| A | B |
|---|
| The process of making proteins inside cells is called ______. | protein synthesis |
| Inside which organelle is DNA located? | nucleus (Remember, prokaryotes don't have a nucleus, so their DNA is located out in the cytosol/cytoplasm) |
Which type of nucleic acid can't leave the nucleus?, 
| DNA |
| On which organelle are proteins made? | ribosomes (This is true of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic ribosomes are a little bit smaller, but otherwise very similar to the eukaryotic ribosome), 
|
| Where are ribosomes located? | out in the cytosol (Most of the time, they are free-floating. Sometimes, they attach to ER to make rough ER), 
|
| The process of making a strand of m-RNA in the nucleus is called _____. | transcription |
| What are four differences between RNA and DNA? | 1) RNA is single-stranded instead of double 2) RNA has the nucleotide uracil in place of thymine 3) RNA can leave the nucleus and DNA can't 4) RNA includes the sugar called ribose while DNA includes the sugar called deoxyribose |
Which nucleotide do you find in RNA but not DNA?, 
| uracil |
| Uracil bonds to _____ at the nitrogenous base. | adenine |
| The process of using the instructions on RNA to make a long chain of amino acids in the correct order to form a protein is called _____. | translation |
| Which type of molecule brings amino acids to the site of protein synthesis? | transfer RNA (t-RNA) |
| Which molecule attaches to a ribosome and serves as instructions for putting amino acids together? | messenger RNA (m-RNA) |
How many nucleotides are needed to code for 1 amino acid?, 
| 3 |
| How many different types of amino acids are used to make proteins? | 20 |
Each set of 3 nucleotides on a strand of m-RNA is called a(n) _____., 
| codon |
| How many nucleotides are found at the bottom of a molecule of t-RNA and are involved with bonding to m-RNA? | 3 (The part labeled B in the diagram below), 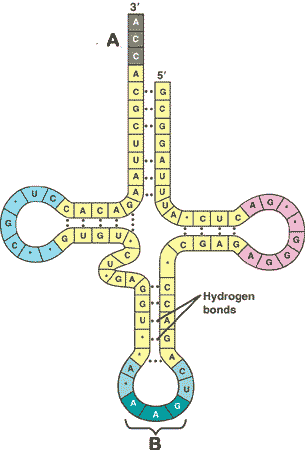 |
| How many amino acids are found attached to a molecule of t-RNA? | 1,  |
A change in the sequence of nucleotides in a molecule of DNA is called a(n) ____., 
| mutation |
| Mutations that are harmful are usually weeded out by ______. | natural selection |
| Mutations in a gene that are helpful usually become part of the gene pool as a new ____. | allele (a different form of a gene) |
Which amino acid would the codon sequence AGU call for?,  | Serine,  |
| Which enzyme is required for transcription? | RNA Polymerase (remember, you are making RNA during transcription) |
| What are three types of RNA? | m-RNA (messenger RNA), t-RNA (transfer RNA) and r-RNA (ribosomal RNA) |
| Where does transcription occur? | In the nucleus (In prokaryotes, it occurs out in the cytosol because prokaryotic organisms don't have a nucleus) |
| Where does translation occur? | Out in the cytoplasm on ribosomes. |
| Genes contain instructions for assembling ___. | proteins |
| Proteins are made out of ____. | amino acids |
The picture below is called the ____.,  | genetic code (All organisms, from prokaryotic bacteria all the way up to humans, use this same genetic code),  |
| What type of proteins are made by the endoplasmic reticulum and what type of ER makes them? | The rough ER usually makes proteins that will be exported from the cell (For example, hormones like insulin would be made using the ribosomes on rough ER and then further modified in the golgi before transported to the cell membrane by vesicles. The digestive enzymes in lysosomes would also be made in the ER and further modified in the golgi) |
| What is the name of the organelle that can modify proteins after they have been made in the rough ER? | golgi |
| What type of proteins are usually made on free-floating ribosomes in the cytosol? | Proteins that will stay in the cytosol (like enzymes) |
| True or False: All organisms share the same genetic code. | TRUE (All organisms will translate a strand of m-RNA into the same sequence of amino acids according to the genetic code shown below),  |