| A | B |
|---|
| Name the first 10 alkanes in order from smallest to largest.. | methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, heptane, octane, nonane, decane |
| Straight chain hydrocarbons with double bonds are called ______. How would you name one with 3 carbons? | alkenes, propene |
| Straight chain hydrocarbons with triple bonds are called _____. How would you name one with 2 carbons? | alkynes, ethyne |
What type of molecule is this?, 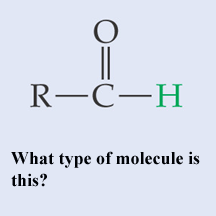 | A basic aldehyde,  |
What type of molecule is this?,  | carboxylic-acid,  |
What type of molecule is this?, 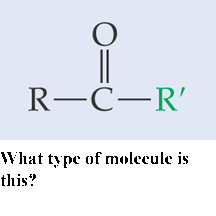 | Ketone, 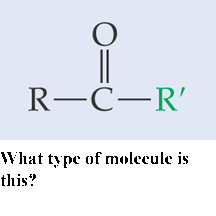 |
| One of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures, and therefore, different properties. | isomer |
| A functional group that is often written as --COOH. | carboxyl group It's -COOH because it is a C double-bonded to an O and single-bonded to OH),  |
| A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. | amino group, 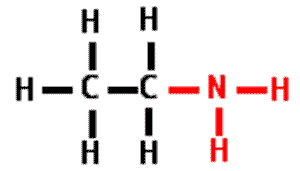 |
| An organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen is called a(n) _____. | hydrocarbon (the butane molecule below is a hydrocarbon because it has only hydrogens and carbons), 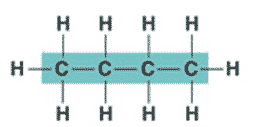 |
| A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeleton of organic molecules and usually involved in chemical reactions. | functional group (the carboxyl-group in red below is a functional group that makes the molecule acidic because it often loses the hydrogen as a hydrogen ion into the solution which lowers the pH of the solution),  |
| A functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols. | hydroxyl group,  |
What is the name of the molecule shown below?, 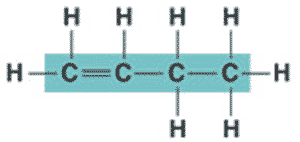 | butene (more specifically, it is 1-butene because the double bond starts at the first carbon),  |
What type of molecule is this?,  | An aldehyde (It's an aldehyde because the carbonyl group is coming off a terminal carbon. If it wasn't, it would be a ketone.),  |
What is the name of the functional group in red?,  | amino group,  |
What is the name of this hydrocarbon?,  | Butane,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule?, 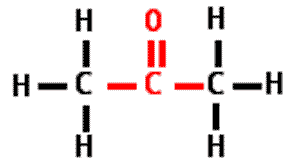 | ketone,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | Carboxylic acid, carboxyl group (This molecule is called ethanoic acid but is more commonly referred to as acetic acid which is the acid in vineger),  |
What is this diagram showing?, 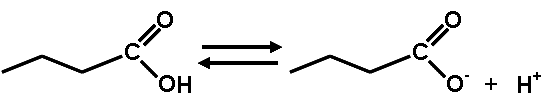 | This shows how carboxylic acids (notice the carboxyl group at the end of the abbreviated structural formula of hydrocarbons) will release a hydrogen ion into water solutions. Hydrogen ions decrease the pH of the solution. That is why it is a carboxylic ACID., 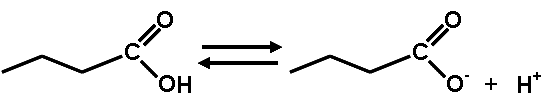 |
What is the name of this hydrocarbon?,  | Ethane,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | An alcohol, hydroxyl group (This is ethanol because it has two carbons like ethane. The common name is ethyl alcohol),  |
What is the name of this hydrocarbon?, 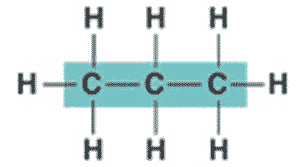 | propane,  |
| Carbon can form a wide variety of compounds because it forms ____ bonds. | 4 |
Hydrocarbons (like the one shown below) are ______ and therefore don't dissolve in water.,  | Non-polar or hydrophobic |
Which type of molecule is shown below?, 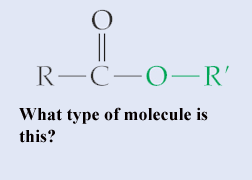 | an Ester, 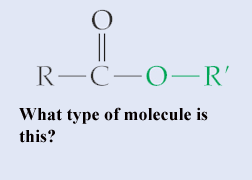 |
What type of organic molecule is this? (Don't worry about naming it), .gif) | an ester, .gif) |
| Which element do all organic compounds contain? | carbon |
| What's the only thing that can survive being exposed to an organic acid? | Chuck Norris (actually, organic acids are generally pretty weak, as they don't always let go of their hydrogen ion when dissolved in water. Strong acids like hydrochloric acid come apart completely in water, maximizing the number of hydrogen ions in solution which causes the pH to drop) |