| A | B |
|---|
| The scientific study of the interactions between organisms and the environment is called _____. | ecology |
| Ecology is the scientific study of ______. | the interactions between organisms and the environment |
| What are three questions that ecologists often ask about organisms? | 1) Where do they live? 2) Why do they live there? 3) How many live there? |
| The non-living components of an environment, including temperature, light, water, and nutrients, are called _____ factors. | abiotic |
| The living components of an environment are called ____ factors, or _____ | biotic, biota |
| The abiotic components of the environment are the ____ components of that environment. | non-living |
| The biotic components of the environment are the ____ components of that environment. | living |
| The geographic range (where you can find an organism) of an organism is also known as its ________. | geographic distribution |
| The geographic distribution (where you can find an organism) of an organism is also known as its ________. | geographic range |
| A(n) ____ is a group of individuals of the same species living in a particular geographic area. | population |
| A(n) ______ consists of all the organisms of all the species that inhabit a particular geographic area. | community |
| A(n) ______ consists of all the communities plus the abiotic factors in a particular geographic area. | ecosystem |
| The _____ is the sum of all the planet's ecosystems. | biosphere |
| The movement of individuals away from centers of high population, or their areas of origin, is called ______. | dispersal |
| To see whether a species could inhabit an area that it is not already inhabiting, an ecologist might perform a _____ experiment by moving that organism into the new area. | transplant (Note: This type of experiment is rarely conducted on purpose anymore because of the negative effect that invasive species often have on their new ecosystem) |
| To see what effect an organism has on an ecosystem, ecologists can conduct ____ experiments. | removal and addition (either removing the species from the ecosystem or adding more to an ecosystem) |
| A better word for describing "warm blooded" organisms is to call them ____. | endotherms (Only birds and mammals are endotherms today. Some people believe that certain dinosaurs may have also been endotherms) |
| The process of regulating the amount of water in your cells is called _____. The ability to do this determines whether aquatic organisms can live in fresh or saltwater. | osmoregulation |
| The substrate of an ecosystem refers to _____. | the bottom surface (could be soil, rocks, sand, etc. for a terrestrial ecosystem or mud, silt, rock, coral, etc. for an aquatic ecosystem) |
| What are the four abiotic factors that define climate? | temperature, sunlight, water and wind |
| Climate on the global, regional, or local level is called ______. | macroclimate |
| Climate that differs from the local climate due to proximity to a cool stream, or shade from a log or a thick canopy of trees is called _____. | microclimate |
| Coastal regions are generally _____ than inland areas at the same latitude. | moister |
| The intensity of sunlight that hits the Earth in any given place or season is determined by the ____. | angle that the sunlight strikes the surface of the Earth (Sunlight strikes the Earth most directly at the equator and the angle becomes greater as you move away from the equator. Winter is caused by the fact that due to the Earth's tilt, the angle that the sun strikes the parts of Earth experiencing winter is much less than when it strikes the same places in summer. A 90 degree angle would be straight overhead. Many people falsely believe that the seasons are caused by the elliptical orbit of Earth around the sun. In the northern hemisphere, the Earth is actually closer to the sun in the winter),  |
| In general, oceans and large lakes _____ temperature of nearby land masses. | moderate (This means that temperature doesn't fluctuate as much on land that is close to large bodies of water. This is due to the high specific heat of water which absorbs a lot of heat during the day, keeping the land cooler, and then releases it back at night, keeping land from cooling down as much as it would have without the nearby water) |
