| A | B |
|---|
| Organisms, such as plants, that make their own food are called ___. | autotrophs |
| Organisms that can't make their own food and must obtain their energy from food they consume are called ___. | heterotrophs |
| How many phosphate groups does ATP have? | Three (that's why it is called adenosine tri-phosphate) |
| How many phosphate groups does ADP have? | Two (that's why it is called adenosine di-phosphate) |
| Energy is released from an ATP molecule when __. | a phosphate group is removed. |
| When ATP releases energy, ___ is formed. | ADP |
| ATP provides ____ for the mechanical function of cells. | energy |
| The energy in most food comes originally from ___. | sunlight |
| The formation of ADP from ATP ____ energy. | releases |
| The formation of ATP from ADP ____ energy. | requires |
| The energy required to convert ADP into ATP usually comes from burning ___. | carbohydrates |
What is the name of the molecule pictured below?,  | ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate). Notice the three phosphate groups.,  |
What is the name of the molecule pictured below?, 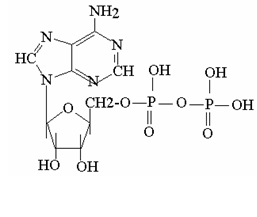 | ADP (adenosine di-phosphate). Notice it has two phoshate groups),  |
| About how many kilocalories does the average teenager need per day? | About 2200 - 2800 depending on your size and sex |
| _____ are substances that the body needs for energy, growth, repair and maintenance. | Nutrients |
| Inorganic nutrients, like iron, that the body needs (usually in small amounts) are called ___. | minerals |
| The raw materials that the body needs for growth and repair come mostly from ____. | proteins |
| Proteins are made of many ____ bonded together. | amino acids |
| Vegetable oil is an example of a(n) ____ fat. | unsaturated |
| Butter and red meats are high in ____ fat. | saturated |
| Which type of fat do you want to minimize in your diet? | Saturated fats |
| You should drink a minimum of how many liters of water per day? | one liter (one liter is slightly more than a quart) |
| Name three different ways that the body loses water. | Sweating, urination, respiration |
| Which type of nutrient is the main energy source for your body? | carbohydrates |
| What are lipids (fats and oils) mainly used for in your body? What are three other uses? | Lipids are used to store calories for times of need. They are also useful for building cell membranes and some hormones. Fat that is stored under the skin is useful as insulation and fat that is stored around your organs protects them in the same way that styrofoam packing peanuts protect things that are sent in boxes through the mail. |
| ______ in your diet provides undigestible bulk that helps move things through your digestive tract. It is composed mostly of ___ which is a type of carbohydrate. | Fiber, cellulose |
| You can get a lot of carbohydrates by eating _____. | plant based foods such as fruits, vegetables and potatoes |
| You can get a lot of protein in your diet by eating ___. | meat (meat is animal muscle and muscle fibers are made of protein) |
| One of the major reasons that water is important in your diet is that ___ take place in water. | chemical reactions |
| Vitamins that are ____- soluble cannot be stored in the body. | water |
| Vitamins that are ____- soluble can be stored in the body. | fat |
| Blood, lymph, and other body fluids consist mostly of ___. | water |
| Sugars that are not used immediately for energy can be stored in the liver and muscles bonded together as a complex carbohydrate called ___. | glycogen |
| A complex carbohydrate that comes from plants and that humans can use for energy is called ___. | starch |
