| A | B |
|---|
| What are the building blocks of all matter? | atoms |
| The nucleus of an atom is made up of ____ and ____ | protons and neutrons |
| Electrons have a ___ charge | negative |
| Protons have a ___ charge | positive |
| Neutrons have a ___ charge | neutral (no) charge |
| Which type of particle orbits the nucleus? | electrons |
| Positive charges are attracted to ____ charges | negative |
| Positive charges are repelled by ____ charges. | positive |
| Negative charges are repelled by ____ charges | negative |
| An electron would be attracted to a _____ | proton |
| The center region of an atom is called a(n) ____. | atomic nucleus |
| Each element is different because they have a different number of ____. | protons |
| All of the elements are listed in the ____. | periodic table |
| The ____ is equal to the number of protons in an atom. | atomic number |
| The mass number is equal to the | number of protons and neutrons |
| The number below the chemical symbol on the periodic table that usually has a few decimal places is known as the ____. | average atomic mass |
| Two or more different elements bond together to form ____. | compounds |
| A compound held together by covalent bonds is called a(n) ___. | molecule |
| Atoms or molecules that become charged because they gain or lose electrons are called ___. | ions |
| A negatively charged ion would be ____ by another negatively charged ion. | repelled |
| A positively charged ion would be ____ by another positively charged ion. | repelled |
| A negatively charged ion would be ___ by a positively charged ion. | attracted |
| A liquid that has a uniform mixture of two or more substances is know as a(n) ___. | solution |
| Acids have a pH that is ____ seven. | below |
| Bases have a pH that is ___ seven. | above |
| Distilled water has a pH of ___. | seven |
| As temperature ____, particles move faster and faster | increases |
| As temperature ____ particles move slower and slower. | decreases |
| Increasing the ___ or ___ of the reactants will cause a reaction to speed up. | temperature, concentration |
| Matter is _____. | Anything that takes up space and has mass. |
| A(n) ______ is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. | element |
| Two types of compounds are ____ and ____. | molecules and ionic compounds. |
| A compound in which atoms are joined together by ionic bonds is called a(n) ___. | ionic compound |
| Which 4 elements make up 96% of living matter? | Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen |
| A(n) ___ is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element. | atom |
| The tiny bits of matter that make up an atom are called ___. | subatomic particles |
| Elements that differ from each other because of the number neutrons, but not protons, are called ____. | isotopes |
| _____ is defined as the capacity to cause change. | Energy |
| ____ is the energy that matter possesses due to its location or structure. | Potential energy |
| Matter has a natural tendency to move to the ____ possible state of potential energy. | lowest |
| Electrons gain potential energy when they move ____ from the nucleus. | away |
| When an electron falls back toward the nucleus, energy is ___. | released (or lost) |
| The first electron shell of an atom can hold no more than ___ electrons. | 2 |
| The second electron shell of an atom can hold no more than ___ electrons. | 8 |
| The chemical behavior of an element depends mostly on ____. | the number of electrons in its outermost shell |
| The outermost shell of an atom is called the ___. | valence shell |
| An atom with a full valence shell of electrons is chemically _____ (a.k.a. _____) | unreactive, inert |
| In _____ bonds, pairs of electrons are shared between two or more atoms. | covalent |
| Single covalent bonds share ___ pair(s) of electrons. | one pair (two electrons total) |
| Double covalent bonds share ___ pair(s) of electrons. | two pairs (4 electrons total) |
| The attraction of a particular kind of atom for the electrons of a covalent bond is called its ___. | electronegativity |
| The more ____ an atom is, the more strongly it pulls shared electrons toward itself. | electronegative |
| Bonds in which electrons aren't shared at all (because one atom has a MUCH higher electronegativity than the other) are called ______. | ionic bonds |