| Why do parts of the world around 30 degrees north and south latitude tend to have arid (dry) climates? | Air rises at the equator due to solar heating. As the air rises, it releases a lot of moisture at the equator, but the now drier air starts travelling away from the equator. Around 30 degrees, either north or south of the equator, this dry air sinks back toward land. Sinking air warms as it comes under more and more pressure the closer it gets to the ground. Warm air can hold (the opposite of release) more water, so it rarely rains in these regions.,  |
| Global wind patterns are caused by the fact that _____. | Land and air moves faster at the equator than it does away from the equator. As air rises and moves north (or south), the ground below it slows down relative to the air. It's a bit like throwing a tennis ball out of a moving car's window. |
| The windward side of a mountain range is usually ______ than the leeward side which is usually ____ due to the _____ effect | moister, drier, rainshadow effect,  |
| During summer and winter, many lakes in temperate regions are ______ with little mixing of warmer layers with the cooler layers. In spring and fall, these lakes experience a phenomenon called ____ in which nutrient rich water from the bottom rises to the surface and oxygen rich water from the surface sinks to the bottom and mixing of all layers occurs. | thermally stratified, turnover, 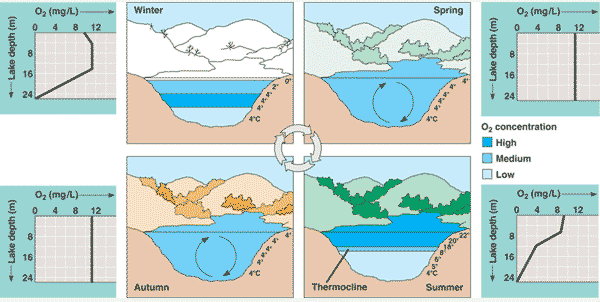 |
| Any of the world's major ecosystems, classified according to the predominant vegetation and characterized by adaptations of organisms to that environment. | Biome |
| Marine biomes are found in ____ water. | salt |
| The upper part of an aquatic biome, where enough light penetrates for photosynthesis to occur, is called the ____. | photic zone,  |
| The lower layer of an aquatic ecosystem, which doesn't receive enough light to support photosynthesis, is called the _____ . | aphotic zone,  |
The bottom substrate of all aquatic ecosystems is called the ____ zone and the organisms that live there are called the ____.,  | benthic zone, benthos,  |
| Dead partially decayed organic matter with the consistency of silt is called _____. | detritus |
| The zone of open water that includes both the photic and aphotic zone is called the _____ zone. | pelagic,  |
The pond in the picture below is classified as being ______ because of its murky (turbid) nutrient ____ water that supports a lot of life (especially algae).,  | eutrophic, nutrient rich,  |
The lake in the picture below is classified as being ____ because of its clear nutrient ____ waters that support little photosynthetic life.,  | oligotrophic, nutrient poor,  |
| The part of a lake that is shallow enough to support rooted aquatic plants is called the _____ zone. | littoral,  |
| The part of a lake that is too deep to support rooted aquatic plants is called the _____ zone. | limnetic,  |
The layer of a lake that shows a rapid temperature change, as in the areas between the red lines in the graph and image below, is called a _____., 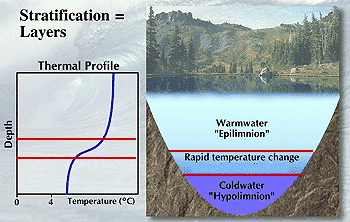 | thermocline (the thermocline separates the warm surface waters from the colder, denser, deep waters., 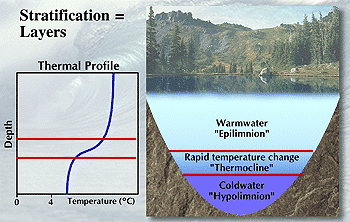 |
| A(n) ____ is an area covered with water for a long enough period to support aquatic plants. | wetland |
| A wetland is an area covered with water for a long enough period to support ______. | aquatic plants |
| A swamp is a type of wetland dominated by ______. | woody plants,  |
| A bog is a type of wetland dominated by ______. | sphagnum mosses,  |
A(n) _____ is a type of wetland dominated by sphagnum mosses., 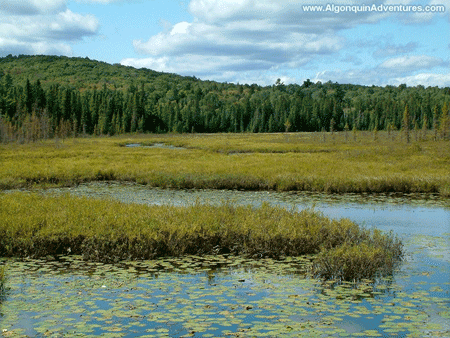 | bog,  |
A(n) ______ is a type of wetland dominated by woody plants.,  | swamp,  |
The type of wetland pictured below is a(n) _____.,  | .,  |
The type of wetland pictured below is a(n) ___.,  | .,  |
| Two important benefits of a wetland are their ability to provide habitat to a large number of organisms and their ability to _____. | filter nutrients and pollutants from water |
| Two important benefits of a wetland are their ability to _____________ and their ability to filter nutrients and pollutants from water.. | provide habitat to a large number of organisms |
