| A | B |
|---|
| Different forms of the same gene are called _____. | alleles |
| Dominant alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | capital (ex:T= tall in pea plants) |
| Recessive alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | lower case (ex: t = short in pea plant; notice that the letter is the first letter of the dominant trait.) |
| The types of alleles that an organism inherits is known as the ______. | genotype (example = Bb) |
| The physical expression of two alleles is known as the organism's _____. | phenotype |
| Bb would be called the organism's _____ while "brown eyes" would be the organisms _____. | genotype, phenotype |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is BB? | Brown eyes |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is Bb? | Brown eyes (remember that B is dominant) |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is bb? | blue eyes |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organisms genotype be if the organism was heterozygous? | Bb (remember that 'hetero' means 'mixed') |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organisms genotype be if the organism is homozygous dominant? | BB (remember that 'homo' means 'same') |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organisms genotype be if the organism is homozygous recessive? | bb (remember that 'homo' means 'same') |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 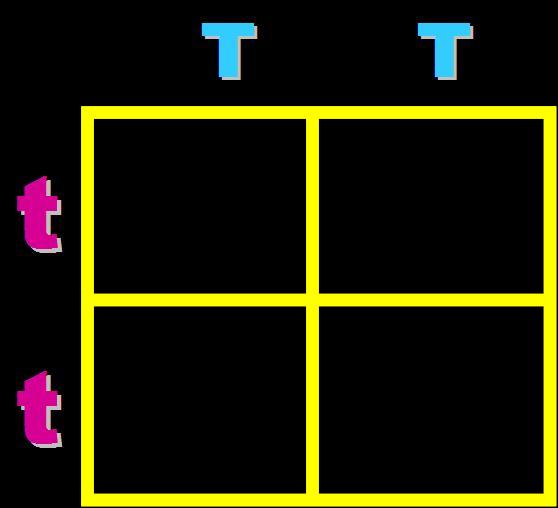 | Genotype = 100% Heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% tall, 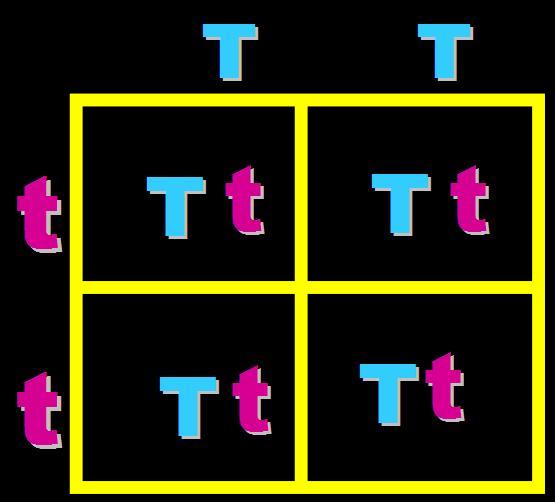 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 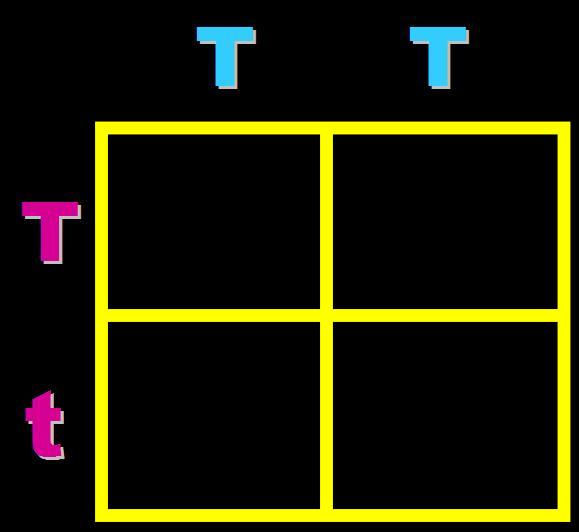 | Genotype = 50% homozygous dominant (TT) and 50% heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% Tall, 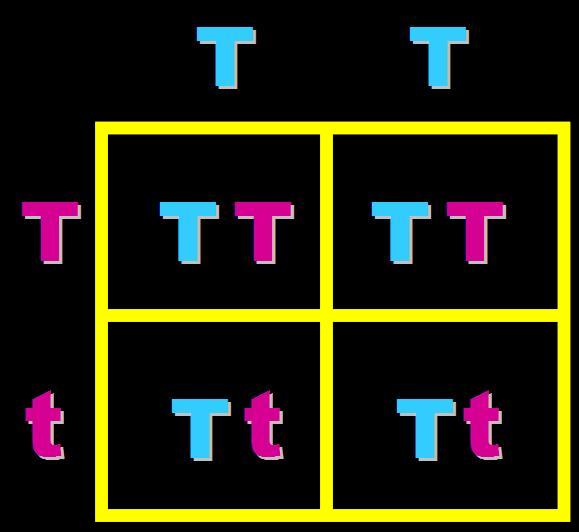 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 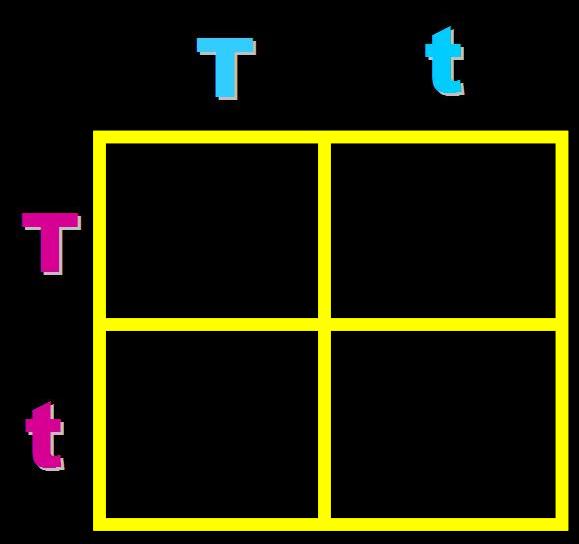 | Genotype = 25% Homozygous dominant (TT), 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 25% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 75% Tall and 25% short,  |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages.,  | Genotype = 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 50% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 50%Tall and 50% short, 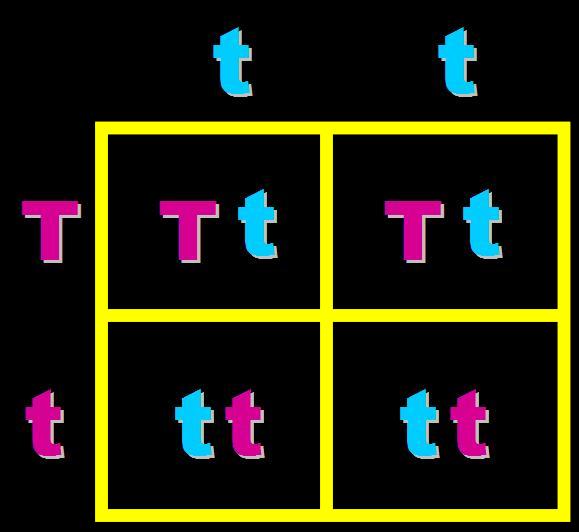 |
