| A | B |
|---|
| The process of making proteins inside cells is called ______. | protein synthesis |
| Which organelle is DNA located in? | nucleus |
Which type of nucleic acid can't leave the nucleus?, 
| DNA |
| On which organelle are proteins made? | ribosomes, 
|
| Where are ribosomes located? | out in the cytoplasm, 
|
| The process of making a strand of m-RNA in the nucleus is called _____. | transcription |
| What are four differences between RNA and DNA? | 1) RNA is single-stranded instead of double 2) RNA has the nucleotide uracil in place of thymine 3) RNA can leave the nucleus and DNA can't 4) RNA includes the sugar called ribose while DNA includes the sugar called deoxyribose |
Which nucleotide do you find in RNA but not DNA?, 
| uracil |
| Uracil bonds to _____ at the nitrogenous base. | adenine |
| The process of using the code on RNA to make a long chain of amino acids in the correct order to form a protein is called _____. | translation |
| Which type of molecule brings amino acids to the site of protein synthesis? | transfer RNA (t-RNA) |
| Which molecule attaches to a ribosome and serves as a code for putting amino acids together? | messenger RNA (m-RNA) |
How many nucleotides are needed to code for 1 amino acid?, 
| 3 |
| How many different types of amino acids are used to make proteins? | 20 |
Each set of 3 nucleotides on a strand of m-RNA are called a _____., 
| codon |
| How many nucleotides are found at the bottom of a molecule of t-RNA and are involved with bonding to m-RNA? | 3 |
| How many amino acids are found attached to a molecule of t-RNA? | 1 |
A change in the sequence of nucleotides in a molecule of DNA will cause a ____., 
| mutation |
| Mutations that are harmful are usually weeded out by ______. | natural selection |
| Mutations in a gene that are helpful usually become part of the gene pool as a new ____. | allele (a different form of a gene) |
Which amino acid would the codon sequence AGU call for?,  | Serine,  |
| Which enzyme is required for transcription? | RNA Polymerase (remember, you are making RNA during transcription) |
| What are the three types of RNA that have major roles in protein synthesis? | m-RNA (messenger RNA), t-RNA (transfer RNA) and r-RNA (ribosomal RNA) |
| Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells? | In the nucleus |
| Where does translation occur? | Out in the cytoplasm on ribosomes. |
| Genes contain instructions for assembling ___. | polypeptides (It is often said that genes code for making proteins, but this is not always technically correct. Many proteins have a quaternary structure, with several intertwined polypeptides. In this case, no single gene has the code for making the finished protein. Each polypeptide that makes up the protein is coded for by a different gene) |
| Proteins are made out of ____. | amino acids |
The picture below is called the ____.,  | genetic code,  |
| What was the name of the scientist(s) whose work on bread mold, using X-rays to disable genes, provided strong support for the one-gene one enzyme hypothesis? | Beadle and Tatum (the one-gene one enzyme hypothesis was later modified to the one gene, one polypeptide hypothesis since not all proteins are enzymes and proteins with a quaternary structure are coded for by several genes) |
| Only one of the two DNA strands is transcribed during transcription. This strand is called the _____ strand. | template strand (Interestingly enough, one of the two DNA strands may serve as the template strand for some of the genes on the chromosome, but not others) |
| Messenger RNA codons are read in the _______ direction by the translation machinery. | 5' --> 3' direction |
| A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene is called a(n) _______. | insertion |
| A noncoding, intervening sequence within a eukaryotic gene is called a(n) ______. | intron (the part of the mRNA that is transcribed from DNA introns, but is cut out before the mRNA exits the nucleus, is also called an intron) |
| The specialized base triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that recognizes a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule is called a(n) _______. | anticodon ("B" in the picture below), 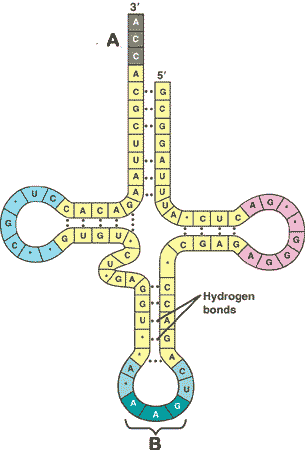 |
Which amino acid is represented by the shape with the question mark in the picture below? Use the chart to find the answer.,  | Serine,  |
| A _____ mutation occurs when the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is NOT a multiple of three, resulting in the improper grouping of the following nucleotides into codons. | frameshift |
| Which type of mutations can lead to frameshift mutations? | insertions or deletions that are not in multiples of three |
| The DNA strand that temporarily binds RNA nucleotides during transcription is called the _________. | template strand |
| Where are ribosomes constructed and what are they composed of? | nucleolus, r-RNA and protein (the large and small subunits of the ribosome are constructed in the nucleolus but never come together until they start the process of transcription in the cytoplasm, after which, they come apart again),  |
| A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation is called a(n) ______. | mutagen |
What is "A" in the picture below?,  | polyribosome (a.k.a. polysome),  |
| A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase and indicates where to start transcribing RNA is called the _____. | promoter,  |
| A type of point mutation; the replacement of one nucleotide and its partner in the complementary DNA strand by another pair of nucleotides is called a(n) ______. | base-pair substitution |
| The enzyme that links together the growing chain of ribonucleotides during transcription is called _____. | RNA polymerase, 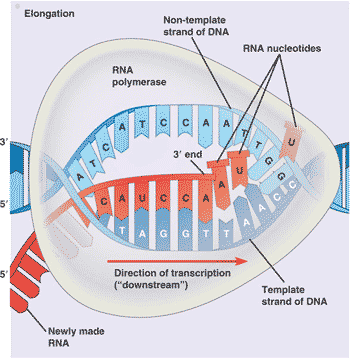 |
| A point mutation in which one or more nucleotides pairs from a gene are lost is called a(n) ______. | deletion (deletions can also happen at the chromosomal level in which case they are called chromosomal deletions) |
| An enzymatic RNA molecule that catalyzes reactions during RNA splicing is called a(n) ______. | ribozyme |
| What are two names for the initial RNA transcript? | primary transcript or pre-mRNA,  |
| One of a ribosomes three binding sites; it holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain. | P site (P stands for peptidyl tRNA site),  |
| Modification of RNA before it leaves the nucleus in eukaryotes is called _____. | RNA processing, 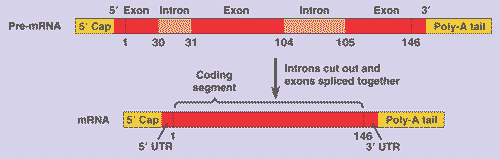 |
| DNA and RNA are read as a _____ code. | triplet code |
| A change in a gene at a single nucleotide pair. | point mutation |
| The coding region of a eukaryotic gene; when transcribed into mRNA, it is the coding part of mRNA that leaves the nucleus. | exon,  |
Which process belongs in the darker red box in the picture below?,  | transcription,  |
Which process belongs in the pink box in the picture below?,  | RNA processing,  |
Which process belongs in the light blue box in the picture below?,  | translation,  |