| A | B |
|---|
| magma | hot liquid rock beneath the earth's surface |
mineral,  | solids that form from one or more chemicals in the earth |
crystal,  | solid formed from a repeating pattern of atoms |
| cleavage | breaking of mineral along smooth, definite surfaces |
| color | one of the properties of minerals including red, yellow, green, and blue |
hardness, 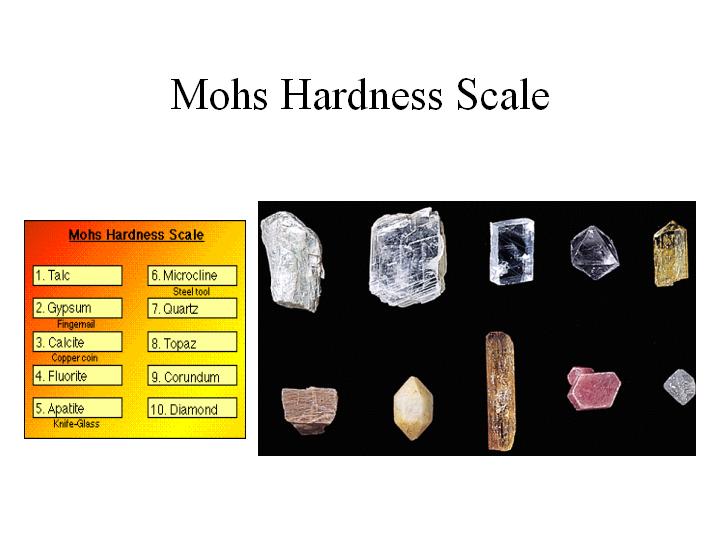 | ability of a mineral to resist being scratched |
| gem | mineral that is rare beautiful and durable |
streak,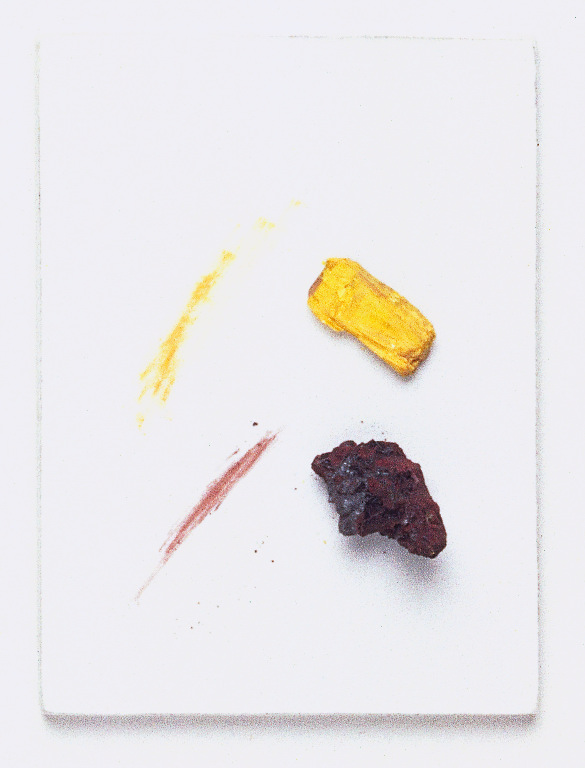  | color of the powder left behind when a mineral is rubbed against a hard rough surface |
| fracture | breaking of a mineral along rough, jaggered surfaces |
| ore | rock deposit that contains minerals that can be mined as a profit |
| geologist | scientist who studies rocks and minerals |
igneous rock,  | rock formed by the cooling and hardening of magma |
| sediment | small pieces of rock, shells, or remains of plants and animals that have been carried along and deposited by wind, water and ice. |
| sedimentary rock | rocks fromed from sediments that have been pressed and cemented into rock |
| metamorphic rock | formed when sedimentary or igneous rocks are changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactons. |
rock cycle, 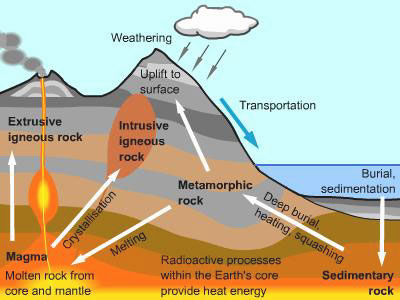 | continuos changing of rock from one type to another |
luster, 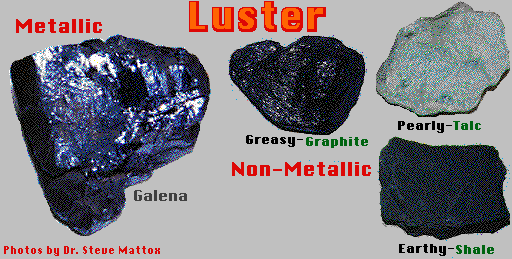 | relection of light from a mineral's surface |
Mohn's scale of Hardness,  | ten minerals that are listed to compare the softest to the hardnest |
basalt,  | common igneous rock that is sometimes called basement rock |
| minerals | used for medicines, foods, dishes, cleaning products, pencils and etc. |