| A | B |
|---|
| The arrangement of electrons in an atom is known as the atom’s _________. | electron configuration |
| The lowest-energy arrangement of the electrons for each element is called the element’s _______ electron configuration. | ground state |
| The _______ arrangement of the electrons for each element is called the element’s ground state electron configuration. | lowest energy |
| According to the Aufbau principle, an electron occupies the __________ - energy orbital that can receive it. | lowest |
| According to the _______, an electron occupies the lowest - energy orbital that can receive it. | Aufbau principle |
| According to the ___________, no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. | Pauli exclusion principle |
| According to the Pauli exclusion principle, no two electrons in the same atom can have _____. | the same set of four quantum numbers. |
| According to _________, orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin state. | Hund's rule |
| Why can't elements in the first or second periods have d or f electrons? | Because Chuck Norris said so!! |
| In which order do electrons fill in the orbitals as you add electrons across the first period? | 1s (That's it. There is only an s orbital in the first period) |
| In which order do electrons fill in the orbitals as you add electrons across the second period? | 2s, 2p |
| In which order do electrons fill in the orbitals as you add electrons across the third period? | 3s, 3p |
| In which order do electrons fill in the orbitals as you add electrons across the fourth period? | 4s, 3d, 4p |
| In which order do electrons fill in the orbitals as you add electrons across the fifth period? | 5s, 4d, 5p |
| In which order do electrons fill in the orbitals as you add electrons across the sixth period? | 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p |
| In which order do electrons fill in the orbitals as you add electrons across the seventh period? | 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p |
What type of notation is shown below?, 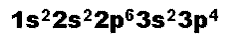 | electron configuration notation, 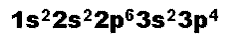 |
How many electrons are in the atom represented below?, 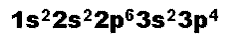 | 16 (just count the superscripts), 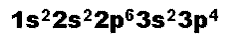 |
What is the atomic number of the atom represented below? What element is it?, 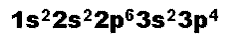 | The atomic number is 16 and the element is sulfur (The atom has 16 electrons by counting the superscripts. Therefore it must have 15 protons. Therefore its atomic number is also 16. If you look on the periodic table, sulfur has an atomic number of 16), 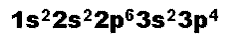 |
What is the orbital notation of the atom represented below?, 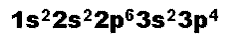 | .,  |
What is the electron configuration of the atom represented below?,  | ., 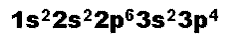 |
How many electrons are in 2nd energy level of the atom shown below?, 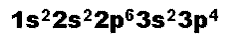 | 8, 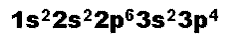 |
How many electrons occupy p-orbitals in the atom represented below?, 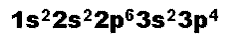 | 10, 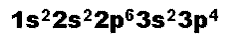 |
| Sulfur has 16 electrons. How would you represent its electron configuration using orbital notation? | * notice that the 2-orbitals fill up with 1 electron each before the 4th p-electron is paired with an electron in an orbital),  |
How many unpaired electrons are in the atom represented below?,  | 2,  |
| What is the noble-gas notation of an element with 13 electrons? | .,  |
What is the name of the element represented below?,  | Aluminum (Neon has 10 electrons. This element has an additional 3 electrons for a total of 13. Therefore, it has 13 protons, an atomic number of 13, and aluminum is the only element on the periodic table that has an atomic number of 13),  |
What type of notation is shown below?,  | noble gas notation,  |
What type of notation is shown below?,  | orbital notation,  |
| An element with 8 electrons in its outer shell has a(n) ______ of electrons in its highest energy level. | octet |
| Elements with an octet of electrons in their outer shell are called ______, | noble gases |