| How would you set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a short male pea plant and a heterozygous tall female? | .,  |
| Another word for heterozygous is ____. | hybrid |
| Another word for homozygous is ____. | purebred or true breeding |
| Gregor Mendel used ____ to study the inheritance of traits. | pea plants |
| Mendel removed the male parts (stamens) from the flowers of some plants in order to ___. | prevent self-pollination |
| The person considered to be the father of genetics is ___. | Gregor Mendel |
| Plants with the ___ form of a trait are always true-breeding. | recessive |
| Plants with the ____ form of a trait can be true-breeding while other plants with that trait might not be true-breeding. | dominant |
| True-breeding plants that produced constricted pods were crossed with true-breeding plants that produced inflated pods. The resulting offspring produced inflated pods. It can be concluded that the ____ pod allele is dominant. | inflated |
| When alleles ___ from each other, they separate. | segregate |
| Alleles segregate from each other when ___ form during the process of ___. | sex cells (or gametes) form during the process of meiosis. |
| The type of inheritance where neither allele is dominant and they tend to produce a mix of the two traits such as blue + white = light blue would be _____. | incomplete dominance |
| The type of inheritance where both alleles are dominant, such as red fur + white fur = red and white fur hairs in roan cattle is known as ____. | codominance |
| The type of inheritance where there is more than two alleles for a single trait, such as A, B, and O alleles for blood type, is known as ____. | multiple alleles |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring of this cross? (The A stands for IA and the O stands for i),  | 25% type AB blood, 25% type A blood, 25% type B blood, 25% type O blood,  |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring and what are the odds of each?, 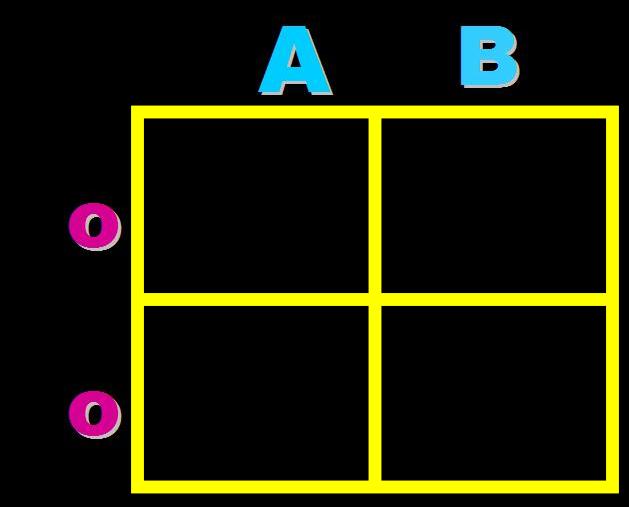 | 50% of the offspring are expected to have type A blood and 50% are expected to have type B blood. All offspring will be heterozygous. Remember that the O allele is recessive.,  |
