| A | B |
|---|
| a person who is given an injection containing only antibodies would most likely develop | passive immunity |
| Which type of vessel normally contains valves that prevent the backward flow of materials? | vein |
| The phrase "is not a cell but has the ability to reproduce wihtin a living cell" can be used to describe | a virus |
| The passage of the end products of digestion into the cells of an organism is an example of | absorption |
| Vegetable oils, such as corn oil, belong to which general class of organic substances? | lipids |
| A substance which causes an immunological reaction when introduced into the body of man is | an antigen |
| Two examples of carbohydrates are | sugars and starches |
| The immune system of humans may respond to chemicals on the surface of an invading organism by | synthesizing antibodies that mark these organisms to be destroyed |
| Transport in mammals generally involves absorption and | circulation |
| Which activity is NOT a response of human white blood cells to pathogens? | removing carbon dioxide |
| What is a major difference between red blood cells and white blood cells? | Red blood cells contain hemoglobin but white blood cells do not |
| Which statement describes two unsafe laboratory practices? | Opening of a test tube is pointed towards student and student is not wearing goggles |
| A structure that performs a specialized function within a cell is known as an | organelle |
| The thick muscular vessels that transport blood away from the heart are the | arteries |
| Hemoglobin, insulin, albumin, and maltase, which are composed of chains of amino acids, are examples of | proteins |
| The largest amount of DNA in a plant cell is contained in | a nucleus |
| Dissolved nutrients, wastes, and oxygen are exchanged between the blood and intercellular fluid through the walls of | capillaries |
| Many vaccinations stimulate the immune system by exposing it to | weakened microbes |
| Microbes that enter the body, causing disease, are known as | pathogens |
| Plants store carbohydrates in the form of | starch |
| Which structure is best observed using a compound light microscope? | a cell |
| Put the following in the sequence from simple to complex: organs; tissues; cells; organ systems | cells>tissues>organs> organ systems |
| Which condition would most likely result in a human body being unable to defend itself against pathogens and cancerous cells. | the presence in the body of the virus that causes AIDS |
| Red blood cells are produced in the | bone marrow |
| Which organic compound is correctly matched with starch? | glucose |
| Which function is associated with phagocytes in the blood? | engulfing bacteria |
| The digestion of starch begins in the | mouth |
| Which type of digestion occurs in the mouth when an individual chews a piece of bread? | both mechanical and chemical digestion |
| Peristalsis occurs in | esophogus and small intestines |
| Where does extracellular chemical digestion of protein begin? | Stomach |
| In humans, chemical digestion is accomplished by enzyme action that begins in the mouth and ends in the | small intestines |
| The principal function of the large intestines is | absorb water |
| The digestive enzymes in the pancreas are important because they | change food substances into molecules that can pass into the bloodstream and cells |
| A disorder of the digestive system that can cause severe dehydration is known as | diarrhea |
| Feces is usually about 40 percent water and 60 percent solid. Reducing the water will most likely result in | constipation |
Which letter indicates a cell structure that controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell?, 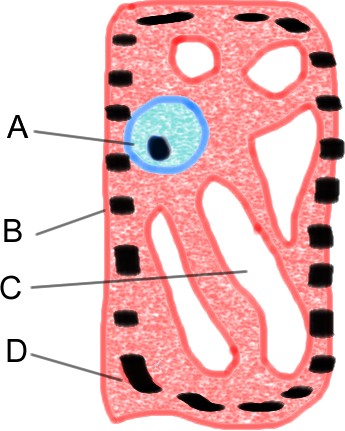 | B |
Which two activities in the chart best describe the process of transport?,  | C and D |
The diagram represents human blood cells. Which function is associated with cell x?, 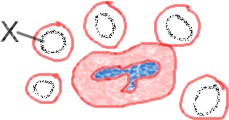 | oxygen transport |