| A | B |
|---|
| A(n) _______ is any substance that has a definite composition. | chemical (EVERYTHING except energy and empty space is a chemical) |
| _____ research is carried out for the sake of increasing knowledge. | Basic |
| C | carbon |
| N | nitrogen |
| Na | sodium |
| Mg | magnesium |
| P | Phosphorus |
| K | potassium |
| Ca | calcium |
| Mn | manganese |
| Ni | nickel |
| Ag | silver |
| Au | gold |
| ______ are the buildng blocks of matter. | Atoms |
| ______ are pure substances that are made of one type of atom. | Elements |
| _____ are made of two or more different elements bonded together. | compounds |
| Melting a candle would be an example of a _____ change. | physical change |
| In what state would you find matter that makes up the core of the sun? | plasma |
| Has definite volume and shape. | solid |
| Has definite volume but not shape | liquid (liquids will conform to the shape of the bottom portion and sides of their container but retain the volume their overall volume) |
| Has neither definite volume nor shape. | gas (gases will spread out to conform to the shape of their container, increasing in volume as they do) |
| The substances that are required for a chemical reaction to occur (ie- the raw materials) are called the ____ of the reaction. | reactants |
| The substances that are produced as a result of a chemical reaction are called the _____ of the reaction. | products |
| A uniform mixture is known as a(n) ________ mixture. | homogeneous mixture (the prefix "homo" means "same") |
| A mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout is known as a(n) ______ mixture. | heterogeneous mixture (the prefix "hetero" means "differen.") |
| If a pure substance can be decomposed by ordinary chemical means it is a(n) ____. | compound |
| If a pure substance cannot be decomposed by ordinary chemical means it is a(n) ____. | element |
| A homogenous mixture is also called a(n) ____. | solution |
One method of separating heterogeneous mixtures (like blood) into layers based on the density of the components can be accomplished by using a machine called a ______ that spins the mixture at very high speeds, forcing the most dense particles to the bottom., 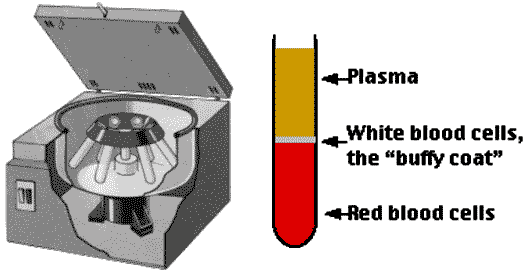 | centrifuge (To separate plasma from the red and white blood cells, blood is put in a centrifuge tube and spun around very quickly, sending the heavier red blood cells to the bottom. The liquid component of blood, called plasma, forms a layer on top),  |
| A method of separating mixtures based on the fact that different substances in the mixture have different boiling points is called ______. | distillation (the apparatus below is used to distill liquids), 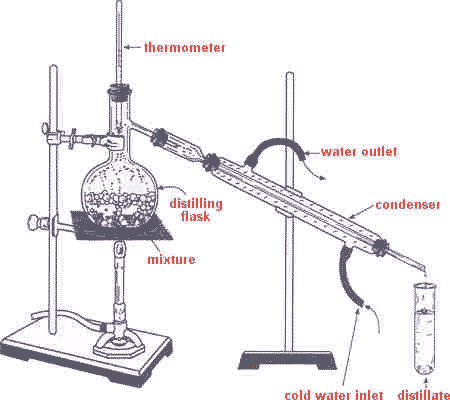 |
A method for separating substances in a mixture based on the facts that larger molecules move slower than smaller molecules through paper when dissolved in a solvent is called _____., 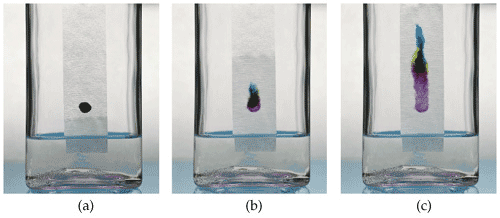 | chromatography (In the picture below, different molecules that make up a type of ink are separated. The far left jar shows the beginning and the far right jar shows the end of the separation),  |
A method of filtration in which molecules stick (adhere) to some surface (such as activated charcoal) while other molecules pass by is called _____.,  | adsorption (the process of sticking is called adhesion),  |
A method for separating mixtures based on a barrier that allows small particles to pass through but not larger ones is called ____., 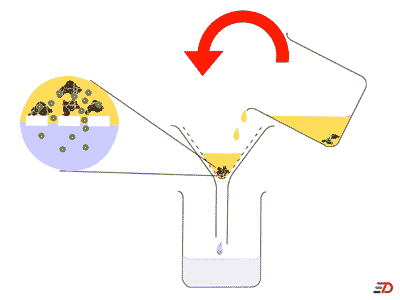 | filtration (Coffee filters work this way. Sometimes swimming pools filter the water through sand or diatomaceous earth),  |
| Elements with very similar chemical properties are organized into ______. | groups |
| The horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table are called _______. | periods |
| Metals are _______, which means they can be hammered or rolled into thin sheets. | malleable |
| Metals are _______, which means they can be drawn into a fine wire. | ductile |
| A metal that is liquid at room temperature is ______. | mercury (Hg) |
| ______ are generally unreactive. | noble gases |
Name this piece of lab equipment.,  | Beaker (used to hold liquids and estimate, not measure precisely, their volumes),  |
Name this piece of lab equipment.,  | Crucible and cover,  |
Name this piece of lab equipment.,  | flask,  |
Name this piece of lab equipment.,  | Evaporating dish,  |
Name this piece of lab equipment., 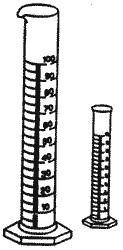 | Graduated cylinder (Used to measure volumes of liquid. DO NOT use beakers for this purpose because the volume lines on beakers are only estimates),  |
Name this piece of lab equipment., 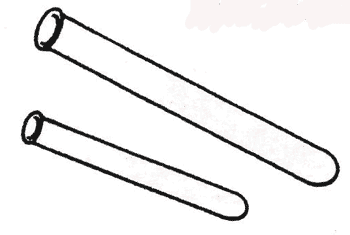 | Test-tubes,  |
Name this piece of lab equipment.,  | Watch glass,  |