| A trait, like human skin color, that involves several different genes is called a(n) _____. | polygenic trait (remember, "poly" means many and "genic" refers to genes) |
| A _____ is a heritable feature, such as flower or eye color, that varies among individuals. | character |
| Each variant for a character, such as purple or white flowers, is called a(n) ______. | trait |
| Mendel made sure he started his experiments with plants that were ______. This type of plant produces offspring of the same variety when it self-pollinates. | true breeding |
| The mating, or crossing, of two true-breeding varieties is called _________. | hybridization |
| Which law states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate during gamete formation and end up in separate gametes? | The Law of Segregation |
| To determine whether an organism with a dominant characteristic is heterozygous or homozygous, a ______ is made with an individual that is _____ for the characteristic in question. | testcross, recessive |
| A dihybrid cross between 2 individuals that are heterozygous for two independently assorting characterisitics (such as seed color and seed shape), produces the classic ________ ratio. | 9:3:3:1 ratio,  |
| Which law states that each pair of alleles segregate independently of other pairs during gamete formation? When is this law not true? | Law of independent assortment. This law does not hold true if the alleles for two different characteristics are located on the same chromosome. |
| Dominant alleles are _______ more common populations than recessive alleles. | not necessarily (for example, the O allele for the ABO blood groups is recessive but is more common in the human gene pool than the A and B alleles combined) |
| New alleles for a gene are formed by _________ that survive the ________ process. | mutations, natural selection |
| The type of inheritance that is shown when a trait is controlled by two or more genes is _______. | polygenic inheritance |
| Human skin color is controlled by ________ inheritance. | polygenic (meaning that more than one gene affects skin color) |
A chart like the one below is called a _____.,  | pedigree,  |