| A | B |
|---|
| Name the first 10 alkanes. | methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, heptane, octane, nonane, decane |
| Straight chain hydrocarbons with double bonds are called ______. How would you name one with 3 carbons? | alkenes, propene (Technically, if there are 2 double bonds, it would be propadiene, but don't worry about that for now) |
| Straight chain hydrocarbons with triple bonds are called _____. How would you name one with 2 carbons? | alkynes, ethyne |
What is the name of this molecule?, 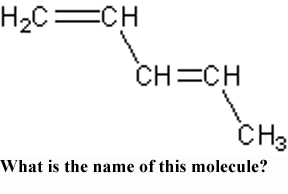 | 1,3-Pentadiene,  |
What is the name of this molecule?, 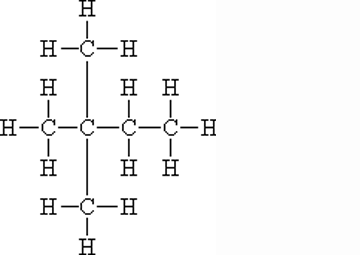 | 2,2-dimethyl-butane (can also be called iso-hexane because of its six carbons, but this name doesn't give you enough information to figure out the structure),  |
What is the name of this molecule?,  | 2,3-dimethyl-butane (can also be called iso-hexane because of its six carbons, but this name doesn't give you enough information to figure out the structure),  |
What type of molecule is this?, 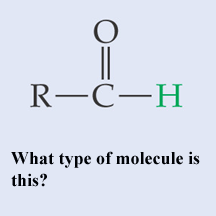 | A basic aldehyde,  |
What type of molecule is this?,  | carboxylic-acid,  |
What type of molecule is this?, -copy.gif) | aldehyde (hexanal), -copy.gif) |
What type of molecule is this?, .gif) | ketone (2-butanone), .gif) |
What type of molecule is this?, 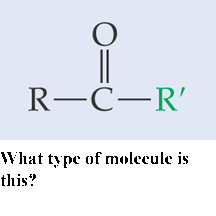 | Ketone, 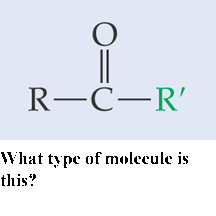 |
| C6H6 in a ring structure is _____. | Benzene, 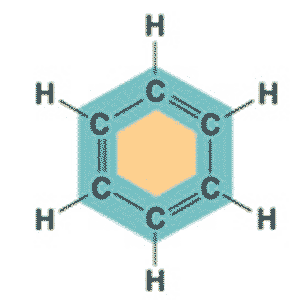 |
| What is the molecular formula and shape of benzene? | C6H6, ring |
| The science of developing and testing drugs is called ____. | pharmacology |
| One of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures, and therefore, different properties. | isomer |
| A functional group present in organic acids consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. | carboxyl group,  |
| A functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (--SH). | sulfhydryl group,  |
| A functional group that is often written as --COOH. | carboxyl group It's -COOH because it is a C double-bonded to an O and single-bonded to OH),  |
| A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. It can act as a base in a solution, accepting a hydrogen ion and acquiring a charge of +1. | amino group, 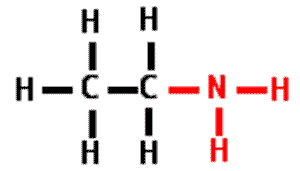 |
| An organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen is called a(n) _____. | hydrocarbon (the butane molecule below is a hydrocarbon because it has only hydrogens and carbons), 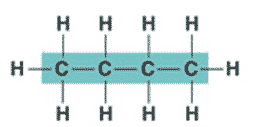 |
| An arrangement of two non-carbon atoms, each bound to one of the carbons in a carbon-carbon double bond,where the two non carbon atoms are on the same side relative to the double bond. | cis, 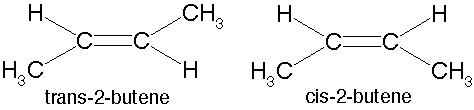 |
| An arrangement of two non-carbon atoms, each bound to one of the carbons in a carbon-carbon double bond,where the two non carbon atoms are opposite sides relative to the double bond. | trans, 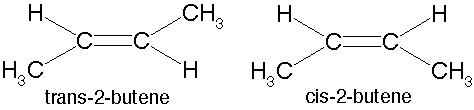 |
| A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeleton of organic molecules and usually involved in chemical reactions. | functional group (the carboxyl-group in red below is a functional group that makes the molecule acidic because it often loses the hydrogen as a hydrogen ion into the solution which lowers the pH of the solution),  |
