| A | B |
|---|
| What are the four phases of the cell cycle? | G1, S, G2, and M |
| Chromosomes are only visible when ___. | the cell is dividing |
| When the cell is most actively growing, it is in the ____ phase. | G1 |
| When DNA is replicating, the cell is in the ___ phase. | S |
| When the cell is preparing for mitosis, it is in the ____ phase. | G2 |
| When the cell is undergoing cell division, it is in the ___ phase. | M |
| In order, what are the five stages of mitosis? | Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (remember "I pinched pretty Martha's arm today" for interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Interphase is NOT a stage of mitosis, but it does come before mitosis) |
| G1, S, and G2 all occur during ____. | interphase |
| Which phases of the cell cycle occur during interphase? | G1, S, and G2 |
| Cell division ends when ___ is complete. | cytokinesis |
| The ____ is a series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. | cell cycle |
| The ___ holds sister chromatids together. | centromere |
| The centromere holds _____ together. | sister chromatids |
| After chromosomes undergo DNA replication, they consist of two identical ____ that are attached to each other. | sister chromatids |
| During which stages of mitosis are sister chromatids attached to each other? | prophase, prometaphase and metaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis do sister chromatids start to separate? | anaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis are sister chromatids lined up along the center of the cell? | metaphase (think metaphase = middle) |
| During which stage of mitosis does the nuclear envelope break down? | prometaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes condense to become visible? | prophase |
| The centrosome helps organize a fan-like group of protein fibers called the ____ that help pull the chromosomes apart. | spindle |
| In animal cells, ________ are found in the centrosome, but don't seem to affect the ability of the cell to under.go mitosis | centrioles, 
|
| The division of the cytoplasm itself is called ___. | cytokinesis |
| In plant cells, cytokinesis is accomplished with the formation of a ___ between the two new cells. | cell plate |
| During which stage of mitosis are the chromosomes divided into the two opposite ends of the cell and the nuclear membrane reforms? | telophase |
| The two main stages of cell division are ___. | mitosis and cytokinesis, 
|
| One main difference between cell division in plants versus animals is that plants have ___. | a cell plate |
| During which stage of mitosis does the nucleolus disappear? | prophase |
| During normal cell division, a human cell with 46 chromosomes would produce two daughter cells with ___ chromosomes each. | 46 |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 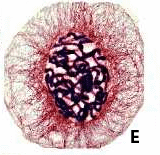 | Prophase,  |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 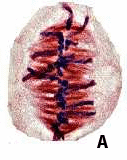 | Metaphase,  |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 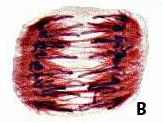 | Anaphase,  |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 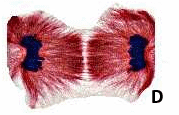 | Telophase,  |
Which stage of the cell cycle is depicted in the picture below?, 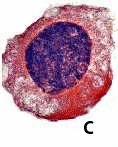 | Interphase,  |
The structures labeled A are,  | sister chromatids,  |
The structures labeled B are,  | kinetechore microtubules (a type of spindle fiber),  |
The structure labeled C is,  | a centromere,  |
The plant cell labeled A is in ____.,  | anaphase,  |
The plant cell labeled B is in ____.,  | telophase,  |
The plant cell labeled C is in ____.,  | interphase,  |
The plant cell labeled D is in ____.,  | prophase,  |
The plant cell labeled E is in ____.,  | metaphase,  |
| Uncontrolled cell division is also known as ______. | cancer |
| When cells divide over and over again because of cancer, a lump of cells called a ____ forms. | tumor |
| A ____ can cause the proteins that control cell division to malfunction, causing the cell to divide uncontrollably. | mutation in DNA |
| Who said "Every cell from a cell." | Rudolph Virchow (A German physician who said this in 1855) |
| Cell division results in genetically identical ______ cells. | daughter |
| Cell division results in genetically _______ daughter cells. | identical |
| All of the genetic information a cell possesses is called the cell's ______. | genome |
| All body cells except reproductive cells are called ____ cells. | somatic |
| Another word for reproductive, or sex cells is ________. | gametes |
| How many molecules of DNA are contained in one chromosome? | one (it's very long) |
| The type of cell division that produces gametes is called ______. | meiosis, 
|
| In humans (and many animals for that matter), the two types of gonads are ______ and _____. | ovaries and testes |
| Another word to describe both the ovaries and testes is ______. | gonad |
| What do the asters attach to by the time the cell is in metaphase? | the plasma membrane |
| Non-kinetechore microtubules are responsible for _____ the cell during anaphase. | elongating |
| What causes the cleavage furrow in animal cells? | Actin microfilaments contracting with myosin (the same proteins responsible for muscle contraction) |