| A charged atom, (or molecule) is called a(n) ___. | ion |
| Compounds formed by ionic bonds are called ____. | ionic compounds |
| The most important characteristic about a biological molecule is its ____. | shape |
In the chemical reaction picture below, the molecules on the left side of arrow are called the ____ while the molecules on the right side of the arrow are called the ____., 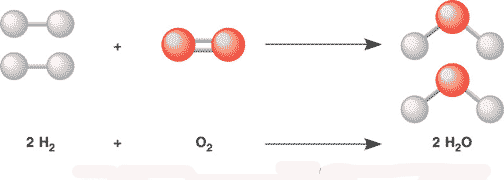 | reactants, products (notice how there are the same number of each type of atom on both sides of this balanced chemical reaction),  |
The picture below shows the formation of a(n) _____ bond.,  | ionic,  |
| A chemical reaction in which arrows are pointing both ways is said to be ____. | reversible |
| In a reversible reaction, when the forward and reverse reactions are happening at the same rate, _____ is achieved. | chemical equilibrium |
| Name 3 types of weak bonds that are important to life in order from strongest to weakest. | (strongest) ionic, hydrogen, London dispersion force (weakest): Your book calles London Dispersion forces Van der Waals forces, but Van der Waals forces are actually any type of intermolecular force, including hydrogen bonds. |
| A weak attraction between hydrogen in one molecule and either an oxygen or nitrogen atom in another molecule is called a(n) _____. | hydrogen bond |
| A very weak bond that can form between a non-polar region of a molecule and another molecule (as long as the molecules are very close together) is called a(n) ____. | London Dispersion Forces (Your book calles London Dispersion forces Van der Waals forces, but Van der Waals forces are actually any type of intermolecular force, including hydrogen bonds.) |
| Because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the electrons of the polar covalent bonds spend more time closer to the _______ atom, giving it a partial _____ charge. | oxygen, negative |
| The hydrogen atoms in a water molecule have a _____ _____ charge. | partial positive charge |
| Molecules in which opposite ends of the molecule have opposite charges are called ______. | polar molecules |
| The fact that water molecules are attracted to each other is an example of ____. | cohesion |
| The attraction of water molecules to the surfaces of some materials is called _____. | adhesion |
| The ____ of a substance is defined as the amount of heat (energy) that must be absorbed or lost by a substance to change its temperature by 1 degree Celsius. | specific heat |
| Compared with most other substances, water has an unusually high ____ which explains why it can store a lot of energy and it takes a lot of energy to change its temperature. | specific heat |
| The transformation from a liquid to a gas is called ____ or ____. | evaporation or vaporization (boiling is the temperature at which the average molecule has enough energy to overcome the attractions that hold molecules together as a liquid. Therefore, the molecules vaporize quite quickly once the boiling point has been reached) |
| Water helps moderate Earth's temperature by _____ a lot of heat to become water vapor at the equator and then moving toward the poles to ____ that heat as it _____. | absorbing, release, condenses |
| The _____ of water from humans and other organisms helps keep them cool. | evaporation |
| If ice didn't float, lakes and oceans would ______. | eventually freeze solid because ice would sink, exposing liquid water to cold winter temperatures instead of insulating it from the cold temperatures. |
| The type of substances that dissolve best in water are ____. | ionic substances and polar covalent substances |
| 1 mole of a substance is equal to ____ particles of that substance | 6.02 X 10 ^23 (6.02 times ten to the twenty third power) |
Which type of bond is represented by the dotted line? By the straight line inside the water molecule?,  | Dotted lines = hydrogen bonds, straight lines = covalent bonds,  |
The picture below shows water dissociating into ___ and ___ ions., 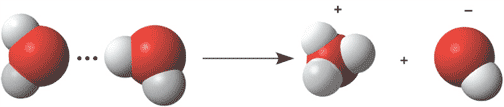 | hydronium and hydroxide ions,  |
| If the concentration of hydrogen (hydronium) ions in a solution is higher than the concentration of hydroxide ions, the solution will be ____. | acidic |
| _____ are substances that minimize (or dampen) changes in pH. | Buffers |
| Who was your chemistry teacher last year? | If you were lucky.,  |