| A | B |
|---|
cell(pg.36), 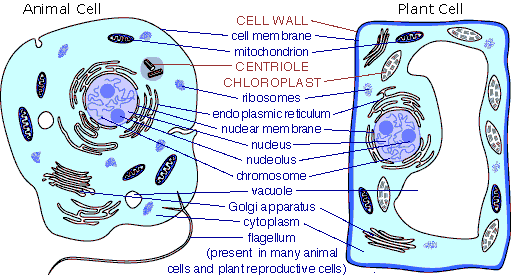 | a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life |
stimulus - response (pg.37), 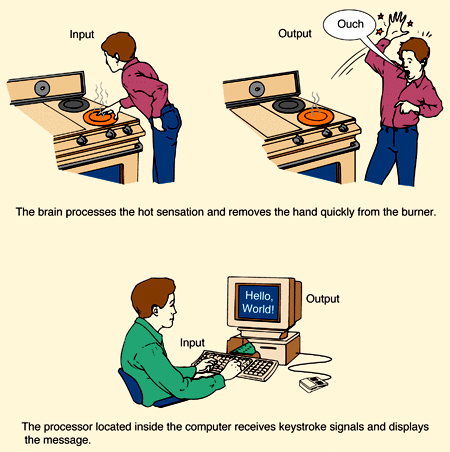 | anything that affects the activity of an organism,organ,or tissue---the action caused by the stimulus is the response |
homeostasis (pg. 37),  | the maintenance of a stable internal environment |
asexual reproduction (pg.38), 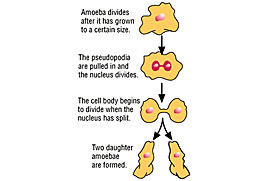 | reproduction in which a single parent produces offspring that are genetically identical to that parent |
sexual reproduction (pg.38),  | reproduction in which two sex cells join to form a zygote;produces offspring that share characteristics of both parents |
DNA (pg.38), 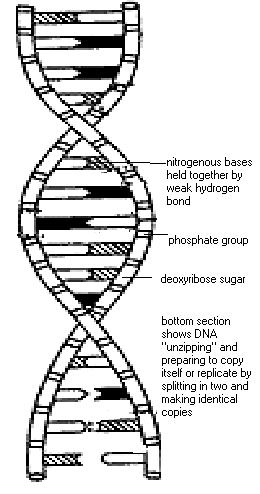 | deoxyribonucleic acid; hereditary material that controls all the activities of a cell,contains the info to make new cells, and provides instructions for making proteins |
heredity (pg.38),  | the passing of traits from parent to offspring |
metabolism (pg.38),  | the combined chemical processes that occur in a cell or living organism |
tissue (pg.57),  | a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific job in the body |
organ (pg. 57), 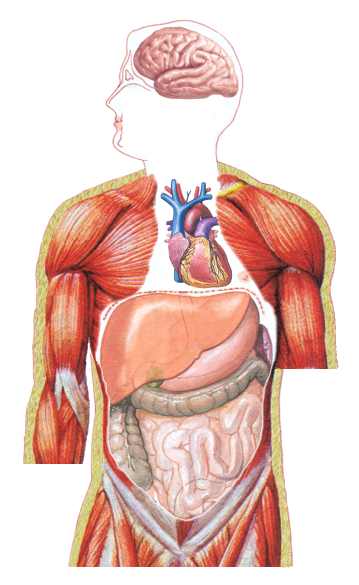 | a combination of two or more tissues that work together to perform a specific function in the body |
organ system (pg.58), 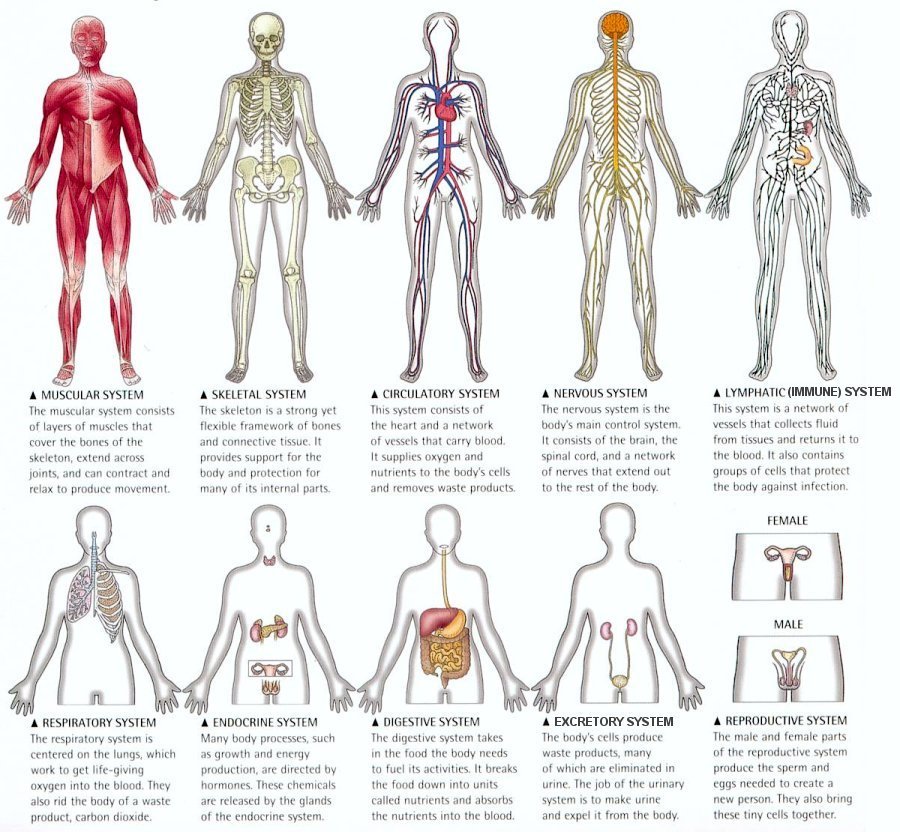 | a group of organs that works together to perform body functions |