| Because of periodic high rates of decomposition in wetlands, both the water and wet soils can become low in _____. | dissolved oxygen (because bacteria use a lot of oxygen while decomposing rotting vegetation in wetlands) |
| A(n) ______ is a transition area between river and sea. | estuary,  |
| A(n) ______ is found where fresh and saltwater mix. | estuary,  |
| Because of the abundance of food in estuaries, many marine organisms use them as ______. | breeding grounds |
| _______ streams are usually, narrow, clear, and fast moving with plenty of dissolved ______ while the _____ they feed into get wider, slower, murkier (more _______) with lower dissolved oxygen and more _____. | headwater streams, dissolved oxygen, rivers, more turbid, pollution |
The picture below shows a tide pool in the _____ zone.,  | intertidal zone,  |
The organisms in an intertidal zone, like the ones shown below, must be adapted to be able to survive wide ranges of _____ and _____.,  | water temperature and salinity (saltiness),  |
| The ______ is the area that falls between high and low tide. | intertidal zone |
| The largest biome in the world is the ____. | oceanic pelagic biome (the open-ocean covers nearly 70% of the Earth) |
Which biome is shown in the picture below?,  | coral reef,  |
| Coral reefs are found in ______ _______ waters. | warm clear,  |
| _____ largely determines the distribution and structure of terrestrial biomes. | Climate |
| ___________ lakes are generally oxygen poor. | Eutrophic (They are oxygen poor because even though they support a lot of photosynthetic algae, that algae dies on a regular basis, sinks to the bottom and is decomposed by bacteria which use a lot of oxygen),  |
The graph below is called a(n) ______.,  | climograph,  |
According to the climograph, which factor is most important in determining whether an area will be a broadleaf forest versus a coniferous forest?,  | Average annual temperature (You find the dominant trees changing from broadleaf deciduous to conifers as you go north or up in elevation),  |
According to the climograph, which factor is most important in determining whether an area will be a grassland versus a forest?,  | precipitation (Less precipitation causes a shift to grasslands. Even less precipitation would cause a grassland to turn into a desert),  |
| The area that marks a transition from one type of biome into another is called a(n) _____. | ecotone |
| What are the two main types of tropical forests and what is the main difference between them? | Tropical rain forest and tropical dry forests. The main difference is that in tropical dry forests, you have a dry season and a rainy season. Tropical rain forests are rainy pretty much year around. |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Tropical forest,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Chaparral,  |
Which biome is pictured below?, 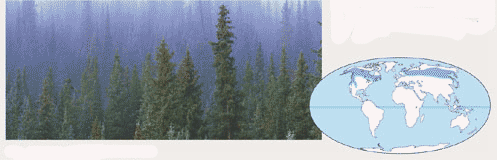 | Coniferous forest,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Desert,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Savanna,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Temperate broadleaf forest,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Temperate grasslands,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | tundra,  |
| Another name for the northern coniferous forest is the ______. | Taiga (This term refers to the part of the biome that borders the tundra but still has conifers, though they are usually a bit on the stunted side due to the cold and wind),  |
| Which terrestrial biome has the greatest biodiversity? | Tropical forests (biodiversity refers to the number of different species that can be found in an area) |
| Cacti and other plants with thick fleshy leaves that store water are called _____. | succulents |
| Which biome is very warm with a dry season that can last eight or nine months? | savanna,  |
| Which biome is usually found close to the coast and has mild rainy winters and long dry summers? | chaparral,  |
| Which biome is characterized by short drought resistant trees and shrubs? | chaparral,  |
| Which biome is characterized by cold dry winters and hot humid summers? | temperate grasslands |
| Deciduous trees are trees that ______. | drop their leaves in the fall,  |
