| A | B |
|---|
| What are the four components that make up blood? | Blood is made of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. |
| Why is it important to know your blood type? | A person receiving blood may die if the blood is of a type not compatible with his or her own. |
| What are the functions of the two sides of the heart? | right side: pumps oxygen-rich blood to the lungs |
| What is the primary function of red blood cells? | carry oxygen to to other cells in the body |
| Why can both high and low blood pressure be a problem? | too high: blood vessels can be weakened |
| Your heart, veins, capillaries, and arteries work together to | transport materials throughout your body |
| Any substance that causes your immune system to produce antibodies against it | antigens |
| Blood pressure is the pressure that blood exerts on your | veins |
| A blood vessel with strong walls that carries blood away | artery |
| Battling blood cells - fight disease | white blood cells |
| Structures that work together as part of the circulatory system include | blood vessels and heart |
| What component of blood transports oxygen? | red blood cells |
| What is the substance that makes red blood cells red? | hemoglobin |
| Blood cells responsible for stopping the blood flow in a cut | platelets |
| Force that blood exerts on your arteries is called | blood pressure |
| A, B, AB, and O are different what? | blood types |
| Mucus traps and destroys pathogens to prevent them from entering the body as part of the defenses of the | respiratory system |
| The body system that includes the skin and its associated | integumentary system |
| A system that interacts with the environment and with | respiratory system |
| More scientific name for red blood cells | erythrocytes |
| Which systems are your first line of defense against pathogens? name three | The integumentary, respiratory, and digestive systems are the first line of defense against pathogens. |
| How does the lymphatic system help the immune system? | The lymphatic system transports white blood cells throughout the body, so that when they are needed in a part of the body, they are ready to attack. |
| What causes a fever when you are sick? | Many tissues produce histamine, which raises the body's temperature to help fight illness. |
| Why is it important for the body to store B cells? | So that antibodies will be available when they are needed to destroy pathogens. |
| What is the difference between active and passive immunity? | In active immunity, a body makes its own antibodies. In passive immunity, a body does not develop immunity on its own, as in the case of a baby who inherits immunity from its mother. |
| Who would most likely have a passive immune system? | a baby |
| Why don't vaccinations usually make you sick? | You receive a very small amount of a weakened pathogen in a vaccine, which is not usually enough to make you sick. |
| What are white blood cells and what is their function in the body? | White blood cells are types of blood cell that destroy foreign materials |
| What are two ways to develop immunity? | through illness and through vaccination |
| The cells that deliver oxygen to other cells are | red blood cells |
| When skin gets damaged, the body releases histamines, which cause | swelling, redness, and heat |
| You develop active immunity to a pathogen by | producing specific antibodies |
| Give an example of a nonspecific response in which a tissue responds to irritation or damage | it releases histamines |
| Vaccines help your body develop | active immune system |
| What are the functions of oil glands? | moisten the skin and hair and keep them from drying out. |
| What are the functions of hair and nails? | Hair protects your skin and keeps you warm |
| What are the five types of sensory receptors in skin? | heat, cold, pain, touch, and pressure |
| What types of weather can damage your skin? | Severe heat and severe cold can damage the skin. |
| List four functions of the skin. | Repels water, guards against infection, helps maintain homeostasis, and senses the environment. |
| How do pathogens enter your body through the skin? | through a cut or an injury |
| When foreign material enters the body, one way the immune system responds is by producing | antibodies |
| Which structure in the skin helps control body temperature? | sweat glands |
| Redness and swelling of an inflamed area is due to increased | blood flow |
| What is the most important function of the integumentary system? | guarding against infection |
| What part of the skin interacts with the nervous system to communicate temperature, pressure, or pain? | sensory receptors |
| Your heart, veins, capillaries, and arteries work together to | transport materials throughout your body |
| Blood pressure is the pressure that blood exerts on your | veins |
| Mucus traps and destroys pathogens to prevent them from entering the body as part of the defenses of the | respiratory system |
What is structure 1 in the diagram?, 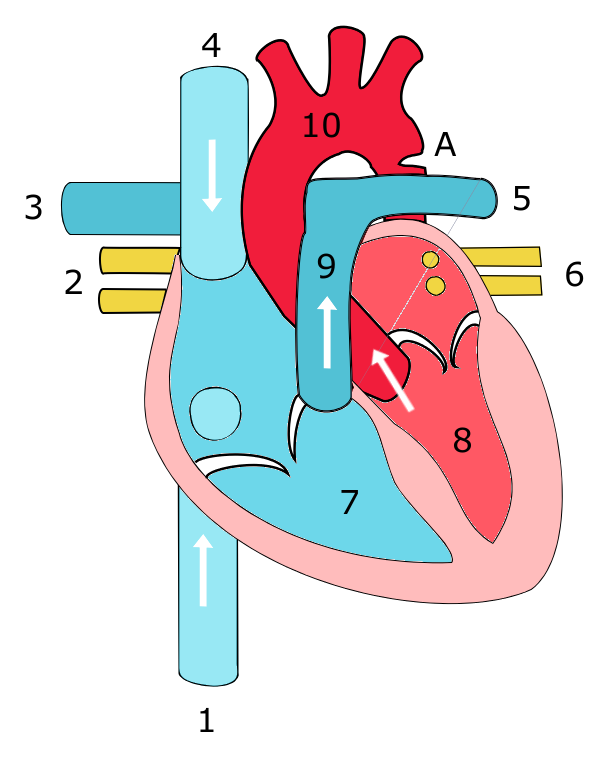 | inferior caval vein |
What is structure 2 in the diagram?,  | right pulmonary veins |
What is structure 3 in the diagram?,  | right pulmonary artery |
What is structure 4 in the diagram?,  | superior caval vein |
What is structure 5 in the diagram?,  | left pulmonary artery |
What is structure 6 in the diagram?,  | left pulmonary veins |
What is structure 7 in the diagram?,  | right ventricle |
What is structure 8 in the diagram?,  | left ventricle |
What is structure 9 in the diagram?,  | pulmonary artery |
What is structure 10 in the diagram?,  | Aorta |