| A | B |
|---|
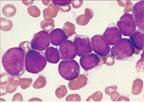 | Precursor B cell: CD19, CD10, TdT |
 | t(12;21) – CBFα /ETV6, t(9;22), t(4;11) |
 | lobulated nucleus, starry sky with tingible body macrophages |
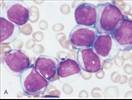 | M0-M7 |
| CD 34, CD33, CD15 |  |
 | t(8;21) and inv(16) form CBF1α and CBFβ fusion protein, blocks terminal differentiation |
 | acute promyelocytic leukemia: |
 | Deletions in xsomes 5,7 following myelodysplastic syndromes or exposure to DNA-damaging chemo/radiation |
 | Translocation of MLL gene on xsome 11q23 after topoisomerase II inhibitor treatment |
 | Myeloblasts: delicate nuclear chromatin, 2-4 nucleoli,fine, azurophilic, peroxidaze + granules, red peroxidase + Auer rods |
| Monoblasts: folded or lobulated nuclei, no Auer rods, peroxidase - nonspec. esterase + |  |
 | Monocyte tumors in the skin and gingival, CNS spread |
| Good prognosis for t(8;21) or inv(16) w/ chemo |  |
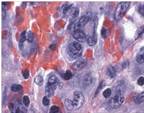 | Cytotoxic CD8 T cell |
| Rearranged 2p23 with ALK gene |  |
 | Tumor cells cluster around venules and infiltrate lymphoid sinuses |
| Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma |  |
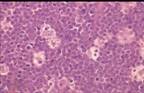 | Translocationof c-myc and Ig loci, t(8;14), t(8;22), t(2;8) |
 | CD19, CD20, CD10, BCL6, IgM, κ or λ light chain-- LIKE DARK ZONE |
| EBV in endemic African cases, 15-20% of sporadic and 25% HIV |  |
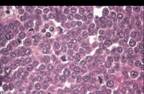 | EBV in endemic African cases, 15-20% of sporadic and 25% HIV |
| AGGRESSIVE:Responds well to short-term, high dose chemo |  |
 | Jaw (mandible) or extranodal abdominal masses, |
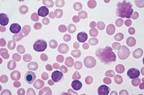 | Trisomy 12, deletions of 11q, 13q, 12q, 17p |
| Naïve B-cell or post germinal center memory B-cell |  |
 | CD19, CD 20, C23, CD5 |
| Prolymphocytic transf. to diffuse lg B-cell lymphoma (Richter syndrome) |  |
 | Node: Larger prolymphocytes aggregate into mitotically active proliferation centers |
| Indolent, median sv.4-6 y, worse pronois w/ 11q 17p | 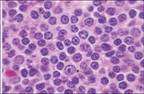 |
 | Diffuse pattern of small lymphocytes peripheral blood may be leukopenic |
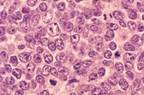 | Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma |
| BCL6 dysregulation on 3q27,t(14;18), cREl amplification |  |
| Single rapidly growing mass, extranodal, common at Waldeyer ring, liver, spleen |  |
 | Immunodef.- associated (HIV, SCID, transplants, EBV) |
| Rapidly fatal if untreated; Chemo: 60-80% remission |  |
 | germinal or < center B cell CD19, CD20, TdT -; vrble exprssn of CD10, BCL6, SIg, |
| All ages (5% childhood lymphomas), most commonly adults (60 yrs), slight male predominance |  |
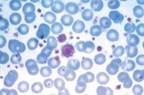 | Megakaryocytes have decrease requirement for growth factors |
| Hematopoietic stem cell that gives rise mainly to megakaryocytes |  |
 | Erythromelalgia – burning and throbbing in hands and feet caused by occlusion of small arterioles with platelet aggregates |
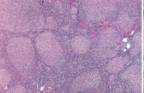 | CD19, CD20, CD10, SIg, BCL2, BCL6 |
 | t(14;18)-BCL2 and IgH - antiapoptotic |