| Complex carbohydrates give you a slower, but longer lasting energy because they must be broken down into ___ before they can enter your bloodstream. | simple sugars |
| Fats, oils and waxes are called ___. | lipids |
| Vitamin ___ can be made by ___ in your intestines. | K, bacteria |
| Vitamin ___ can be made by your ____ when exposed to sunlight. | D, skin |
What structure is #1 pointing to?,  | .,  |
What structure is #2 pointing to?,  | ., 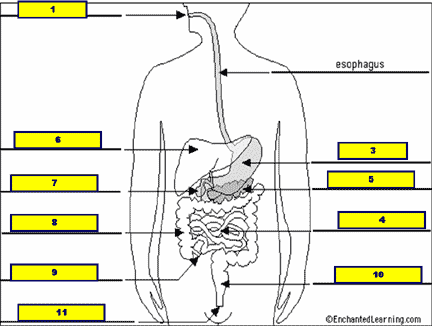 |
What structure is #3 pointing to?,  | ., 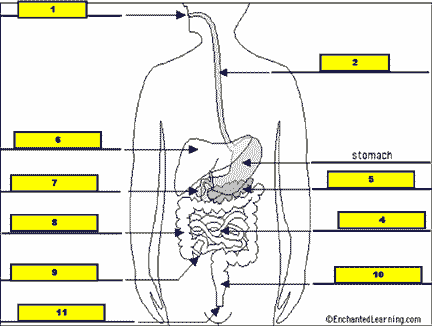 |
What structure is #4 pointing to?,  | ., 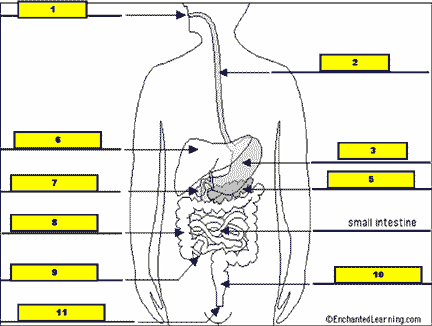 |
What structure is #5 pointing to?,  | ., 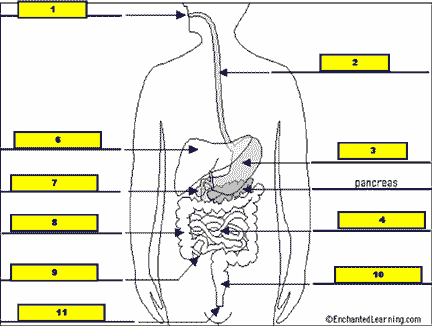 |
What structure is #6 pointing to?,  | .,  |
What structure is #7 pointing to?,  | ., 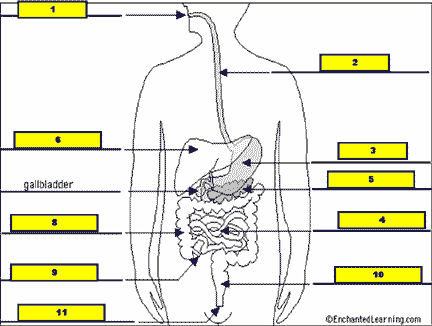 |
What structure is #8 pointing to?,  | ., 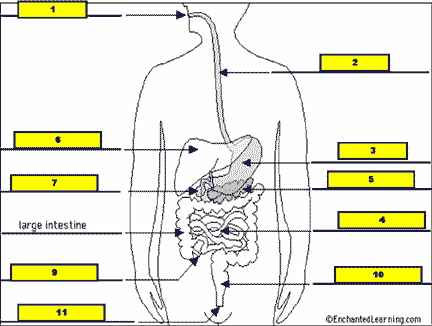 |
What structure is #9 pointing to?,  | ., 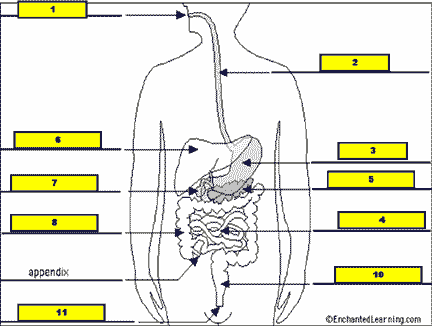 |
What structure is #10 pointing to?,  | .,  |
What structure is #11 pointing to?,  | ., 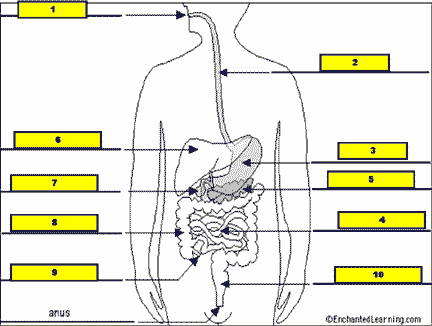 |
| What is the name of the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach? | esophagus |
| Which organ produces a substance that helps neutralize stomach acids as they enter the small intestine? | The pancreas |
| Where does chemical digestion of food start? | In the mouth when salivary amylase starts breaking down complex carbohydrates |
| Where does physical digestion of food start? | In the mouth when food is broken into smaller chunks by mastication (chewing) |
| How is food mechanically digested in the stomach? | Strong muscular contractions of the stomach grind the food |
| The stomach breaks down food into a soft partially digested mixture called ____. | chyme |
| The enzyme called amylase breaks down ___. | carbohydrates |
| Water is extracted from undigested food and sent into the bloodstream while the food passes through the ___. | large intestine |
| The stomach breaks down mainly ___. | proteins |
| Lipids are broken down in the ___. | small intestine |
| Carbohydrates are broken down in the ___. | mouth and small intestine |
| Where in the digestive tract do digested foods leave the digestive tract to enter the bloodstream? | small intestine |
| Where do digested foods go after they leave the small intestine? | bloodstream |
| Where does undigested food go after it leaves the bloodstream? | large intestine-->rectum-->anus-->out |
| _____ pushes food down your esophagus into your stomach. | Peristalsis (wave-like contractions of the muscles surrounding the esophagus), 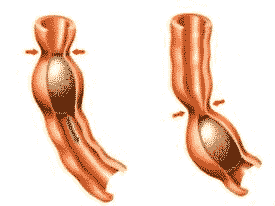 |
| Lipase is an enzyme that breaks down ___. | Lipids (which include fats and oils) |
| Pepsin and peptidase are enzymes that break down ___. | proteins |
| The large organ that lies above the stomach and produces bile is called the ____. | liver |
| ____ is a substance that is produced in the liver and is released by the gall bladder into the small intestine in order to break up fats into smaller droplets. | Bile |
| If part of the stomach wall digests itself, a(n) ___ will develop. | ulcer |
| Stomach juices have a ___ pH and would be described as being ___. | low pH, acidic |
| What are two organs that are part of the digestive system, but not the digestive tract? | Pancreas and liver (food doesn't pass through them. They produce substances that get dumped into the digestive tract to help with digestion), 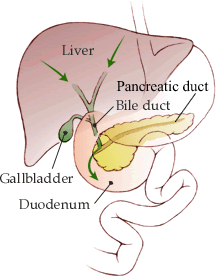 |