organism (pg.59),  | anything that can independently carry out life processes |
unicellular (pg.59), 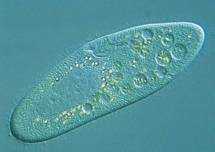 | made of a single cell |
multicellular (pg.59), 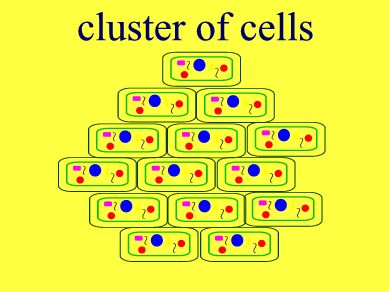 | made of many cells |
epithelial tissue (pg.522), 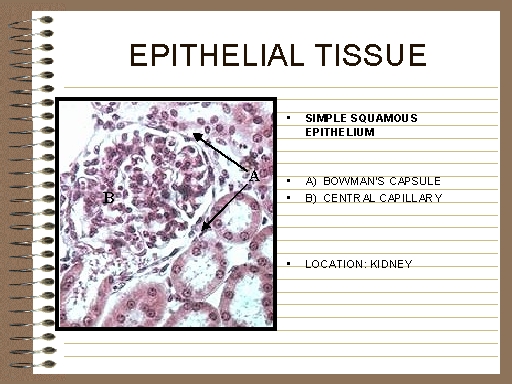 | one of the four main types of tissue in the human body;the tissue that covers and protects underlying tissue |
nervous tissue (pg.522), 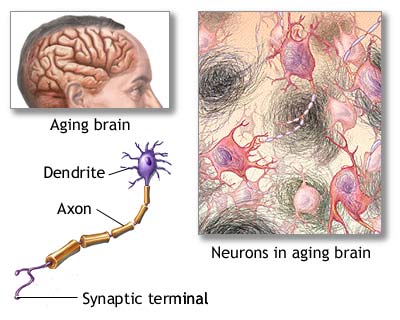 | one of four main types of tissue in the human body;the tissue that sends electrical signals through the body |
muscle tissue (pg.523), 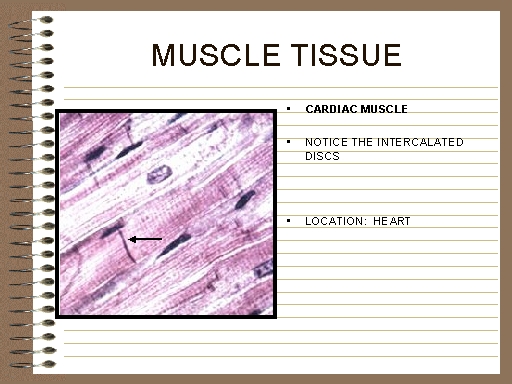 | one of the four main types of tissue in the human body;contains cells that contract and relax to produce movement |
connective tissue (pg.523), 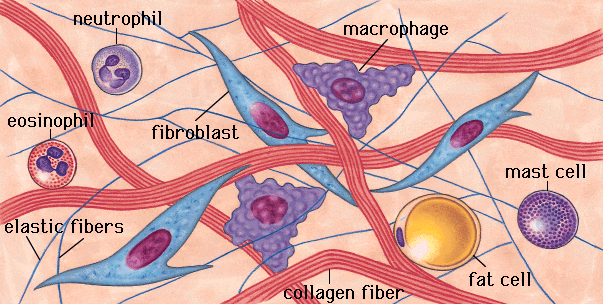 | one of the four main types of tissue in the human body; functions include support,protection,insulation,and nourishment |
characteristic(pg.36),  | a recognizable trait or habit of an organism |
living (pg.36),  | something that can carry out such processes as responding(adaptation),reproduction, growth, use of energy, and change(variation). |
growth (pg.39),  | getting larger or increasing in size: in a single-celled organism, the one cell gets bigger....in a multi-celled organism growth is mainly due to an increase in the number of cells |