 | Nodes:Centrocytes – small cleaved cells (majority) |
 | most common form of NHL in the U.S. |
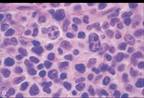 | Centroblasts – larger, open chromatin, several nucleoli, modest cytoplasm |
 | 30-50% transform to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with survival |
 | Follicular Lymphoma |
 | Indolent, Incurable, median survival 7-9 years (good prognosis, low grade) |
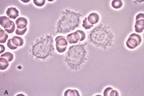 | CD19, CD20, IgG, κ or λ light chain, CD11c, CD25, CD103 |
 | hairlike projections, round, oblong or reniform nuclei, moderate pale blue cytoplasm |
 | Pancytopenia, |
 | Post germinal center memory B cell |
 | Older Caucasian males, Indolent, Sensitive to chemo |
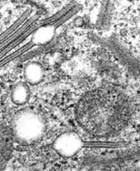 | Monoclonal,HLA-DR, S-100, CD1A, CCR6 and CCR7 |
 | Abundant, vacuolated cytoplasm containing Birbeck granules (tennis-racket), vesicular nuclei with linear grooves or folds |
 | Multifocal multisystemic: rapidly fatal if untreated, intensive chemo – 50% survive 5 yrs |
 | Secreted IgM for plasma cells |
 | B-cells, plasma Cells, deletion on 6q; Older adults (60-70 yrs) |
 | Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma |
 | Bone Marrow:Lymphocytes, plasma cells and intermediate plasmacytoid lymphocytes, hyperplasia of mast cells |
 | PAS positive inclusions of Ig in cystoplasm (Russell bodies) or nucleus (Dutcher bodies) |
 | IgM causes Hyperviscosity syndrome |
 | Weakness, fatigue, weight loss, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia (autoimmune hemolysis by cold agglutinins at <37 C) |
 | (Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia) – visual impairment, headaches, dizziness, deafness, bleeding, cryoglobulinemia (precipitation of macroglobulins at low T) |
 | Plasmapheresis alleviates hyperviscosity and hemolysis, incurable, progressive Meidan survival: 4 yrs |
 | Transformation to large-cell lymphoma |
 | Mantle Cell Lymphoma |
 | CD19, CD20, IgM, IgD, κ or λ light chain, CD5, Cyclin D |
 | t(11;14) involving BCL1 (cyclin D1) and IgH |
 | Node:Tumor cells surround reactive germinal centers |
 | Disseminated disease, painless lymphadenopathy, bone marrow, splenic white pulp, hepatic periportal areas, gut, lymphomatoid polyposis |
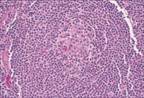 | Naïve B cell |
 | Small lymphocytes with round or clefted nuclei, condensed chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, scant cytoplasm |
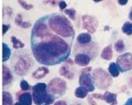 | Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Pawn ball megakaryocytes (single nuclear lobes or multiple separate nuclei) |
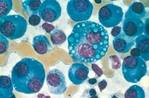 | Survival dependent on IL-6 produced by neoplastic plasma cells and normal stromal cells in the marrow |
 | Neoplastic plasma cells produce osteoclast factors MIP1α and RANKL (R’ for NF-κB) |
 | Multiple Myeloma, Solitary Plasmacytoma, Monoclonal Gammopathy of Uncertain Significance (MGUS) |
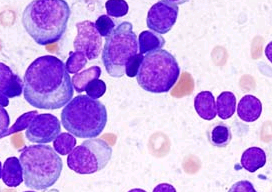 | Most common symptomatic monoclonal gammopathy |
 | Chemo with alkylating agents 50-70% remission with survival of 3 yrs |
