| A | B |
|---|
| The enzyme that catalyzes the elongation of new DNA at a replication fork by the addition of nucleotides to the existing chain is called _____. | DNA polymerase (the orange molecules in the picture below),  |
| _____ is a linking enzyme essential for DNA replication. It catalyzes the covalent bonding of the 3' end of a new DNA fragment to the 5' end of a growing chain. Specifically, it bonds the sugar from one nucleotide to the phosphate of another nucleotide. | DNA ligase,  |
| The change in genotype and phenotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell is called ____. | transformation |
| A short segment of DNA synthesized on a template strand during DNA replication which is joined to other short segments to form the lagging strand is called a(n) _____. | Okazaki fragment,  |
| The process of copying a cell's DNA is called _______. | DNA replication,  |
| When does DNA replication occur in eukaryotic cells? | S phase of interphase |
| The shape of a DNA molecule is referred to as a(n) _____. | double helix,  |
| The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction. | leading strand,  |
| A virus that infects bacteria is called a(n) _____. | bacteriophage,  |
| The protective structure at each end of a eukaryotic chromosome that consists of repetitive extra DNA. | telomere |
| The y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing is called the ______. | replication fork,  |
| The discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates in a direction away from the replication fork is called the ______. | lagging strand,  |
The picture below shows a(n) _____.,  | bacteriophage (this virus infects bacteria only),  |
What type of bonds (represented by the pink dotted lines) hold the bases of complementary DNA together?,  | hydrogen bonds,  |
| According to _____, there is the same percentage of adenine and thymine in the genome of a given species and the same percentage of guanine and cytosine. | Chargaff's rules |
The letter A is pointing to the ______.,  | leading strand,  |
The letter B is pointing to the ______.,  | lagging strand,  |
The letter C is pointing to the ______.,  | Okazaki fragments,  |
The letter D is pointing to ______.,  | DNA polymerase,  |
The letter E is pointing to the ______.,  | replication fork,  |
The letter F is pointing to ______.,  | DNA ligase (notice that it is catalyzing the bonding of the sugar end of one Okazaki fragment to the phosphate end of the other Okazaki fragment),  |
What is the last name of the scientist(s) who performed the experiment shown below?, 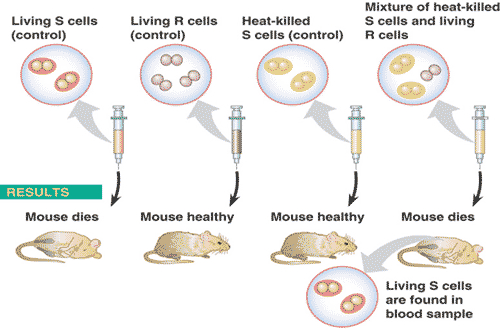 | Griffith (be able to explain this experiment in detail),  |
What is the last name of the scientist(s) who performed the experiment shown below?,  | Hershey and Chase (be able to explain this experiment in detail),  |
The letter C is pointing to ______.,  | a primer (This is a short segment of either DNA or RNA that is needed to initiate DNA synthesis because DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to existing new strands. In humans, the primer is made of RNA nucleotides which will need to be replaced by DNA nucleotides to complete the strand),  |
| The nitrogenous base adenine always bonds to ______ in a DNA molecule. | thymine |
| The nitrogenous base cytosine always bonds to ______ in a DNA molecule. | guanine |
| What is the last name of the scientist(s) who used DNA destroying enzymes and protein destroying enzymes to determine that DNA was responsible for the transformation seen in Frederick Griffiths experiment (the one where the mice die). | Avery (Be able to explain Oswald Avery's experiment in detail) |
| What was the name of the scientist(s) who produced an image of DNA using X-ray crystallography that helped Watson and Crick decipher the structure of DNA? | Rosalind Franklin (below is an image of DNA that she produced),  |
| What is the last name of the scientist(s) who first published a paper explaining the correct structure of DNA in 1953? | Watson and Crick |