develop (pg.39), 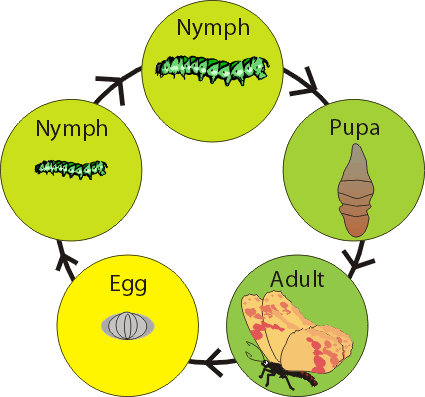 | to change over time(sometimes a lot...sometimes only a little)usually as an organism grows....complete metamorphosis is how some insects develop |
atom (pg.42), 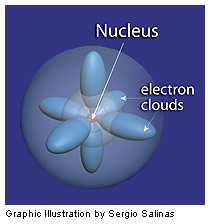 | tiny building blocks of all matter...there are just over 100 types of atoms |
element (pg.42), 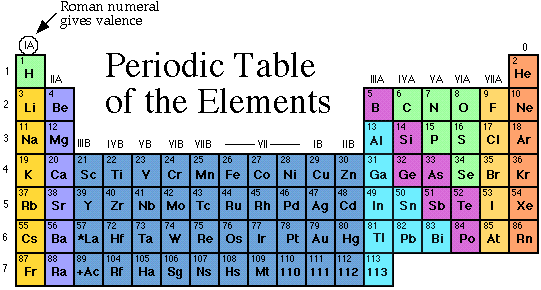 | a substance made up of only ONE TYPE of atom: 6 important elements make up much of the matter of life....they are carbon(C), hydrogen(H), oxygen(O), nitrogen(N), phosphorous(P),and sulfur(S) |
molecule (pg.42), 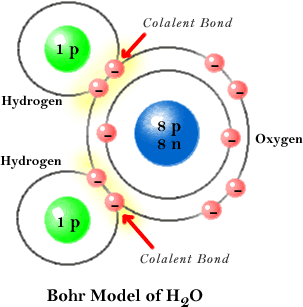 | made of 2 or more elements that are chemically combined |
proteins (pg.42), 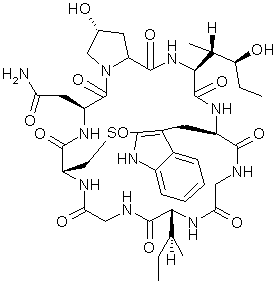 | large molecules made up of "subunits" called "amino acids"...after water,the most abundant material in cells...almost ALL LIFE PROCESSES involve proteins |
amino acids (pg.42), 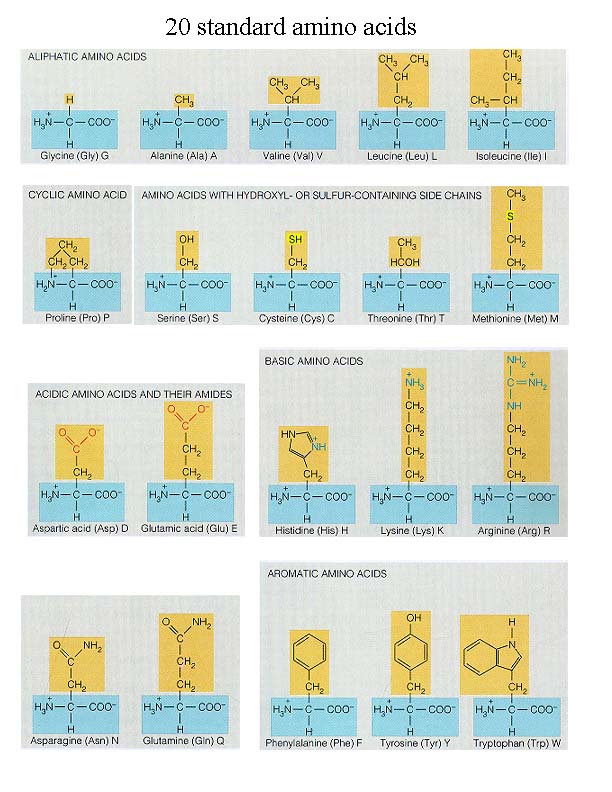 | the smallest unit of a protein("subunits")...20 amino acids make up 100s of different proteins |
hemoglobin (pg.42), 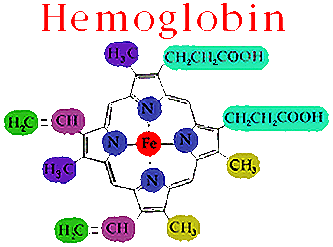 | a protein found in red blood cells that attaches to oxygen(because of an atom of IRON(Fe) in the center of the molecule) so that the oxygen can be delivered throughout a body |
enzyme (pg.42), 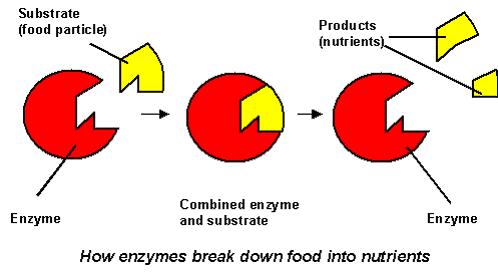 | very special proteins that allow the chemical reactions needed for life to occur quickly |
