| A | B |
|---|
| The signals received by cells, whether originating from other cells or from changes in the physical environment, take various forms, including light and touch. However, cells most often communicate with each other by _____ signals. | chemical |
| Scientific evidence that shows similarities between cell signaling mechanisms in many different types of organisms suggests that these signaling pathways first evolved in ____________. | single-celled organisms |
| The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response is a series of steps called a(n) ______________. | signal transduction pathway,  |
The type of signaling called cell-cell recognition is important in such processes as ______ and ______.,  | embryonic development and immune response (Cells in developing embryos start to differentiate due to their location and proximity to other cells, so they have to know what other cells they are near. Immune cells need to be able to tell the difference between cells that belong and invading cells) |
| Messenger molecules that travel only short distances are called _________. | local regulators (the red molecules below), 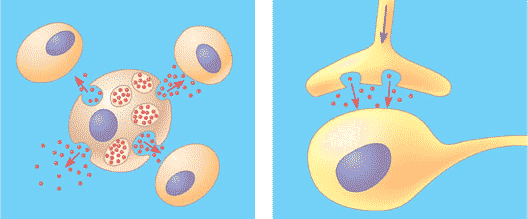 |
| Local signaling involves the secretion of signaling molecules that act on ______ cells. | nearby,  |
| A type of local signaling in which a cell secretes signaling molecules into the extracellular fluid and those molecules diffuse through the fluid to nearby target cells. | paracrine signaling, 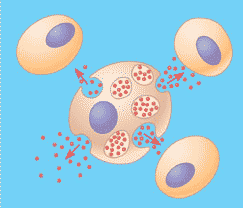 |
| The narrow space between a nerve cell and its target cell is called the _____. | synapse, 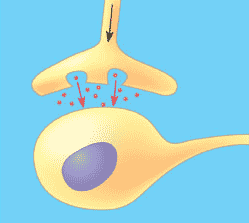 |
| ________ signaling occurs in an animals nervous system when molecules secreted by one nerve cell diffuse across the narrow space that separates it from the target cell (often another nerve cell). | synaptic signaling,  |
| Signaling molecules that communicate with distantly located cells by entering and travelling through the circulatory (in animals) system until their target is reached are called _____. | hormones (plants have hormones also), 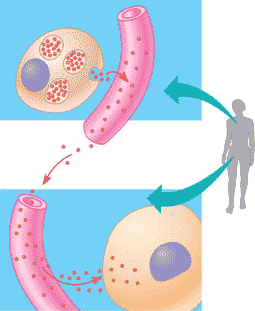 |
| Another word for hormonal signaling is ________. | endocrine signaling,  |
| Another word for endocrine signaling is ______. | hormonal signaling,  |
| The transmission of a signal from one end of a long neuron to the other end is accomplished by transmitting a(n) ______ signal down the neuron. | electrical signal (This can be considered a form of long distance communication due to the long length of most nerve cells) |
| One of the effects of epinephrine (which is secreted by the adrenal gland during times of stress) is to cause liver and muscle cells to break down their stores of _______ to make ______ available for quick energy. | glycogen, glucose |
| The process going on at the receiving end of a cellular conversation can be broken down into three steps; ______, ______, and _______. | reception, transduction, and response,  |
| A chemical signal is "detected" when it binds to a _____ protein located at the cell's surface or inside the cell. | receptor protein |
| A ______ is a molecule that specifically binds to another, usually larger molecule. Often times, the larger molecule is a receptor protein. | ligand |
| Genes can be activated by chemical signals that activate ______________ (special proteins that activate the transcription of DNA into messenger-RNA molecules) | transcription factors |
| During the reception stage, a signal molecule binds to a ________ protein, causing it to ____________ | receptor protein, change shape |
| ____________ factors control which genes are turned on and transcribed into m-RNA. | Transcription factors |
| Most receptors are found on the _______. | outside of the plasma membrane |
