| A | B |
|---|
| The name of the late stages of HIV infection, defined by a specific reduction of T cells and the appearance of characterisitic secondary infections. | AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) |
| The type of virus that can lead to AIDS is called ____. | HIV (human immunodeficiency virus),  |
| ______ is an enzyme encoded by some certain viri (retroviri) that use RNA as a template for DNA synthesis. | Reverse transcriptase (The HIV virus pictured below is a retrovirus. Notice the reverse transcriptase and how it is used once in the host cell),  |
| A(n) _______ is a membrane that surrounds the capsid of some viri. | viral envelope (The picture below shows how viri acquire a viral envelope from the membrane of the host with extra components coded for by the virus), 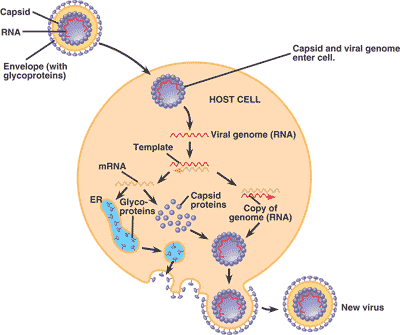 |
| A(n) _____ is a virus that infects bacteria. | bacteriophage (can also be called "phage"),  |
| Viral DNA that inserts into a host genome is called a(n) _____. | provirus (notice the provirus in this diagram of HIV infection),  |
| A phage replication cycle in which the viral genome becomes incorporated into the bacterial host chromosome as a prophage and does not kill the host. | lysogenic cycle (the phage will eventually be triggered to enter the lytic cycle and kill the host),  |
| An RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome. | retrovirus (these include some cancer-causing viri and HIV pictured below),  |
| A(n) _____ is an infectious form of mis-shaped protein that may increase in number by converting related proteins to mis-shaped protein. | prion (Prions are responsible for brain wasting diseases in animals such as mad cow disease and Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease in humans), 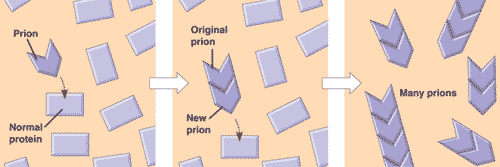 |
| A(n) _____ is a plant pathogen composed of naked circular RNA only several hundred nucleotides long. | viroid |
| A(n) ______ is a harmless variant or derivation of a pathogen that stimulates a host immune system to mount defenses against the pathogen. | vaccine |
| A disease causing agent is called a(n) _______. | pathogen |
| The protein shell that encloses the viral genome is called the _____. | capsid,  |
| A type of viral (phage) replication cycle resulting in the release of new phages by lysis (and death) of the host cell. | lytic cycle,  |
| To lyse something means to _____. | break it open |
What is the little green enzyme that the letter "A" is pointing to in this diagram of HIV infection?,  | reverse transcriptase (remember, it's an RNA retrovirus),  |
What is the letter "B" pointing to in this diagram of HIV infection?,  | provirus (viral DNA incorporated into the host cell's genome),  |
What type of virus is this and what is its specific name?,  | retrovirus, HIV,  |
What is the letter "B" pointing to in this picture of HIV?, 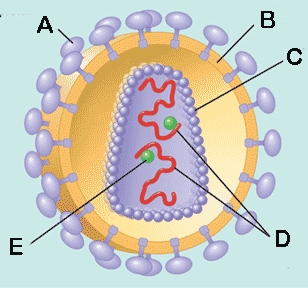 | viral envelope,  |
What is the letter "C" pointing to in this picture of HIV?,  | capsid (the protein coat surrounding the nucleic acids),  |
Which type of phage lifecycle is pictured on the right?,  | lysogenic,  |
Which type of phage lifecycle is pictured on the left?,  | lytic,  |