| A type of isomer where the different organic compounds have the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangements of their atoms. | geometric isomer, 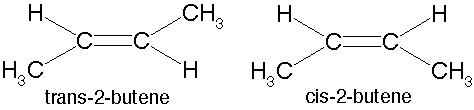 |
| A functional group that is important in energy transfer. | Phosphate group (think of ATP-->ADP + P + energy), 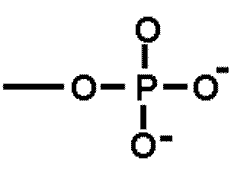 |
| One of several organic compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms. | structural isomer, 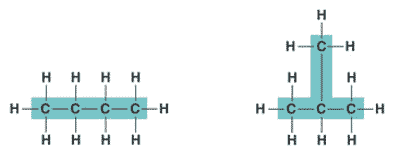 |
| A functional group present in aldehydes and ketones that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. | carbonyl group, 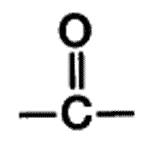 |
| A functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols. | hydroxyl group,  |
| One of two molecules that are mirror images of each other. | enantiomer (also called a stereo-isomer), 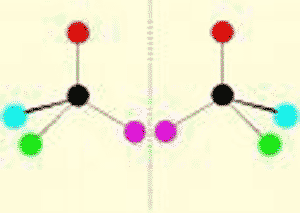 |
| A(n) ______ carbon is a carbon atom that is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms. The result is to allow for the possibility of another molecules that can be an enantiomer (mirror image) of the first molecule. | asymmetric carbon (In the diagram below, the #2 carbon is the asymmetric carbon. Even though it bonds to two carbons, the #1 carbon can be considered an aldehyde GROUP and the number #3 carbon can be considered a propyl group. Therefore, all 4 groups coming off the #2 carbon are different), 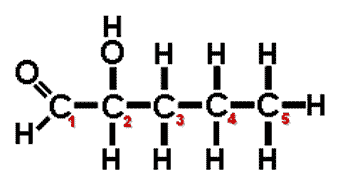 |
What is the name of the molecule shown below?, 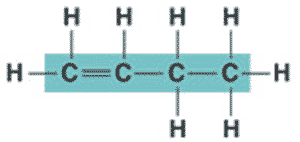 | 1-butene (the 1 signifies that the double bond starts at the first carbon),  |
What is the name of the molecule shown below?, 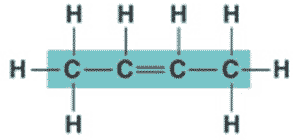 | 2-butene (the 2 signifies that the double bond starts at the second carbon),  |
What type of molecule is this?,  | An aldehyde (It's an aldehyde because the carbonyl group is coming off a terminal carbon. If it wasn't, it would be a ketone. The name of this molecule is ethanal, since it has two carbons like ethane),  |
What is the name of the functional group in red?,  | amino group,  |
Which carbon on this molecule is the asymmetrical carbon?,  | In the diagram below, the #2 carbon is the asymmetric carbon. Even though it bonds to two carbons, the #1 carbon can be considered an aldehyde GROUP and the number #3 carbon can be considered a propyl group. Therefore, all 4 groups coming off the #2 carbon are different.,  |
What is the name of this ring structure?, 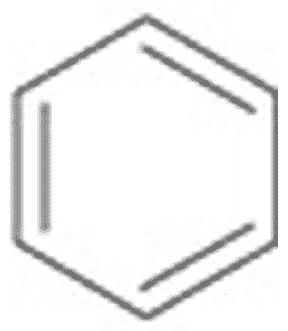 | Benzene (The structure you saw on the other side of this card was an abbreviated structural formula. These formulas assume a carbon at each corner and enough hydrogens to make 4 bonds coming off each carbon. Below is the unabbreviated structural formula for comparison),  |
What is the name of this ring structure?,  | Benzene,  |
What is the name of this hydrocarbon?,  | Butane,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | carbonyl group,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?, 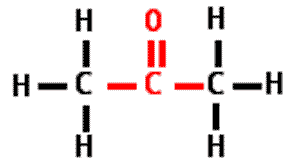 | ketone, carbonyl group (The specific name of the molecule pictured is propanone because it is a ketone with 3 carbons like propane),  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | Carboxylic acid, carboxyl group (This molecule is called ethanoic acid but is more commonly referred to as acetic acid which is the acid in vineger),  |
