| A | B |
|---|
| The stalk of a flower's carpel, with the ovary at the base and the stigma at the top is called the ______. | style |
| ______ is the mutual evolutionary influence between two different species interacting with each other and reciprocally influencing each other's adaptations. | coevolution (an example is the adaptations that flowers have made to attract pollinators and pollinators have made to extract pollen) |
| Embryonic seed leaves are called ______. | cotyledons (the two leaves are the cotyledons in the picture of the dicot below), 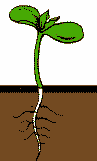 |
What is "A" in the picture below?, 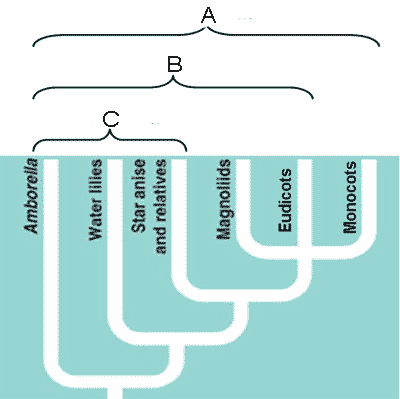 | Angiosperms,  |
The flower below is typical of (monocots or dicots).,  | dicots (floweral organs are usually in multiples of four or five in dicots),  |
What type of angiosperm seedling is shown below (monocot or dicot)?,  | dicot (notice the two cotyledons "embryonic seed leaves" of this seedling),  |
The angiosperm leaf below is typical of (monocots or dicots),  | Dicot (the veins in dicot leaves are usually net-like),  |
This cross section of an angiosperm stem is typical of (monocots or dicots).,  | dicots (vascular bundles of xylem and phloem are typically arranged in an orderly fashion around the periphery of the stem),  |
Roman numeral I refers to the ______., 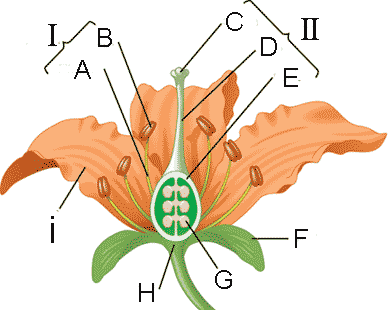 | stamen (male reproductive structure),  |
Roman numeral II refers to the ______.,  | Carpel (female reproductive structure),  |
The letter "B" refers to the _____.,  | Anther (where the microsporangium which produces pollen is located),  |
The letter "C" refers to the _____.,  | stigma,  |
The letter "D" refers to the _____.,  | style,  |
The letter "E" refers to the _____.,  | ovary,  |
The letter "F" refers to the _____.,  | sepal,  |
The letter "G" refers to the _____.,  | ovule,  |
The letter "i" refers to the _____.,  | petal,  |
The flower below is typical of (monocots or dicots), 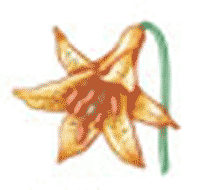 | Monocot (monocot floral organs are usually found in multiples of 3),  |
What type of angiosperm seedling is shown below (monocot or dicot)?,  | monocot (notice the single cotyledon,  |
The angiosperm leaf below is typical of (monocots or dicots),  | Monocot (monocots typically have parallel vein structure),  |
This cross section of an angiosperm stem is typical of (monocots or dicots)., 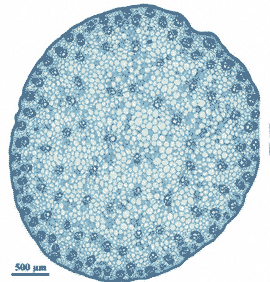 | Monocot (The vascular bundles of xylem and phloem are typically scattered and unorganized in monocots),  |
What should go in the number 1 space below?, 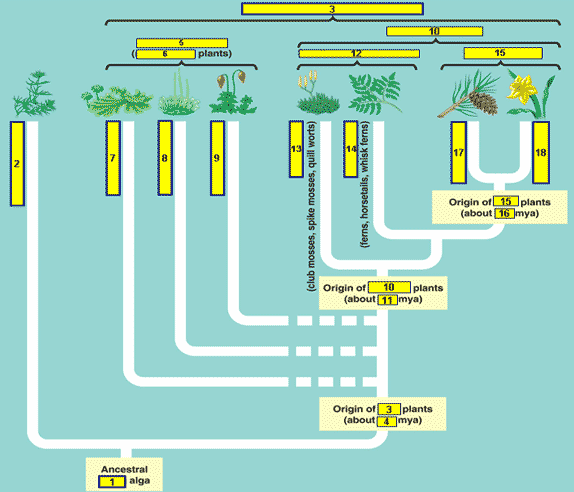 | green,  |
What should go in the number 3 space below?,  | Land plants (a.k.a. Embryophytes),  |
What should go in the number 5 space below?,  | Bryophytes,  |
What should go in the number 6 space below?,  | Non vascular,  |
What should go in the number 9 space below?,  | Mosses,  |
What should go in the number 10 space below?,  | Vascular plants,  |
What should go in the number 12 space below?,  | seedless vascular plants,  |
What should go in the number 15 space below?,  | seed plants,  |
What should go in the number 17 space below?,  | Gymnosperms,  |
What should go in the number 18 space below?,  | Angiosperms,  |
What type of plant is shown below?,  | Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) - Most trees other than conifers are flowering plants. Notice the maple flowers in the picture below.,  |
| The pollen-producing male reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of an anther and filament is called a(n) _____. | stamen,  |
| The sticky part of a flower's carpel, which traps pollen grains, is called a(n) _____. | stigma,  |
| In flowers, the _____ is the portion of a carpel in which the egg-containing ovules develop. | ovary,  |
| The structure that develops within the ovary of a seed plant and contains the female gametophyte is called the _____. | ovule,  |
| The _____ is the female reproductive organ of a flower consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary. | carpel |
| An adaptation for terrestrial plants consisting of an embryo packaged along with a store of food within a resistant coat is called a(n) ______. | seed |
| The structure that contains the male gametophyte of a seed plant. | pollen grains |
| A(n) _____ is the mature ovary of a flower that protects dormant seeds and aids in their dispersal. | fruit |
| The clade consisting of flowering plants that have one embryonic seed leaf, or cotyledon. | monocots |