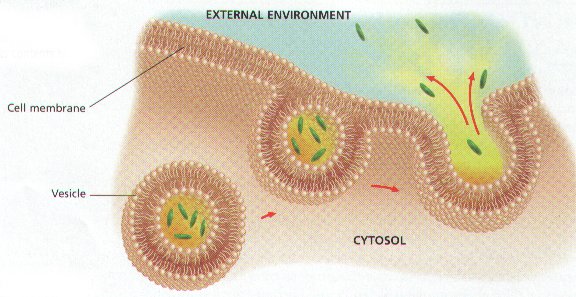 | exocytosis, 
|
The elodea cells pictured below have been soaking in a ____ solution.,  | hypertonic |
| A type of protein that travels through the blood stream and attaches to receptor proteins on a cell's surface in order to deliver a chemical message is known as a ____. | hormone |
The process pictured below is called ____., 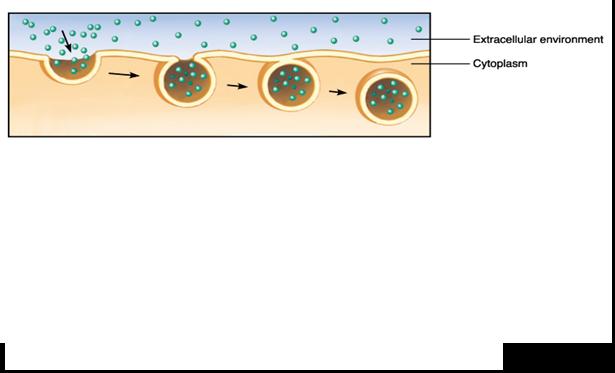 | endocytosis, 
|
| When large molecules need the help of protein channels to cross the cell membrane, the process that is occurring is called ______. | facilitated diffusion |
| The type of endocytosis that takes in solid particles (usually food) is called ____. | phagocytosis |
| The type of endocytosis that takes in liquids is called ___. | pinocytosis |
| Name 3 types of active transport. | protein pumps, endocytosis and exocytosis. |
| The type of cell membrane protein that moves molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration is called a ___. | protein pump |
| _____ is the term that refers to different cells having different jobs in an organisms. | Cell specialization |
| Muscle, connective and nerve are types of ____ in the body. | tissues |
| Heart, lungs, pancreas, and liver are examples of ____ in the body. | organs |
| A group of similar cells that perform a particular function in the body is called ___. | a tissue |
| The mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine are all part of the ____. | digestive system |
| A group of organs that work together to perform a specific function is called ___ | an organ system |
| What are the four levels of organization in multicellular organism, starting with the simplest and ending with the most complex? | cells, tissues, organs, organ systems |
| True or False: "Both active and passive transport work to cause equilibrium of substances on each side of the cell membrane. | FALSE (While passive transport does do this, active transport rarely does this. Active transport usually moves substances from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration, making one side of the membrane have an even higher concentration while the other side gets an even lower concentration. This is the opposite of moving towards having even concentrations, a.k.a. equilibrium, on both sides of the membrane) |