 | Gelatinous soft, red tumor masses esp. in vertebral column, ribs, skull. |
 | Osteoprotegrin inhibits RANKL, |
 | multiple myeloma Intracellular accumulation of degraded Ig – flame cells with red cytoplasm |
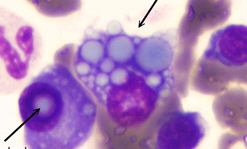 | (Russell bodies – cytoplasmic, Dutcher bodies – nuclear) Multiple myeloma |
blue grapelike cytoplasmic droplets, inclusions of fibrils, crystalline rods and globules, 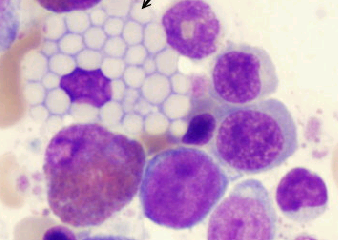 | multiple myeloma, Mott cells |
 | Plasmacytosas and MGUS may progress to MM |
 | Older adults (50-60 yrs), men, African descent |
 | Plasma cells infiltrate marrow diffusely or in sheetlike masses. |
 | Lytic bone lesions, pathologic fractures, renal failure (myeloma kidney), primary amyloidosis, hypercalcemia |
 | Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (Nodal) |
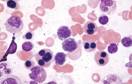 | Nucleated Red Cell Progenitors |
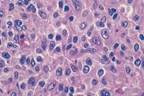 | CD2, CD5, CD3, αβ or γδ receptor, sometimes CD4, CD8 |
 | Diffuse involvement of lymph node:Variable sized T cells, eosinophils, macrophages, angiogenesis |
 | Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma, Unspecified |
 | Mature T cells: Diffuse involvement of lymph node |
 | Lymphadenopathy, eosinophilia, pruritus, fever, weight loss |
 | Worse than comparable B cell neoplasms; poor prognosis but some cures reported |
 | Multipotent myeloid stem cell that gives rise to erythrocytes, granulocytes, megakaryocytes |
 | Peripheral blood: basophilia, polycythemia, granulocytosis, thrombocytosis |
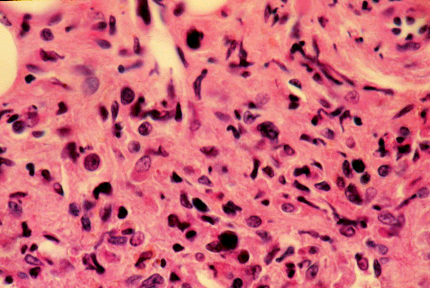 | fibrosis in bone marrow specimen: often referred to as the spent phase of polycythemia vera |
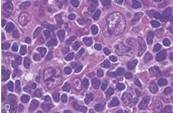 | Lymphocyte predominance Reed Sternberg Cells |
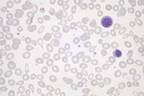 | Primary Myelofibrosis: Identical to spent phase of other chronic myeloproliferative disorders |
 | Rapid dev. of obliterative marrow fibrosis due to inappropriate release of PDGF and TGFβ from neoplastic megakaryocytes |
 | Peripheral blood:dacryocytes (tear-drop erythrocytes), large platelets, basophilia, cytopenias, Leukoerythroblastosis-erythroid/granulocytic precursors |
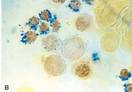 | Ringed sideroblasts- erythroblasts with iron laden mitochondria |
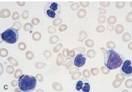 | Pseudo-Pelger-Huet cells – PMNs w/ 2 nuclear lobes |
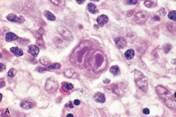 | Reed Sternberg Cell |
 | Hodgkin Lymphoma |
 | Giant RS cells that secrete IL-5, IL-6, IL-13, TNF, GM-CSF, attracting lymphocytes, macrophages and granulocytes which in turn support growth of the tumor cells |
 | -During cell death cell shrinks and becomes pyknotic (mummification) |
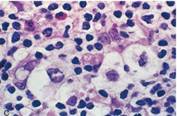 | Mediastinal mass in young females. Moderately aggressive. |
 | Nodular sclerosis most common HL (65-70%) |
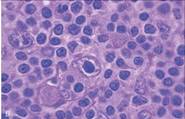 | RS Mononuclear Variant; Single round or oblong nucleus; Large inclusion like nucleolus |
 | R-S cells found in HL of Mixed cellularity,Lymphocyte-rich |