| A | B |
|---|
| A carrot has a diploid number of 18. What is it's haploid number? | 9 |
| Gametes are normally produced by the process of ___. | meiosis, 
|
| Another word for sex cell is ___. | gamete |
| What are the two main types of gametes? | sperm and egg |
| During which stage of meiosis do chromosomes form tetrads? | prophase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell? | metaphase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do sister chromatids separate from each other? | anaphase II |
| What happens between meiosis I and meiosis II that reduces the number of chromosomes? | DNA replication does not occur. |
| When does DNA replication occur during meiosis? | Interphase I only (remember, there is no interphase II) |
| What is the diploid number of chromosomes in humans? | 46 (also written as 2n=46) |
| What is the haploid number for humans? | 23 (also written as n=23) |
| The sex cells of fruit flies have 4 chromosomes each. What is the diploid number of chromosomes for fruit flies? | 8 (remember the diploid number is always twice the haploid number) |
| _________ chromosomes are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, but are not identical. | Homologous, 
|
| _________ are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, and are identical. | Sister chromatids |
| A _____ is a segment of DNA that has the instructions for making one protein. | gene |
| When two homologous chromosomes are lined up right next to each other during meiosis, they are referred to as a ___. | tetrad |
| An organism's gametes have ___ the number of chromosomes as are found in the organism's body cells. | half |
| During which stage of meiosis might crossing over occur? | prophase I |
| When homologous chromosomes are lined up next to each other during meiosis, they might swap pieces of DNA. This phenomenon is called ___. | crossing over |
| Crossing over during meiosis is important because it increases ___. | genetic variation (= the number of different chromosomes, and therefore different combinations of traits, that offspring can inherit) |
Which diagram is mitosis and which is meiosis?,  | Mitosis is on the left and meiosis is on the right.,  |
When chromosomes are lined up like this during meiosis, what are they referred to as?, 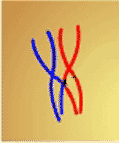 | A tetrad,  |
Which process from meiosis is shown below and during which stage would it occur?, 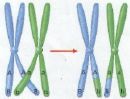 | The picture shows "crossing over" and it usually happens during prophase I.,  |
| The transmission of traits from one generation to the next is called _______ or ________. | inheritance or heredity |
| The scientific study of heredity is called ______. | genetics |
| The fusion of sperm and egg is called _____. | fertilization |
| Segments of DNA that act as hereditary units are called ____. | genes |
| Reproductive cells are called _____. | gametes (they are also called sex cells and include the egg and sperm) |
| The DNA of eukaryotes is subdivided into _____ within the nucleus of the cell. | chromosomes |
| Most human cells have ____ chromosomes. | 46 |
| How many DNA molecules make up a chromosome? | 1 |
| One chromosome includes several hundred to a few thousand _____, each of which is a specific sequence of nucleotides within the DNA molecule. | genes |
| In ______ reproduction, a single individual is the sole parent and passes identical copies of all its genes to its offspring. | asexual |
| In ________ reproduction, two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of _____ inherited from the two parents. | sexual, genes |
| A _____ cell is any cell other than a gamete. | somatic |
| A picture of all the chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell, arranged side-by-side in homologous pairs is called a(n) _____. | karyotype,  |
| The X and Y chromosomes are referred to as the _______. | sex chromosomes |
| All chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes are called _____. | autosomes |
| When considering a homologous pair of chromosomes, one came from the ____ and the other came from the ____. | father, mother |
| Diploid cells are cells that have ____________. | both pairs of homologous chromosomes |
| Haploid cells are cells that have _____________. | a single chromosome set (not both pairs of a homologous set) |
| A fertilized egg is called a(n) _____. | zygote |
| The type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in half is called _____. | meiosis, 
|
| During _______ of meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate. | Anaphase I |
| During ____ of meiosis, sister chromosomes line up in a straight line. | Metaphase II |
| In humans, what type of sex chromosomes do males have? | an X and a Y |
| In humans, what type of sex chromosomes do females have? | two X chromosomes |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 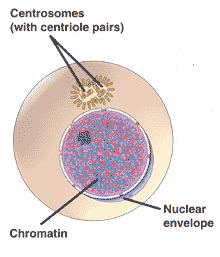 | interphase (there is no interphase II so there is no need to say interphase I),  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | prophase I,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 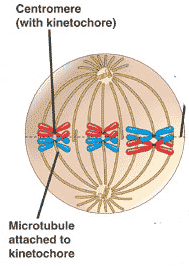 | metaphase I,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | anaphase I,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 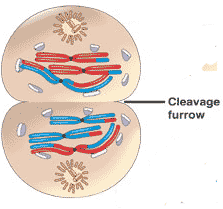 | telophase I,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 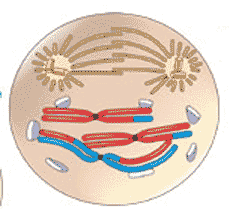 | prophase II,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | metaphase II,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | anaphase II,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 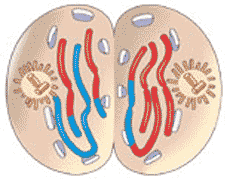 | telophase II,  |
| Meiosis results in ___ daughter cells. | four |