| A | B |
|---|
| The management of the body's water and solute concentration is called _____. | osmoregulation |
| Ocean water is ____ compared to marine vertebrate cytosol. | hypertonic |
| Marine fish are constantly losing water due to their hypertonic environment. What are three things they do to counteract the problem? | produce very little urine and drink large amounts of water, and get rid of salt through their gills by active transport,  |
| Freshwater organisms live in a _____ environment compared to their cytosol. | hypotonic |
Many protists, like this paramecium, use a _______ to get rid of extra water.,  | contractile vacuole,  |
Flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes) like this planarian, use ____ for osmoregulation and excretion.,  | flame cells,  |
| Earthworms (phylum Annelida) use ______ for osmoregulation and excretory purposes. | nephridia (a.k.a. metanephridia),  |
| Insects use _____ for osmoregulation and excretory purposes. | malphigian tubules, 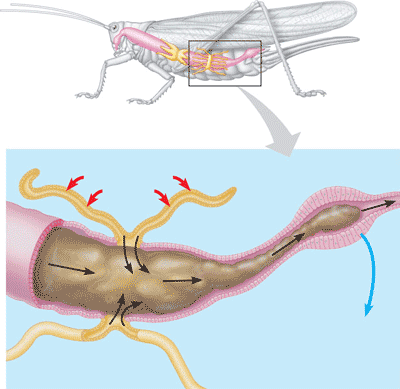 |
| Humans use ______ found in the ______ for osmoregulation and excretory purposes. | nephrons, kidney,  |
| The removal of metabolic wastes is called _____. | excretion |
| Metabolic wastes include _____ and _____ from cellular respiration and ______ from protein metabolism | carbon dioxide and water, nitrogenous waste. |
| Metabolic wastes include carbon dioxide and water from ______ and nitrogenous waste from _________ | cellular respiration, protein metabolism |
| Urea is produced in the ____. | liver |
| The four organs of excretion in humans are the _____, _____, _____, and _____. | skin, lungs, kidneys, liver |
| The three types of nitrogenous waste are ____, _____, and ______. | ammonia, urea, uric acid |
| _____ is a nitrogenous waste that is very soluble, highly toxic and generally excreted by fish and other organisms that live in water. | Ammonia |
| Ammonia is a nitrogenous waste that is very soluble, highly toxic and is excreted by _____. | fish and other organisms that live in water |
| _____ is a nitrogenous waste excreted by earthworms and humans. | Urea |
| _____ is a nitrogenous waste that is pastelike and insoluble. It is excreted by insects, many reptiles and birds to minimize water loss. | Uric acid |
| Which type of nitrogenous waste produces the least water loss? | Uric acid |
| The _____ brings blood to the kidney while the ________ takes blood away from the kidney. | renal artery, renal vein |
| The kidney filters about _______ liters of blood per day. | 1000 to 2000 liters |
| The normal solute concentration of blood is _______. | 300 mosm/L (milli osmoles per liter) |
| If urine has a solute concentration of 70 mosm/L, it would be considered to be _____ urine. | dilute (the normal blood solute concentration is 300 mosm/L, but if the fluid intake is high and the salt intake low, the kidney will produce dilute urine to get rid of the excess water) |
| If urine has a solute concentration of 1200 mosm/L, it would be considered to be _____ urine. | concentrated (the normal blood solute concentration is 300 mosm/L, but if the fluidi ntake is low and the salt intake high, the kidney will produce highly concentrated urine to conserve water) |
| The functional unit of the kidney is the ______. | nephron,  |
| The nephron consists of a cluster of capillaries called the _____ surrounded by a cuplike structure called _____ plus a long narrow tube called the ______. | glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, renal tubule,  |
| The nephron carries out its job in four steps? What are those four steps in chronological order? | filtratration, secretion, reabsorption, and excretion. |
| Filtration of blood takes place between _____ and _____ of a nephron. | the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule, 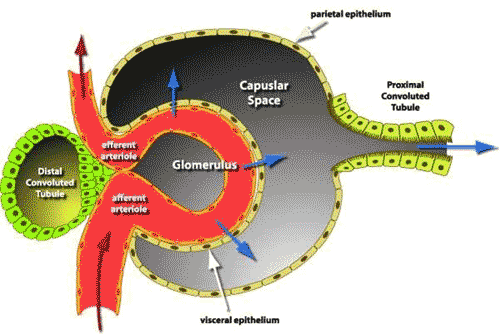 |
| Transport of fluids across a membrane due to high pressure is called ______. | filtration (this occurs in Bowman's capsule because the blood pressure inside the capillaries of the glomerulus is under very high pressure, even higher than blood pressure in most capillaries),  |
| Filtration is considered to be a form of _____ because it occurs by ______ transport and _____ require energy. | diffusion, passive transport, doesn't require energy,  |
| Substances small enough to enter Bowman's capsule by filtration include _____, _____, _____, and _____ as well as water. | glucose, salts, vitamins, and urea,  |
