| A | B |
|---|
| ______ are the buildng blocks of matter. | Atoms |
| _____ are the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element. | Atoms |
| ______ are pure substances that are made of one type of atom. | Elements |
| All of the 115 or so known elements can be found on the _____. | periodic table |
| _____ are made of two or more different elements bonded together. | compounds |
| A _______ property is a characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. | physical property |
| A _____ change is a change in a substance that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance. | physical change |
| Melting a candle would be an example of a _____ change. | physical change |
| Burning a candle would be an example of a _____ change. | chemical change |
| What are the three common states of matter? | Solid, liquid and gas (a fourth state, plasma, occurs when a material becomes so hot that it loses most of its electrons) |
| In what state would you find matter that makes up the core of the sun? | plasma |
| Has definite volume and shape. | solid |
| Has definite volume but not shape | liquid (liquids will conform to the shape of the bottom portion and sides of their container but retain the volume their overall volume) |
| Has neither definite volume nor shape. | gas (gases will spread out to conform to the shape of their container, increasing in volume as they do) |
| Give two examples of changes of state. | Melting and boiling (freezing and condensing are two more examples) |
| Melting, boiling, freezing, and condensing are all examples of ______. | changes of state (sublimation is another example in which a solid skips the liquid phase and goes straight to the gaseous phase. Deposition is the opposite of sublimation) |
| A ________ relates to a substances ability to undergo changes that transform it into different substances. | chemical property |
| A car that is rusting is undergoing a ____ change. | chemical |
| A _____ change happens when there is a chemical reaction that changes the original substances involved into different substances. | chemical |
| The substances that are required for a chemical reaction to occur (ie- the raw materials) are called the ____ of the reaction. | reactants |
| The substances that are produced as a result of a chemical reaction are called the _____ of the reaction. | products |
| What is the relationship between the mass of the products of a chemical reaction and the mass of the reactants of a chemical reaction? | They are the same (matter is not created or destroyed, just rearranged) |
| In the chemical reaction of CARBON + OXYGEN ---> CARBON DIOXIDE, the carbon dioxide is the ____ of the reactions. | product |
| In the chemical reaction of CARBON + OXYGEN ---> CARBON DIOXIDE, the oxygen and carbon on the left side of the reaction arrow are the ____ of the reactions. | reactants |
| A pure substance can be a(n) _______ or a(n) ______. | element or compound |
| _______ contain more than one substance, each of which retains its identity and properties. | Mixtures |
| _____ can usually be separated fairly easily. | Mixtures |
| A uniform mixture is known as a(n) ________ mixture. | homogeneous mixture (the prefix "homo" means "same") |
| A mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout is known as a(n) ______ mixture. | heterogeneous mixture (the prefix "hetero" means "differen.") |
| A sugar or salt solution would be classified as a(n) _____ mixture. | homogeneous mixture (the prefix "homo" means "same") |
| A bucket of dirt would be classified as a(n) _____ mixture. | heterogeneous mixture (the prefix "hetero" means "different") |
| If a pure substance can be decomposed by ordinary chemical means it is a(n) ____. | compound |
| If a pure substance cannot be decomposed by ordinary chemical means it is a(n) ____. | element |
| A homogenous mixture is also called a(n) ____. | solution |
One method of separating heterogeneous mixtures (like blood) into layers based on the density of the components can be accomplished by using a machine called a ______ that spins the mixture at very high speeds, forcing the most dense particles to the bottom., 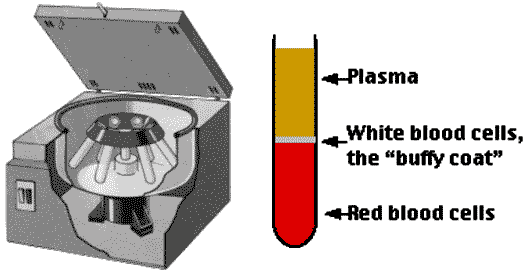 | centrifuge (To separate plasma from the red and white blood cells, blood is put in a centrifuge tube and spun around very quickly, sending the heavier red blood cells to the bottom. The liquid component of blood, called plasma, forms a layer on top),  |
| A method of separating mixtures based on the fact that different substances in the mixture have different boiling points is called ______. | distillation (the apparatus below is used to distill liquids), 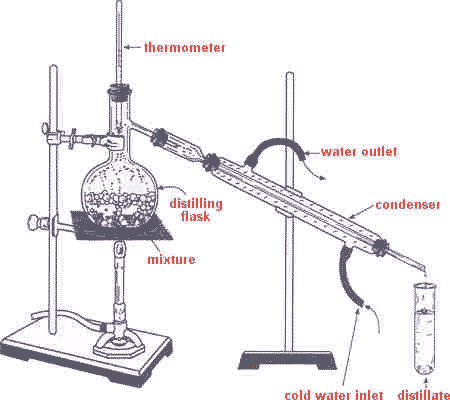 |
A method for separating substances in a mixture based on the facts that larger molecules move slower than smaller molecules through paper when dissolved in a solvent is called _____., 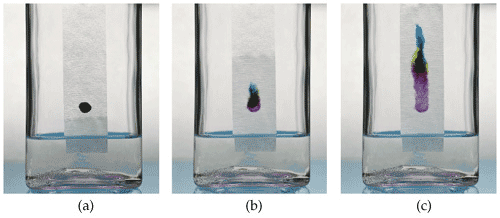 | chromatography (In the picture below, different molecules that make up a type of ink are separated. The far left jar shows the beginning and the far right jar shows the end of the separation),  |
A method of filtration in which molecules stick (adhere) to some surface (such as activated charcoal) while other molecules pass by is called _____.,  | adsorption (the process of sticking is called adhesion),  |
A method for separating mixtures based on a barrier that allows small particles to pass through but not larger ones is called ____., 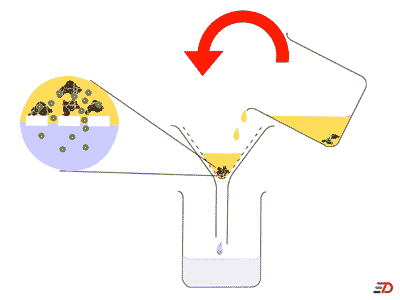 | filtration (Coffee filters work this way. Sometimes swimming pools filter the water through sand or diatomaceous earth),  |