| A | B |
|---|
| the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are the same | equilibrium |
| When the market price or quantity supplied is anywhere but at the equilibrium price. | disequilibrium |
| Two causes of disequilibrium | excess demand and excess supply |
| Occurs when quantity demanded is more that quantity supplied | excess demand |
| When the quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded | excess supply |
| A maximum price that can be legally charged for a good | price ceiling |
| Rent control is an example of ____ | price ceiling |
| A minimum price, set by the government, that must be paid for a good or service. | price floor |
| Sets a minimum price that an employer can pay a worker for an hour of labor. | minimum wage |
| The government's price floor on low wages is called | minimum wage |
| Since markets tend toward equilibrium, a change in _____ will set market forces in motion that lead the market to a new equilibrium price and quantity sold. | supply |
| A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. | surplus |
| As supply decreses producers will raise prices and demand will decrease | fall in supply |
| If a surplus occurs, producers reduce prices to sell their products. | excess supply |
| A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied | shortage |
| The financial and opportunity costs consumers pay when searching for a good/service | search costs |
| When demand falls, suppliers respond by cutting prices, and a new market equilibrium is found. | a fall in demand |
| When a new equilibrium is found after a fall in demand the new equilibrium has a... | lower market price and lower quantity sold |
| What happens when any market is in disequilibrium and prices are flexible? | market forces push toward equilibrium |
| ______ help move land, labor, and capital into the hands of producers, and finish goods in to the hands of buyers | prices |
| Prices creat _______ _____ _____ for producers and a language that both consumers and producers can use. | efficient resource allocation |
| What are some of the advantages of prices? | Incentives, signals, flexibility, "free" |
| A market system, with its fully changing prices, ensures that resources go to the uses that consumers value most highly. | Resource Allocation |
| Imperfect competition between firms in a market can affect prices and consumer decisions | market problems |
| Costs of production (also known as externalities) | spillover costs |
| What prompts efficient resource allocation in a well functioning market system? | bsinesses working to earn a profit |
| How do price changes affect equilibrium? | price changes serve as a tool for distributing goods and services |
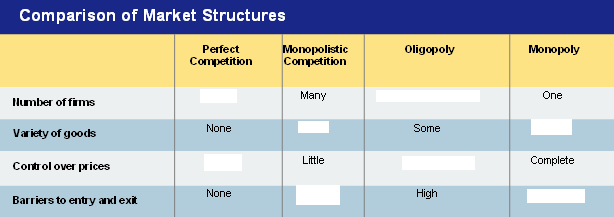
| A market structure in which a large number of firms all produce the same product | perfect competition |
| What are the four conditions for perfect competition? | many buyers and sellers, identical products, informed buyers/sellers, free market entry and exit |
| factors that make it difficult for new firms to enter a market | barriers to entry |
| The expenses that new businesses must pay before the first product reachers the customer are called start-up costs | Start-up costs |
| One of the primary characeristics of a perfectly competitive markets is that they are _____ | efficient |
| What do price and output reach in a perfectly competative market? | equilibrium levels |
| How does the perfect market influence output? | each firm adjusts its output so that it just convers all of its costs. |
| a _____ is a market dominated by a single seller. | monopoly |
| How do monopolies form? | When barriers prevent firms from entering a market that has a single supplier |
| A market that runs most efficently when one larg firm provides all of the output | natural monopoly |
| factors that casue a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises. | economies of scale |
| What can destroy a natural monopoly? | Technology and change |
| A monopoly created by the government | government monopoly |
| licenses that give the inventor of a new product the exclusive right to sell it for a certain period of time | patent |
| a contract that gives a single firm the right to sell its goods within an exclusive market | franchise |
| a government-issued right to operate a business | license |
| When the government grants patents it is called a ______ monoply | technological |
| the division of customers into groups based on how much they'll pay for a good | price discrimination |
| the ability to control prices and total market output | market power |
| What does price discrimiation require? | distinct customer groups, dificult resale, market power |
| monopolists can only set _____ or _____, not both | output or price |
| Where does a monopolis set output? | at a point where the marginal revenue is equal to the marginal cost |
| many companies compete in an open market to sell products which are smilar but not identical | monopolistic cometition |
| What are the four conditions of monopolistic competition? | Many firms, few artificial barriers to entry, slight control over price, differentiated products |
| a way to attract customers through style, service, or location but not a lower price. | nonprice competition |
| Ways that companies use nonprice competition | characteristics of goods, service level, location of sale, advertising image |
| a market dominated by a few large, profitable firms | oligopoly |
| an agreement among members of an oligopoly to set prices and production levels | collusion |
| an agreement among firms to sell at the same time or similar prices | price fixing |
| an association by producers established to coordinate prices and production | cartel |
| What are the four basic market structures that markets can be grouped into | perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly |
 |  |