carbohydrates (pg.43),  | a group of compounds made of sugars...used as as a "source of energy" and for "energy storage" |
simple carbohydrates (pg.43),  | made of one or only a few sugar molecules linked together...ex. table sugar(sucrose),glucose,or fructose(sugar in fruits) |
complex carbohydrates (pg.43),  | made of hundreds of sugar molecules linked together..."starch" is one made by plants |
starch (pg.43),  | a complex carbohydrate made by many plants |
lipids (pg.44), 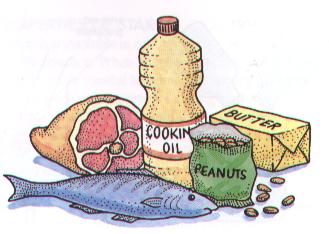 | compounds that CAN NOT MIX WITH WATER...some store energy, and some form cell membranes...can be liquids or solids |
fats (pg.44),  | a solid or semi-solid lipid stored in most animals |
oils (pg.44),  | liquid lipid stored in many plants |
phospholipid (pg.44), 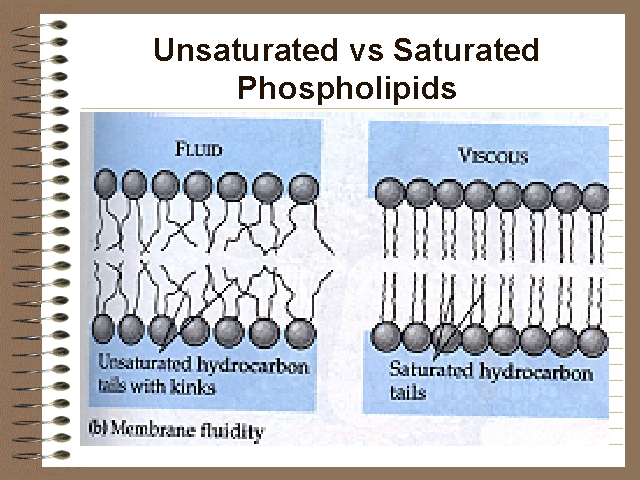 | the molecules that form much of a cell membrane...the "head" of a phospholipid IS ATTRACTED TO WATER...the "tail" is NOT ATTRACTED TO WATER |
nucleic acids (pg.45),  | compounds made of "subunits" called NUCLEOTIDES...2 types; DNA and RNA |
nucleotides (pg.45), 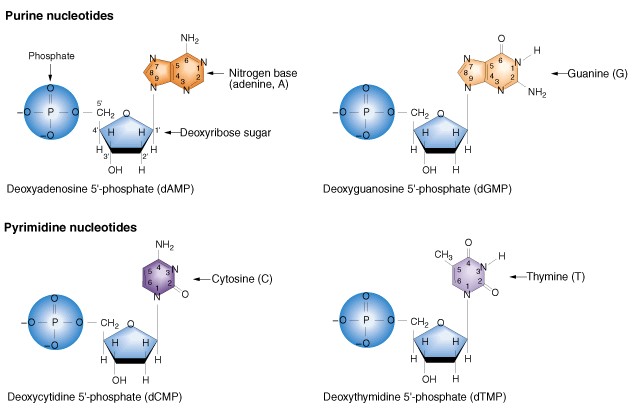 | the subunits of a nucleic acid such as DNA or RNA |
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) pg.45, 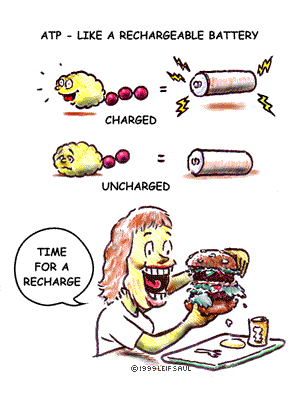 | an important molecule that stores energy released from food molecules until it is needed by cells to "fuel" their life processes |