What is this diagram showing?, 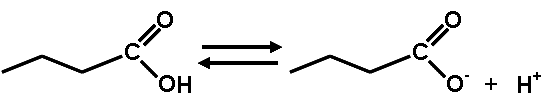 | This shows how carboxylic acids (notice the carboxyl group at the end of the abbreviated structural formula of hydrocarbons) will release a hydrogen ion into water solutions. Hydrogen ions decrease the pH of the solution. That is why it is a carboxylic ACID., 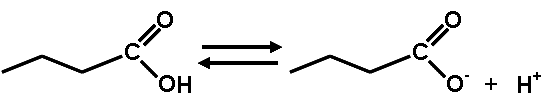 |
What is the name of this molecule?,  | cyclohexane (The structure you saw on the other side of this card was an abbreviated structural formula. These formulas assume a carbon at each corner and enough hydrogens to make 4 bonds coming off each carbon. Below is the unabbreviated structural formula for comparison), 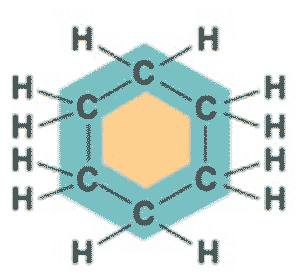 |
What is the name of this molecule?,  | cyclohexane,  |
What do we call these two molecules?,  | enantiomers (or stereoisomers; notice that they are mirror images of each other),  |
What type of isomers are these?, 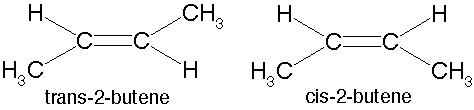 | geometric isomers, 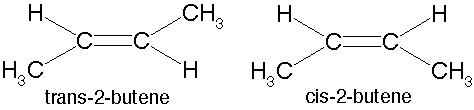 |
Which of these geometric isomers would be considered the "cis" isomer and which would be the "trans" isomer?,  | The one on the left is "cis" and the one on the right is "trans" (the prefix trans means across),  |
What is the name of this hydrocarbon?,  | Ethane,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | An alcohol, hydroxyl group (This is ethanol because it has two carbons like ethane. The common name is ethyl alcohol),  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | phosphate group,  |
What is the name of this hydrocarbon?, 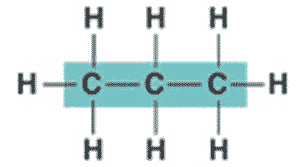 | propane,  |
What type of isomers are these?,  | structural isomers,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | Sulfhydral group,  |
What were the results and conclusions of Stanley Millers 1953 experiment (pictured below)?,  | Stanley Miller tried to recreate the conditions of early earth by placing some simple compounds like water, hydrogen, methane and ammonia in a sealed container. He added energy in the form of electricity to simulate lightning and found that these primitive Earth gasses reacted and formed a variety of organic compounds that would have been necessary for the first life to form),  |
| Carbon can form a wide variety of compounds because it forms ____ bonds. | 4 |
Each line in a structural formula (like the one below) represents a _____., 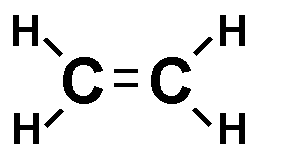 | pair of shared electrons, 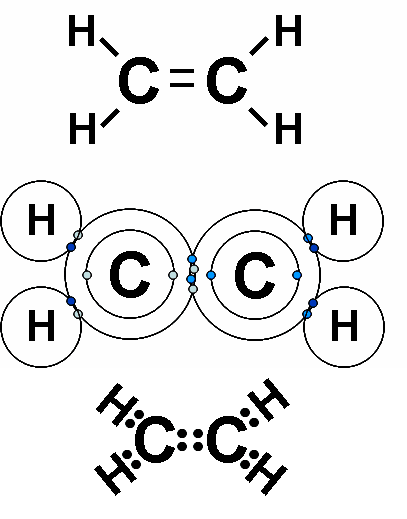 |
| ____ is the source of carbon for all of the organic molecules found in organisms. | carbon dioxide |
Hydrocarbons (like the one shown below) are ______ and therefore don't dissolve in water.,  | Non-polar or hydrophobic |
| An important energy storing molecule that has 3 phosphate groups is called _____. | Adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP), 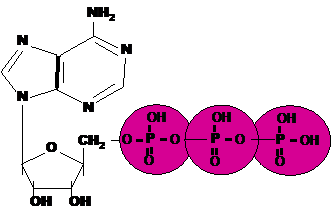 |
| Hydrocarbons can be either _____, _____, or _____ shaped. | straight, branched, or ring shaped |