| A | B |
|---|
| In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, gene expression is most often regulated at the stage of _______. | transcription,  |
| The condensed form of chromatin is called a(n) _______. | chromosome (The karyotype below shows the 46 human chromosomes visible during mitosis),  |
| DNA wraps around ________ to form chromatin. | histone proteins, 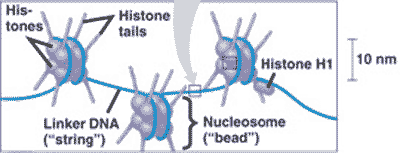 |
| During development of multicellular organisms, cells undergo a process of becoming specialized in form and function in a process called ________. | cell differentiation (this involves activating certain genes and permanently silencing others, such as genes for liver proteins in a pancreas cell) |
| To initiate transcription, eukaryotic RNA polymerase requires the assistance of proteins called ______. | transcription factors,  |
| Name four mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. | 1) RNA processing 2) mRNA degradation 3) Initiation of translation 4) Protein processing and degradation |
| General transcription factors function in assembling the _______ at the promoters for all genes while specific transcription factors bind to control elements and either increase (if they are _______) or decrease (if they are _______) transcription of that gene. | transcription initiation complex; activators, repressors,  |
| Cancer causing genes are called _____. | oncogenes |
| ______ code for proteins that stimulate normal cell growth and division, but can be turned into a cancer-causing gene by mutations. | proto-oncogenes |
| ______ genes encode for proteins that help prevent uncontrolled cell growth. | Tumor-suppressor genes |
| A tumor large enough to impair function of one or several organs is called a _____ or ______. | carcinoma, malignant tumor, 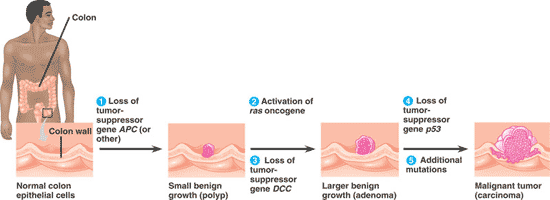 |
| An individual ______ an oncogene or mutant allele of a tumor-suppressor gene is one step closer to accumulating the necessary mutations for cancer to develop by the _____ model of cancer development. | inheriting, multistep,  |
What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?, 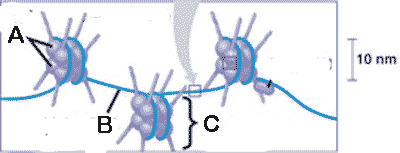 | histone proteins,  |
What is "C" pointing to in the picture below?,  | a nucleosome,  |
| A gene found in viri or as part of the normal genome that is involved in triggering cancerous characteristics. | oncogene |
| The guardian angel of the genome, this gene is expressed when a cell's DNA is damaged. Its product is a transcription factor that transcribes proteins whose job it is to keep mutated cells from diviiding or help repair damaged DNA. | p53 gene, 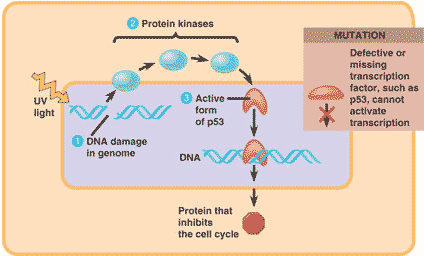 |
| A gene that codes for a type of G protein that relays a growth signal from a growth factor receptor on the plasma membrane to a cascade of protein kinases that ultimately results in the stimulation of the cell cycle. Point mutations in this gene can lead to a hyperactive version of the protein that can lead to excessive cell division and cancer. | Ras gene,  |
| A segment of noncoding DNA that helps regulate transcription of a gene by binding proteins called transcription factors. | control element,  |
| Expression of different sets of genes by cells with the same genome is called _____. | differential gene expression |
| A protein that suppresses the transcription of a gene is called a(n) _____. | repressor |
| A normal cellular gene corresponding to an oncogene; a gene with the potential to cause cancer, but that requires some alteration to become an oncogene. | proto-oncogene |