| A | B |
|---|
What is the structure labeled "A"?,  | A flagellum,  |
What is the structure labeled "A"?,  | rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) - notice the ribosomes on the membrane folds,  |
What is the structure labeled "B"?,  | smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER) - notice the lack of ribosomes on the membrane folds,  |
What are the tiny structures labeled "C"?,  | ribosomes,  |
What is the structure labeled "D"?,  | central vacuole,  |
What is the structure labeled "E"?,  | Chloroplast,  |
What is the structure labeled "G"?,  | Cell wall,  |
What is the structure labeled "H"?,  | plasma membrane (a.k.a. - cell membrane),  |
What is the structure labeled "I"? Hint: It produces and destroys hydrogen peroxide.,  | peroxisome,  |
What is the structure labeled "J"?,  | A mitochondrion,  |
What is the structure labeled "K"?,  | Golgi apparatus,  |
What is the region labeled "L" called?,  | centrosome (notice the lack of centrioles in the plant cell),  |
What is the structure labeled "M"?,  | nucleus,  |
What is the structure labeled "M1"?,  | nuclear envelope (a.k.a. - nuclear membrane),  |
What is the structure labeled "M2"?,  | nucleolus,  |
What is the structure labeled "M3"?,  | chromatin (uncondensed chromosomes),  |
What part of the plasma membrane is "A" referring to?,  | hydrophilic region (phosphate heads of the phospholipid),  |
What part of the plasma membrane is "B" referring to?,  | hydrophobic region (fatty acid portion of the phospholipid bilayer),  |
What part of the plasma membrane is "C" referring to?,  | hydrophilic region (phosphate heads of the phospholipid),  |
What is enclosed by the rectangle that "D" is pointing to?,  | a phospholipid,  |
What is "E" pointing to?,  | membrane proteins,  |
What type of cell is being shown in this diagram?, 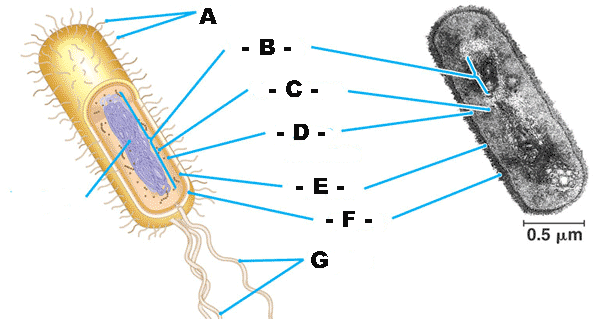 | prokaryotic cell,  |
What is "B" pointing to?,  | nucleoid (region where the cell's DNA is located),  |
What is "C" pointing to? Hint: They are tiny dot-like structures.,  | ribosomes,  |
What is "D" pointing to?,  | plasma membrane (a.k.a. - cell membrane),  |
What is "E" pointing to?,  | Cell wall,  |
What is "F" pointing to?,  | capsule (a jelly-like outer coating of many prokaryotes),  |
What is "G" pointing to?,  | flagella (the plural of flagellum),  |
What type of electron microscope produced this image?, 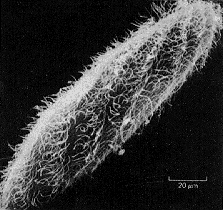 | scanning electron microscope (SEM),  |
What type of electron microscope produced this image?,  | transmission electron microscope (TEM),  |
The cell below is a(n) _____ cell.,  | animal,  |
The cell below is a(n) _____ cell.,  | plant,  |
| The ____ is the simplest collection of matter that can live. | cell |
| The first microscopes, as well as the microscopes that we use in lab, are called ____. | light microscopes (LM) |
| ______ in microscopy is the ratio of an object's image size to its real size. | Magnification |
| _____ is a measure of the clarity of an image under a microscope and is defined as the minimum distance that ______ can be separated and still be distinguished as _____. | Resolution, two points, two points |
| _________ microscopes focus a beam of electrons through the specimen or onto its surface. | Electron microscopes |
| The type of electron microscope that produces 3-D images of the surface of a specimen is called a ____. | scanning electron microscope (SEM),  |
| The type of electron microscope that produces a two dimensional picture of a thinly sliced cross section of a specimen is called a ______. | transmission electron microscope (TEM) |
| The study of cells is called _____. | cytology |
| The basic structure and functional unit of every organism is one of two types of cells; _____ or _____. | prokaryotic or eukaryotic, 
|
| The semifluid substance in which organelles are found is called _____. | cytosol |
| A major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that _________. | eukaryotic chromosomes are located within a nucleus while prokaryotic chromosomes are out in the cytosol in a region called the nucleoid. |
| The entire region between the nucleus and the plasma membrane is called the ____. | cytoplasm, 
|
| The major reason that cells can't get too big is that as they get bigger, their _____ grows faster than their ____. | volume grows faster than their surface area (A cells requirement for nutrients and production of waste is proportional to its volume, but its ability to get nutrients in and waste out through the plasma membrane is proportional to the surface area of the plasma membrane) |
| Which three organelles or cell parts are found in an animal cell but not a plant cell? | lysosomes, centrioles, and flagella (although some plant sperm have flagella) |
| Which four organelles or cell parts are found in an plant cell but not an animal cell? | chloroplasts, large central vacuole, cell wall, plasmodesmata |
| The ________ directs protein synthesis by synthesizing m-RNA according to instructions provided by ______. | nucleus, DNA |
| The nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the ______ which has holes called _____ to allow materials back and forth between the cytoplasm and the interior of the nucleus. | nuclear membrane, nuclear pores |
| DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic organisms is located inside the nucleus as discreet units called _____. They are only clearly visible just before _____. Otherwise, they are uncoiled in a diffuse mass referred to as _____. | chromosomes, cell division, chromatin. |
| The dark structure inside the nucleus is called the _____. It's job is to make the parts of ______. | nucleolus, ribosomes, 
|
| ________ are particles that carry out protein synthesis when _____ attaches to them to deliver the instructions. | Ribosomes, m-RNA |
| You would find free ribosomes ____________. | suspended in the cytosol |
| Bound ribosomes would be found attached to the outside of the _____ or the _____. | endoplasmic reticulum or nucleus |
Which process is depicted in the picture below?, 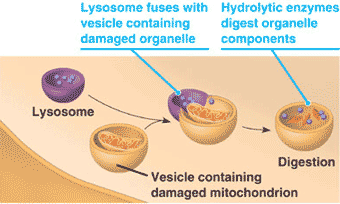 | Autophagy (the recyling of old cell parts),  |
What is "A" in the picture below?,  | A mitochondrion,  |
Which organelle is shown in this micrograph?,  | a mitochondrion,  |
| The ______ ER does not have ribosomes attached to its outer surface. | smooth |
| The ______ ER has ribosomes attached to its outer surface. | rough |
| The smooth ER does not have ________ attached to its outer surface. | ribosomes |
| The rough ER has ________ attached to its outer surface. | ribosomes |
| Which organelle is important in the synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids for membranes and steroid hormones? | Smooth ER |
| Most proteins that end up being secreted from the cell are originally made in the _____. | rough ER |
| The _____ can be thought of as a center for manufacturing, warehousing, sorting, and shipping. | golgi apparatus |
| A _____ is a membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest all kinds of macromolecules. | lysosome |
| When lysosomes fuse with food vacuoles that formed by endocytosis, the overall process of procurring and digesting the food is called ______. | phagocytosis,  |
| Mature plant cells contain a large _________ enclosed by a membrane called a tonoplast. | central vacuole |
| The ____ and _____ are organelles that convert energy into more useable forms for eukaryotic cells. | mitochondria and chloroplasts |
| Which two organelles have an inner and an outer double membrane that work to compartmentalize the organelles? | mitochondria and chloroplasts |
| Which organelle is involved with cellular respiration? | mitochondria |
| The mitochondria is involved with the process of _____. | cellular respiration |
| The chloroplast is involved with the process of _____. | photosynthesis |
| Which organelle is involved with photosynthesis? | chloroplast |
| The space inside of the inner membrane of the mitochondria is called the ____. | mitochondrial matrix |
| The flattened interconnecting sacs inside chloroplasts are called ____. | thylakoids ("E" in the picture below),  |
| A stack of thylakoids is called a ______. | granum ("D" in the picture below),  |
| The space between the thylakoids and the inner membrane of the chlorplast is called the ____. | stroma |
| The green photosynthetic pigment in _____ is called _____. | chloroplasts, chlorophyll |
| _____, especially prominant in the liver, help detoxify alcohol and other poisons by transferring hydrogen from the poisons to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide. | Peroxisomes |
| The _______ is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities of the cell. | cytoskeleton, 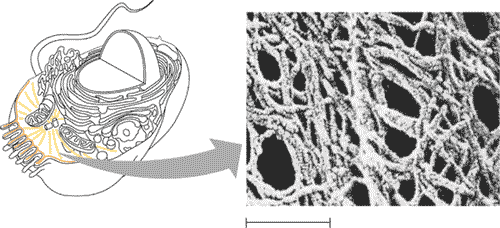 |
| The cytoskeleton is composed of three types of molecular structures. From widest to narrowest, they are _______, _______, and _______. | microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. |
| In many cells, microtubules grow out from a region called the ______, and is considered to be the "microtubule organizing center." In animal cells a pair of centrioles would be found in this region. | centrosome |
| Within the centrosome of animal cells are a pair of ______ that seem to help with separation of chromosomes during mitosis. | centrioles |
| Many single cell organism have either _____ or ______, both with the same "9 + 2" arrangement of microtubules, to help propel them through the water. The ____ are the longer of the two. | cilia, flagella, flagella are longer |
| Microfilaments (actin filaments) often work in conjunction with a protein called _____ to cause contraction in such things as muscle cells, pinching of the cleavage furrow during cytokinesis, or movement of pseudopods in amobae. | myosin, 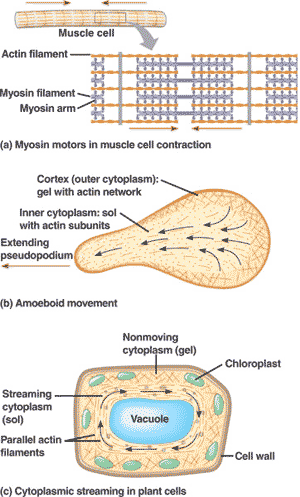 |
| The cell wall of plants is made mostly of ______. | cellulose |
| In animals, which type of intercellular junction function like rivets that fasten neighboring cells together? | desmosomes |
| In animals, which type of intercellular junction function sews cells together to prevent extracellular fluid from leaking across layers of epithelial cells? | tight junctions |
Which two types of cellular structures would have a cross-section like the picture below?, 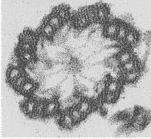 | Basal bodies and centrioles (notice the nine sets of triplet microtubules),  |
Which two types of cellular structures would have a cross-section like the picture below?, 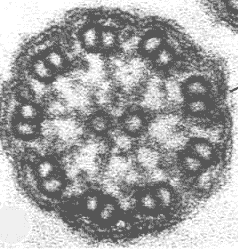 | cilia and flagella,  |