| The small fingerlike projections on the inside of the small intestine that help increase absorption of food by increasing the surface area that food comes in contact with are called ___. | Villi and Microvilli, 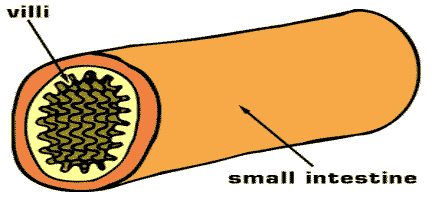 |
| Villi and microvilli are small fingerlike projections on the inside of the small intestine that help increase absorption of food by increasing the ___ that food comes in contact with. | surface area,  |
| How many kilocalories are found in a gram of carbohydrates? | about 4 kilocalories (a.k.a. Calories) |
| How many calories are in a kilocalorie? | 1000 |
| How many kilocalories are found in a gram of protein? | about 4 kilocalories (a.k.a. Calories) |
| How many kilocalories are found in a gram of lipids, such as fat or olive oil? | about 9 kilocalories (a.k.a. Calories) |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using energy from the glycolysis stage? | 2 ATP can be produced for every one molecule of glucose that goes through glycolysis. |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using energy from chemical reactions in the Krebs Cycle? | 2 ATP can be produced for every one molecule of glucose during the Krebs Cycle. |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using the high energy electrons from one molecule of glucose during the electron transport chain? | During the electron transport chain, between 32 and 34molecules of ATP can be produced using the energy of high energy electrons stripped from one molecule of glucose. |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of glycolysis occur? | In the cytosol (cytoplasm) |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of the Krebs Cycle occur? | In the mitochondria |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of the electron transport chain occur? | In the mitochondria |
| Name two different molecules that specialize in stripping high energy electrons from food and carrying the electrons to the electron transport chain. | NADH and FADH2 |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy from high energy electrons that are stripped from food molecules during glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle? | Between 32 and 34 ATP can be recharged from these electrons as they pass through the electron transport chain. |
| What is the only stage in cellular respiration that requires molecular oxygen? | The electron transport chain. |
| Why is oxygen needed during aerobic cellular respiration? | Oxygen is needed to take the electrons away after they go through the electron transport chain. If they don't get taken away, the electron transport chain gets clogged with electrons and stops working. |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy stored in one molecule of glucose if oxygen is available? | Between 36 and 38 |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy stored in one molecule of glucose if oxygen is NOT available? | Only 2 |
| Which of the three stages of cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide as a waste product? | Krebs Cycle |
| Which of the three stages of cellular respiration produces water as a waste product? | The electron transport chain. |
| What is the major difference between aerobic and anaerobic fermentation? | Aerobic cellular respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic fermentation does not (Aerobic respiration is also almost 20 times more efficient at getting useful energy out of food) |
| What is the purpose of turning pyruvic acid into alcohol or lactic acid if no oxygen is available? | Allows glycolyis to make more pyruvic acid which allows glycolysis to continue making 2 ATP per molecule of glucose. |