| _________ trees are trees that drop their leaves in the fall. | Deciduous,  |
| You can find the tundra biome much further south than normal if you ______. | go up in elevation enough (up taller mountains) |
| Which biome is characterized by a layer of permafrost just below the surface soils? | Tundra,  |
| The tundra is characterized by a permanently frozen layer of soil just below the surface called _____. | permafrost |
| The uppermost layer of vegetation in a terrestrial biome is called the _____. | canopy,  |
| The study of energy flow and the cycling of chemicals among the various biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem is called ______ ecology. | ecosystem ecology |
| A biome located throughout midlatitude regions where there is sufficient moisture to support the growth of large, broadleaf deciduous trees. | temperate broadleaf forest,  |
| The branch of ecology concerned with the morphological, physiological, and behavioral ways in which individual organisms meet the challenges posed by their biotic and abiotic environments. | organismal ecology |
| Very fine scale variations of climate, such as the specific climatic conditions underneath a log. | microclimate |
| A guiding principle in making decisions about the environment, cautioning to consider carefully the potential consequences of actions is called the _____ . | precautionary principle |
| Very deep benthic zones are also called the _____ zone. | abyssal zone,  |
| Localized variation in environmental conditions within an ecosystem, arranged spatially into a complex of discrete areas that may be characterized by distinctive groups of species or ecosystem processes. | patchiness |
| Which biome is characterized by sparsely scattered individual trees and large herds of herbivores, large carnivores, and occasional fires and droughts? | savanna,  |
| A highly productive lake, having a high rate of biological productivity supported by a high rate of nutrient cycling. | eutrophic lake,  |
| A warm-water, tropical ecosystem dominated by the hard skeletal structures secreted primarily by the resident cnidarians. | Coral reef (The cnidarians they are talking about are hard corals like the brain coral pictured below. Notice the white patch of calcium carbonate skeleton that is exposed where the coral polyps have died),  |
| The ______ regions of the world are found between 23.5 degrees north and south latitude. | tropical,  |
| The tropical regions of the world are found between _____ degrees north and south latitude. | 23.5,  |
| The shallow region of the ocean overlying the continental shelf. | neritic zone,  |
| A dark, hot, oxygen-deficient environment associated with volcanic activity. The food producers are chemoautotrophic prokaryotes. | Deep-sea hydrothermal vents., 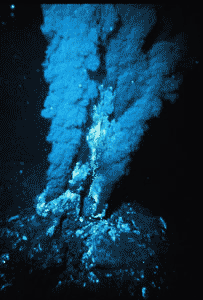 |
| The region of water lying over deep areas beyond the continental shelf. | oceanic zone,  |
| The distribution of individuals within geographic population boundaries. | dispersal |
| A biome at the extreme limits of plant growth. At the northernmost limits, it is called ____, and at high altitudes, it is called ____. | arctic tundra, alpine tundra,  |
| The study of populations in relation to the environment, including environmental influences on population density and distribution, age structure, and variations in population size. | population ecology |
| A scrubland biome of dense, spiny evergreen shrubs found at midlatitudes along coasts where cold ocean currents circulate offshore; characterized by mild, rainy winters and long hot dry summers. | chaparral,  |
| The community of organisms living in the benthic zone of an aquatic biome. | benthos,  |
| The study of past, present, and future patterns of landscape use, as well as ecosystem management and the biodiversity of interacting ecosystems. | landscape ecology |
| The study of how interactions between species affect community structure and organization. | community ecology |
| An ecosystem intermediate between an aquatic one and a terrestrial one. | wetland |
| The mixing of waters as a result of changing water-temperature profiles in a lake. | turnover,  |
| In a lake, the well-lit, open surface waters farther from shore. | limnetic zone,  |