| The three major types of membrane receptors are _____, ______, and ______. | G-protein-linked receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, and ion channel receptors |
| Transduction is usually a _____ step pathway. | multi,  |
| The molecules that interact and pass the information from the original signal molecule to the response at the end of the transduction pathway are called ________ molecules and are usually proteins | relay,  |
| Often times, the conformational change in one protein that allows for the next interaction in a multi-step transduction pathway is brought about the protein being __________________. | phosphorylated,  |
| The general name for enzymes that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to a protein is _______________ | protein kinase |
| The addition of phosphate groups often changes a relay protein in a transduction pathway from an __________ form to an _________ form | inactive to an active form,  |
| Enzymes that rapidly remove phosphate groups from proteins are called _________. The process is called ______. | protein phosphatases, dephosphorylation |
| In addition to using proteins, many signaling pathways also involve small, non-protein, water soluble molecules or ions called ___________. | second messengers (the picture below shows a pathway where the signal is sugar and the transduction pathway involves both cAMP and calcium ions), 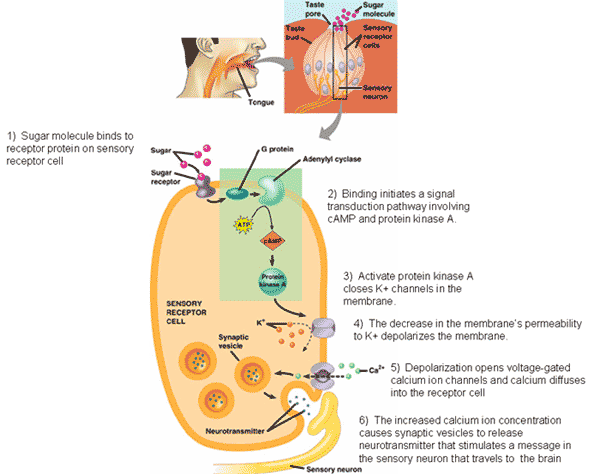 |
| The two most common second messengers are ______________ and ___________ | cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium ions, 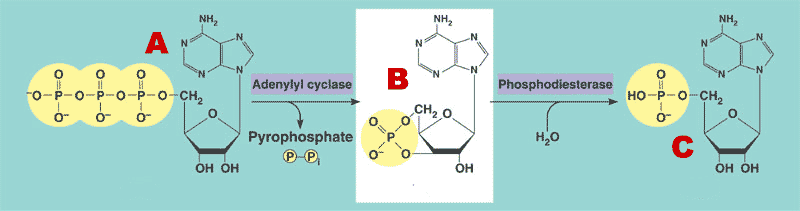 |
| Cell signaling leads to regulation of ______ activities or ______. | cytoplasmic activities or transcription (the process of copying the code from DNA onto m-RNA) |
| Signaling pathways with many steps have three important benefits. What are they? | signal amplification, more opportunities for fine-tuning and regulation, specificity of response (which means that different cells can have different responses to the same signaling molecules by having minor changes along the pathway) |
Name 2 second messengers that are used in the pathway shown below.,  | cAMP and calcium ions,  |
What molecule is the letter "A" is next to.,  | ATP (adensosine tri-phosphate),  |
What molecule is the letter "B" is next to.,  | cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate),  |
What molecule is the letter "C" is next to.,  | AMP (adenosine monophosphate),  |
What is the name of the enzyme that converts ATP into cAMP.,  | Adenylyl cyclase,  |
What is the name of the enzyme that converts cAMP into AMP.,  | phosphodiesterase,  |
Which of the three major types of membrane receptors is shown below?, 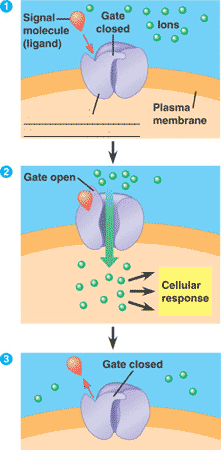 | gated ion channel,  |
Which of the three major types of membrane receptors is shown below?, 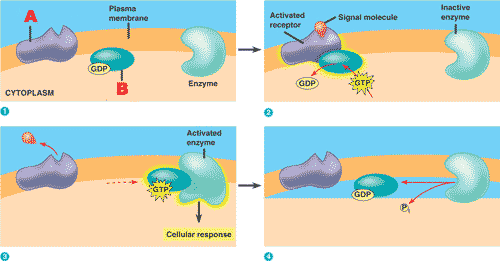 | G-protein-linked receptors,  |
Which of the three major types of membrane receptors is shown below?,  | receptor tyrosine kinases,  |
What type of signaling is being shown in the picture below,  | hormonal (or endocrine) signaling,  |
What type of signaling is being shown in the picture below?,  | local signaling,  |
What type of signaling is being shown in the picture below?, 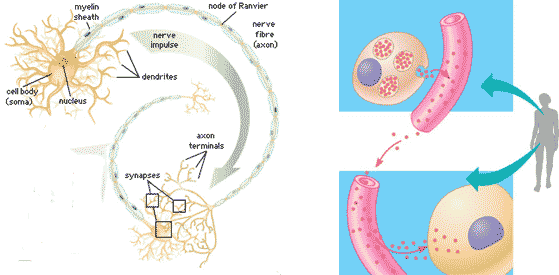 | long-distance signaling,  |
What type of signaling is being shown in the picture below?,  | paracrine signaling,  |
Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #1?,  | reception,  |
Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #2?,  | transduction,  |
Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #3?,  | response,  |
Which type of signaling is shown in the picture below?,  | synaptic,  |
The space between the two cells in the picture below is called the ______.,  | synapse,  |