| Filtrate in the nephron enters _____, then passes through the ____, _____, and _____ before entering the _____. | Bowman's capsule --> proximal tubule --> loop of Henle --> distal tubule --> collecting tube,  |
| Where does the filtrate go after it leaves the kidney? | ureter --> urinary bladder --> urethra --> toilet/diaper/ground,  |
| ______ is the active, selective uptake of molecules that were too large to get filtered into Bowman's capsule | Secretion |
| Where does secretion occur? | In the proximal and distal tubules,  |
| Secretion in the proximal and distal tubules is a type of _____ transport | active,  |
| _______ is the process by which most of the water and solutes that initially entered the tubule during filtration are transported back to bloodstream. | Reabsorption (the capillaries, called peritubular capillaries, that surround the tubules and loop of Henle, are the site of reabsorption back to the bloodstream),  |
| The main purpose of the ascending loop of Henle is to move _____ from the loop into the medulla that surrounds the loop in order to draw water out of the tubules in order to concentrate the urine. | salts,  |
| The last job of the nephron is ______, which is the removal of metabolic wastes. Most of the material that passes into the collecting tubule is ______. | excretion, excreted,  |
| Where in the nephron is urine concentrated by allowing the diffusion of water out of the nephron? | descending loop and the collecting tube,  |
| Where in the nephron is salt removed from the filtrate in order to maintain a hyperosmotic gradient in the renal medulla? | ascending loop of Henle,  |
| Where is most of the filtrate reabsorbed into the bloodstream? | proximal tubule,  |
| Where in the nephron is pH regulated? | Proximal tubule (cells that line the proximal tubule maintain a constant pH by controlling the secretion of hydrogen ions),  |
| The descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to _____ but impermeable to ______. | permeable to water but impermeable to salt,  |
| The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to _____ but impermeable to ______. | permeable to salt but impermeable to water,  |
| Salt _______ out of the lower part of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and _______ out of the upper part of the ascending limb. | diffuses, is actively transported,  |
| What happens in the distal tubule? | secretion, reabsorption, and pH regulation (Like the proximal tubule, the distal is another important site for these events), 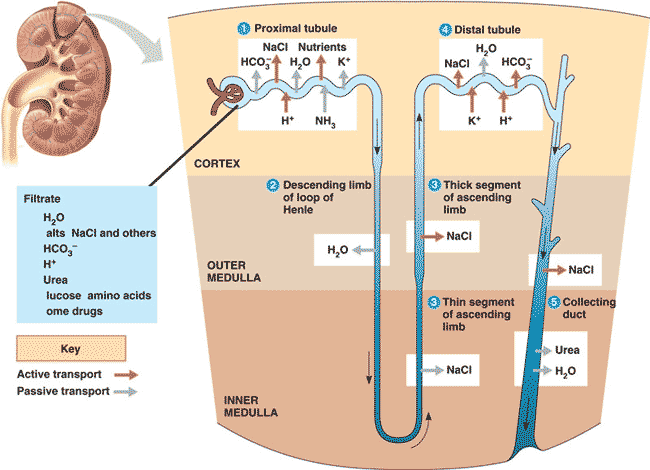 |
| Whether the walls of the collecting tube are permeable or not depends on the presence of _______. Its presence makes the walls permeable so that water can diffuse out of the tubule, making the urine very concentrated. | Antidiuretic hormone (ADH promotes retention of water by the kidneys),  |
| Where is antidiuretic hormone produced, stored and released from, and what is its target? | hypothalamus, posterior pituitary, collecting tubule of the nephron (where it increase permeability of the tubule wall to allow more retention of water, creating more concentrated urine),  |
| ________ cells in the ______ monitor blood solute concentration. When it rises above ______mosm/L, ADH is released into the blood so that more water can be retained and the solutes concentration of urine increases. | Osmoreceptor cells, hypothalamus, 300,  |
| Alcohol ____ the release of ADH, causing less water retention and more urination. | blocks,  |
| Alcohol blocks the release of ____, leading to less water retention and more urination. | ADH,  |
| The ____ system is a complex feedback mechanism that initiates a change in the kidneys in response to a loss of blood pressure. | RAAS (renin-angiotensis-aldosterone-system),  |
| The RAAS (renin-angiotensis-aldosterone-system) system is a complex feedback mechanism that initiates a change in the kidneys in response to __________. | a loss of blood pressure,  |
| The _____, located in a vessel near the glomerulus, senses a decrease in blood pressure and releases renin (not rennin which helps mammals digest milk) to activate the RAAS system. | juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA),  |
| The RAAS system stimulates the kidney to _____. | reabsorb more water (in response to falling blood pressure) |