| Prokaryotes reproduce by a type of cell division called ____. | binary fission |
| Name two types of human cells that never divide once fully mature. | nerve and muscle cells enter G zero once fully formed; a phase that takes cells out of the cell cycle. |
| In mammalian cells, the most important checkpoint for regulating the cell cycle, commonly called the restriction point, is found in the ____ stage of interphase. | G1 |
| What are the two main types of regulatory proteins that work to regulate the cell cycle? | kinases and cyclins |
| A _____ is a protein that gets its name from its cyclically fluctuating concentration in cells. | cyclin |
| Kinases that regulate the cell cycle are activated by attaching to cyclins, and are therefore called _____. | cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) |
| A _______ is a protein released by certain cells that stimulates other cells to divide. | growth factor |
| Density-dependent inhibition is a phenomenon in which _____ cells stop dividing. | crowded (* Cancer cells don't seem to exhibit density-dependent inhibition) |
| Cells cultured on a petri dish will divide until they form a single layer that covers the bottom of the petri dish. If some cells are removed, the remaining cells will start dividing again until the bottom of the petri dish is covered again. These observations are strong evidence that cell division is at least partly controlled by _____ signals. | external signals (the cells must be responding to signals in their external environment to realize that they are crowded, and therefore stop dividing) |
| In order to divide, most cells (excluding cancer cells) must be attached to a substrate, such as the inside of a culture dish, or the extracellular matrix of a tissue. This phenomenon is called ______. | anchorage dependency |
| Which type of cells do not seem to be affected by density-dependent inhibition or anchorage dependency? | cancer cells |
| A tumor that stays at its original site of growth is called a(n) _____ tumor. | benign |
| A tumor that is impacting other organs or tissues (is invasive) and is capable of spreading is called a(n) ______ tumor. | malignant |
| The spread of cancer cells to locations distant from their original site of development is called _____. | metastasis |
| A benign tumor is usually treated by surgery to remove it or by _____. | radiation (radiation seems to mutate cancer cell DNA much more than normal cell DNA because cancer cells seem to have lost the ability to repair mutations. Mutated cells usually stop functioning, just as a grandfather clock usually stops functioning if you throw a monkey wrench into it) |
| Malignant tumors are usually treated by ______. | chemotherapy (Chemotherapy involves the administration of drugs that interfere with the cells ability to divide. Unfortunately, these drugs tend to affect normal cells as well, so that hair can't be replaced, nor the cells on the inside of the intestine, leading to nausea and hair loss) |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | anaphase,  |
The process shown below is a special type of cell division called ______ that occurs in _______.,  | binary fission, prokaryotes,  |
The picture below shows the formation of a _____ in a _____ cell.,  | cell plate, plant cell,  |
The picture below shows the formation of a _____ in a(n) _____ cell., 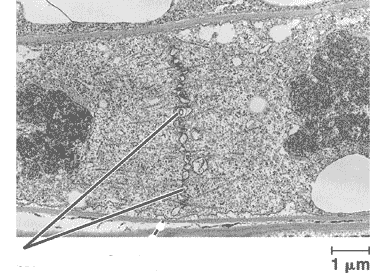 | cell plate, plant cell,  |
The red arrows are pointing to a(n) _____ in a(n) ____ cell.,  | cleavage furrow, animal cell,  |
The line is pointing to a(n) _____ in a(n) ____ cell., 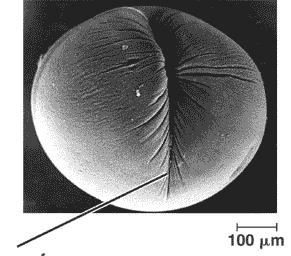 | cleavage furrow, animal cell,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | interphase,  |
The letter "A" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | two sister chromatids,  |
The letter "B" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | the aster,  |
The letter "C" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | the centrosome,  |
The letter "D" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | metaphase plate,  |
The letter "E" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | the kinetechores,  |
The letter "F" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | the kinetechore microtubules (a type of spindle fiber),  |
The letter "G" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | the overlapping non-kinetechore microtubules (a type of spindle fiber; they are used to lengthen the cell during anaphase),  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | metaphase,  |
The dotted line shows an imaginary plane midway between the two centrosomes called the _____.,  | metaphase plate,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | prophase,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | prometaphase,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | telophase,  |
| What are the two types of spindle fibers? | kinetechore microtubules ("F" in the picture below; they attach to kinetechores on the sister chromatids) and non-kinetechore microtubules ("G" in the picture below; used to elongate the cell during anaphase),  |
What is "D" in the picture below pointing to?,  | kinetechores (a protein structure on the outside of the sister chromatids that serves as a place of attachment for the spindle fibers "kinetechore microtubules"),  |