| A | B |
|---|
| What was the mechanism that Darwin and Wallace proposed to explain how evolutionary change could occur? | Natural Selection |
| Remains or traces of organisms from the past are called ______. | fossils |
| Paleontology is the study of _____. | fossils |
________ theory of evolution hypothesized that species evolve through "use" and "disuse" and the inheritance of acquired traits. This idea was later proved to be _____.,  | Lamarck's, wrong,  |
| Who was the other person who proposed a theory of Evolution similar to Darwin's around the same time period? | Alfred Russel Wallace |
| One of the observations that helped Darwin form his theory of evolution is that for any species, population sizes would increase ______ if all individuals that are born reproduce successfully. | exponentially (Thomas Malthus, an economist worried about the ability to feed a growing human population, influenced Darwin's thinking in this area) |
| Another set of observations that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that even though populations tend to grow exponentially, populations in nature tend to be ___ in size because resources are ____. | stable, limited |
| Production of more individuals than the environment can support leads to a _______ among individuals of a population, with only a fraction of the offspring surviving. | struggle for existence |
| An important observation that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that members of a population are not all ____. | alike |
| An important observation that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that individuals in a population have varying characteristics and much of this variation is _____. | heritable |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that individuals whose traits give them a high probability of surviving and ____________ are likely to leave more _________ than other individuals. | reproducing, offspring |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that the unequal ability of individuals to ________ and _________ will lead to a gradual change in a population, with favorable characteristics accumulating over generations. | survive, reproduce |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that the unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to a ________ in a population, with ________ accumulating over generations. | gradual change, favorable characteristics |
| The process of humans modifying other species over many generations by selecting and breeding individuals that possess desired traits is called ________. | artificial selection (farmers have been doing this for the last 10,000 years) |
| Natural selection is differential _______ in reproduction that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | success |
| ________ is differential success in reproduction that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | Natural selection |
| Natural selection is differential success in __________ that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | reproduction |
| Natural selection can produce an increase, over time, in the adaptation of organisms to their ______. | environment |
| Natural selection can produce an increase, over time, in the _____ of organisms to their environment. | adaptation |
| In humans, the use of antibiotic drugs selects for pathogens that through __________ are resistant to the drugs’ effects | chance mutations |
| Homology is similarity resulting from common ______. | ancestry |
| ________ is similarity resulting from common ancestry. | Homology |
| ___________ structures between organisms are anatomical resemblances that represent variations on a structural theme that was present in a common ancestor. | Homologous,  |
The picture below shows ______ structures.,  | homologous,  |
Homologous structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through ________ evolution.,  | divergent,  |
| __________ structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through divergent evolution. | Homologous,  |
| Comparative ________ reveals additional anatomical homologies not visible in adult organisms. | embryology, 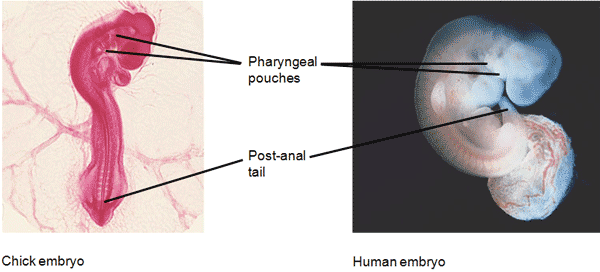 |
______ structures are structures that no longer seem to have a function and are remnants of structures that served important functions in the organism's ancestors.,  | Vestigial,  |
| The human appendix is an example of a(n) ______ structure. | vestigial |
| Biologists also observe homologies among organisms at the molecular level such as ______ that are shared among organisms inherited from a common ancestor. | genes |
| _______ structures are very similar in look and purpose due to convergent evolution, but are not thought to have common origin. | Analogous,  |
Analogous structures (like the wings in the picture below) are very similar in look and purpose due to ______ evolution, but are not thought to have common origin.,  | convergent,  |