| A | B |
|---|
What structure is #1 pointing to?,  | .,  |
What structure is #2 pointing to?,  | ., 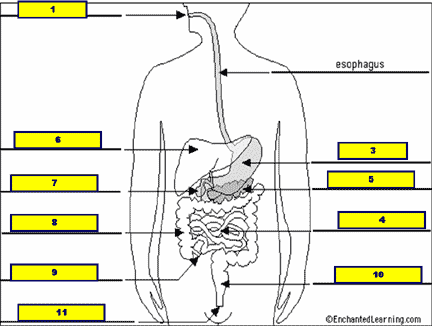 |
What structure is #3 pointing to?,  | ., 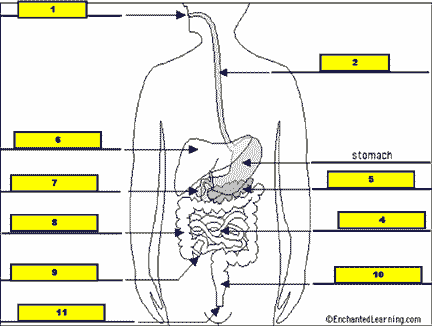 |
What structure is #4 pointing to?,  | ., 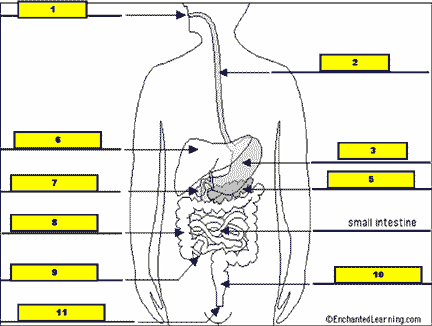 |
What structure is #5 pointing to?,  | ., 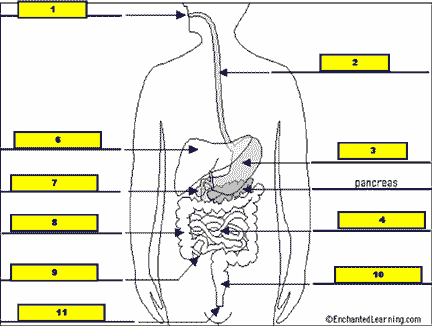 |
What structure is #6 pointing to?,  | .,  |
What structure is #7 pointing to?,  | ., 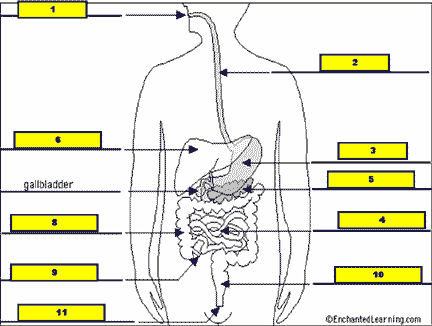 |
What structure is #8 pointing to?,  | ., 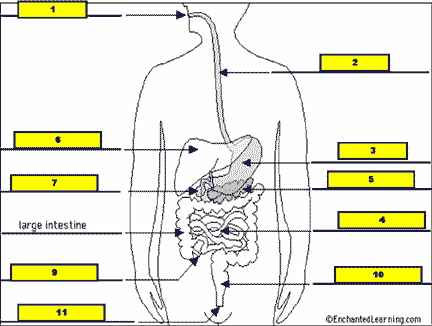 |
What structure is #9 pointing to?,  | ., 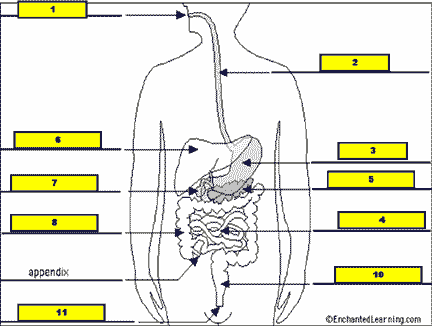 |
What structure is #10 pointing to?,  | .,  |
What structure is #11 pointing to?,  | ., 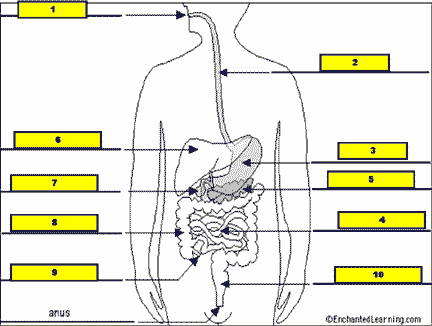 |
| What is the name of the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach? | esophagus |
| Which organ produces a substance that helps neutralize stomach acids as they enter the small intestine? | The pancreas |
| Where does chemical digestion of food start? | In the mouth when salivary amylase starts breaking down complex carbohydrates |
| Where does physical digestion of food start? | In the mouth when food is broken into smaller chunks by mastication (chewing) |
| How is food mechanically digested in the stomach? | Strong muscular contractions of the stomach grind the food |
| The stomach breaks down food into a soft partially digested mixture called ____. | chyme |
| The enzyme called amylase breaks down ___. | carbohydrates |
| Water is extracted from undigested food and sent into the bloodstream while the food passes through the ___. | large intestine |
| The stomach breaks down mainly ___. | proteins |
| Lipids are broken down in the ___. | small intestine |
| Carbohydrates are broken down in the ___. | mouth and small intestine |
| Where in the digestive tract do digested foods leave the digestive tract to enter the bloodstream? | small intestine |
| Where do digested foods go after they leave the small intestine? | bloodstream |
| Where does undigested food go after it leaves the bloodstream? | large intestine-->rectum-->anus-->out |
| _____ pushes food down your esophagus into your stomach. | Peristalsis (wave-like contractions of the muscles surrounding the esophagus), 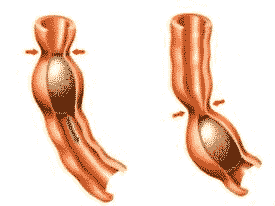 |
| Lipase is an enzyme that breaks down ___. | Lipids (which include fats and oils) |
| Pepsin and peptidase are enzymes that break down ___. | proteins |
| The large organ that lies above the stomach and produces bile is called the ____. | liver |
| ____ is a substance that is produced in the liver and is released by the gall bladder into the small intestine in order to break up fats into smaller droplets. | Bile |
| If part of the stomach wall digests itself, a(n) ___ will develop. | ulcer |
| Stomach juices have a ___ pH and would be described as being ___. | low pH, acidic |
| What are two organs that are part of the digestive system, but not the digestive tract? | Pancreas and liver (food doesn't pass through them. They produce substances that get dumped into the digestive tract to help with digestion), 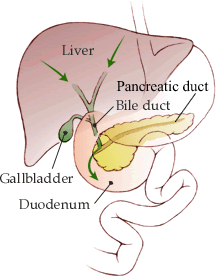 |
| The small fingerlike projections on the inside of the small intestine that help increase absorption of food by increasing the surface area that food comes in contact with are called ___. | Villi and Microvilli, 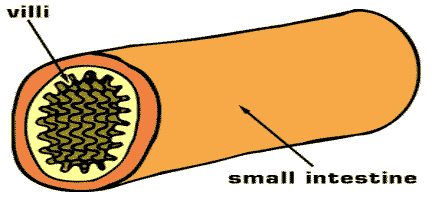 |
| Villi and microvilli are small fingerlike projections on the inside of the small intestine that help increase absorption of food by increasing the ___ that food comes in contact with. | surface area,  |