| A | B |
|---|
| What was the name of the paper that Charles Darwin had published in 1859 that layed out his mechanism for evolution? | On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection |
| What was the mechanism that Darwin and Wallace proposed to explain how evolutionary change could occur? | Natural Selection |
| What is the name of the field that concerns itself with the classification of organisms? | taxonomy |
| Who was the founder of taxonomy? | Linnaeus |
| Remains or traces of organisms from the past are called ______. | fossils |
| Which type of rock are fossils usually found in? | sedimentary (this type of rock is caused by sediments washing down from the weathered rocks and being deposited in layers, or strata) |
| The study of fossils is called _______. | paleontology |
| Paleontology is the study of _____. | fossils |
| Who proposed the idea of catastrophism, which stated that boundaries between strata represent catastrophic events. | Cuvier |
| What is the name of the idea that profound change can take place through the cumulative effects of slow but continuous processes? | Gradualism |
| The idea that changes in Earth's surface can result from slow continuous actions was put forth by the geologists _____ and ______. They exerted a strong influence on Darwin's thinking. | Lyell, Hutton |
| Lamarck's theory of evolution hypothesized that species evolve through ____ and _____ and the inheritance of _____ traits. This idea was later proved to be wrong. | use, disuse, acquired,  |
________ theory of evolution hypothesized that species evolve through "use" and "disuse" and the inheritance of acquired traits. This idea was later proved to be _____.,  | Lamarck's, wrong,  |
| Where was Darwin's most famous stop during his travels around the world on the HMS Beagle? | The Galapagos Islands (off the west coast of South America) |
| Who was the other person who proposed a theory of Evolution similar to Darwin's around the same time period? | Alfred Russel Wallace |
| The phrase "______" summarizes Darwin's perception of the unity of life, stating that all organisms are related through descent from an ancestor that lived in the remote past. | Descent with modification |
| One of the observations that helped Darwin form his theory of evolution is that for any species, population sizes would increase ______ if all individuals that are born reproduce successfully. | exponentially (Thomas Malthus, an economist worried about the ability to feed a growing human population, influenced Darwin's thinking in this area) |
| Another set of observations that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that even though populations tend to grow exponentially, populations in nature tend to be ___ in size because resources are ____. | stable, limited |
| Production of more individuals than the environment can support leads to a _______ among individuals of a population, with only a fraction of the offspring surviving. | struggle for existence |
| An important observation that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that members of a population are not all ____. | alike |
| An important observation that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that individuals in a population have varying characteristics and much of this variation is _____. | heritable |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that individuals whose traits give them a high probability of surviving and ____________ are likely to leave more _________ than other individuals. | reproducing, offspring |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that the unequal ability of individuals to ________ and _________ will lead to a gradual change in a population, with favorable characteristics accumulating over generations. | survive, reproduce |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that the unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to a ________ in a population, with ________ accumulating over generations. | gradual change, favorable characteristics |
| The process of humans modifying other species over many generations by selecting and breeding individuals that possess desired traits is called ________. | artificial selection (farmers have been doing this for the last 10,000 years) |
| Natural selection is differential _______ in reproduction that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | success |
| ________ is differential success in reproduction that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | Natural selection |
| Natural selection is differential success in __________ that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | reproduction |
| Natural selection can produce an increase, over time, in the adaptation of organisms to their ______. | environment |
| Natural selection can produce an increase, over time, in the _____ of organisms to their environment. | adaptation |
| In humans, the use of antibiotic drugs selects for pathogens that through __________ are resistant to the drugs’ effects | chance mutations |
| Homology is similarity resulting from common ______. | ancestry |
| ________ is similarity resulting from common ancestry. | Homology |
| _________ structures between organisms are anatomical resemblances that represent variations on a structural theme that was present in a common ancestor. | Homologous,  |
The picture below shows ______ structures.,  | homologous,  |
Homologous structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through ________ evolution.,  | divergent,  |
| _________ structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through divergent evolution. | Homologous,  |
| Comparative ________ reveals additional anatomical homologies not visible in adult organisms. | embryology, 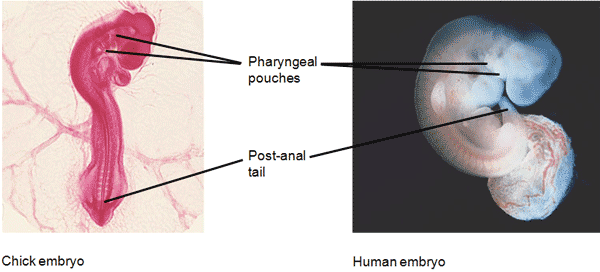 |
______ structures are structures that no longer seem to have a function and are remnants of structures that served important functions in the organism's ancestors.,  | Vestigial,  |
| The human appendix is an example of a(n) ______ structure. | vestigial |
| Biologists also observe homologies among organisms at the molecular level such as ______ that are shared among organisms inherited from a common ancestor. | genes |
| Molecular homologies can be inferred by comparing _____ sequences in DNA from different organisms. | nucleotide |
| Molecular homologies can be inferred by comparing _____ sequences in proteins from different organisms. | amino acid |
| _______ structures are very similar in look and purpose due to convergent evolution, but are not thought to have common origin. | Analogous,  |
Analogous structures (like the wings in the picture below) are very similar in look and purpose due to ______ evolution, but are not thought to have common origin.,  | convergent,  |
The two structures below are examples of _______ structures.,  | analogous,  |
| In science, a ______ accounts for many observations and data, and attempts to explain and integrate a great variety of phenomena. | theory |
| In science, a _____ is a well tested explanation that represents the most likely explanation given the present evidence. | theory |
| The study of the past and present distribution of species is called _____. | biogeography |
| ______ is an accumulation of inherited characteristics that enhance organisms' ability to survive and reproduce in specific environments. | evolutionary adaptations |
| The hypothesis by George Cuvier that each boundary between strata corresponded in time to a catastrophe, such as a flood or drought, that had destroyed many of the species living there at that time. | Catastrophism |