| What is the waste product produced in your muscles if your muscle cells aren't getting oxygen quicly enough to do aerobic cellular respiration? | Lactic acid (the stuff that makes your muscles burn) |
| A method for getting energy out of food that produces lactic acid or alcohol when no oxygen is available. | Fermentation |
Besides plants, what are two other types of organisms that can conduct photosynthesis?, 
| Bacteria and protists both have members that do photosynthesis. |
| A student notices bubbles coming off of an aquatic plant when it is exposed to bright sunlight. These bubbles are most likely ___. | oxygen (because the plant is doing photosynthesis), 
|
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into ___., 
| oxygen and high energy sugars or starches |
What are three things needed for photosynthesis?, 
| water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight |
| Plants gather the sun's energy with light absorbing molecules called ___. | pigments |
| Which type of pigment is used to capture most of the sun's energy? | chlorophyll, 
|
| An orange pigment that captures some of the sun's energy is called ___. | carotene |
| Most plants appear green because chlorophyll ____ green light. | reflects |
| Which region of the visible spectrum is not absorbed well by chlorophyll? | green |
| Which region of the visible spectrum is not absorbed well by carotene? | orange |
| What is a granum (singular of grana)? | It's a stack of thylakoids inside a chloroplast. |
| The region of the chloroplast that is outside of the thylakoids is called the ___. | stroma |
| Where in the chloroplast can chlorophyll be found? | In the thylakoids |
Where do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place?, 
| Within the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast |
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?, 
| Oxygen gas, ATP and NADPH |
Where do the electrons that travel through the electron transport chain of photosynthesis originally come from?, 
| They are stripped from water molecules. |
| What happens to water molecules when they are stripped of electrons during photosynthesis? | The water molecules fall apart, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen gas. |
During which stage of photosynthesis is water needed?, 
| light-dependent reactions |
During which stage of photosynthesis is carbon dioxide needed?, 
| the Calvin Cycle (a.k.a. the light-independent or dark reactions) |
During which stage of photosynthesis is oxygen produced?, 
| light-dependent reactions |
During which stage of photosynthesis is the energy from ATP and NADPH used to produce high energy sugars?, 
| the Calvin Cycle (a.k.a. the light-independent or dark reactions) |
| Which products of the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis are needed during the Calvin Cycle? | NADPH and ATP |
For a tree doing photosynthesis, where does the carbon dioxide that is needed during the Calvin Cycle dome from?, 
| the atmosphere |
The Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis is another name for the _____., 
| light-independent reactions |
| What is the product of the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis? | High energy sugars |
| Where does the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis take place? | In the stroma of the chloroplast |
What is the name of this entire structure?,  | chloroplast,  |
What is #1 pointing to?,  | A thylakoid inside a chloroplast,  |
What is #2 pointing to?,  | The grana of the chloroplast (a granum is a single stack of thylakoids),  |
What is #3 pointing to?,  | The stroma of the chloroplast,  |
What is the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis?, 
| .,  |