| A | B |
|---|
| 2 characteristics of seed plants | vascular tissue and use seeds to reproduce |
| phloem | food moves through this tube |
| xylem | water and nutrients move through this tube |
| seeds | a young plant that is enclosed in a protective coating |
| 3 important parts of a seed | embryo, stored food, seed coat |
| embryo | the beginning of the growing seed |
| germination | the beginning of growth of a new plant from a seed or a spore |
| photosynthesis | leaves capture the sun's energy and carry out the food-making process of this process. |
| stomata | the underside of the leaf that has small openings that let gases in and out |
| transpiration | process which water evaporates from the stomata |
| stems do... | hold the leaves up and provides support for the plant |
| roots | anchor a plant in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil |
| Vascular tissues | xylem and phloem tubes |
| Non- Vascular Plants | Moss-liverworts and hornworts |
| Vascular Plants | Ferns-horsetails, and club mosses |
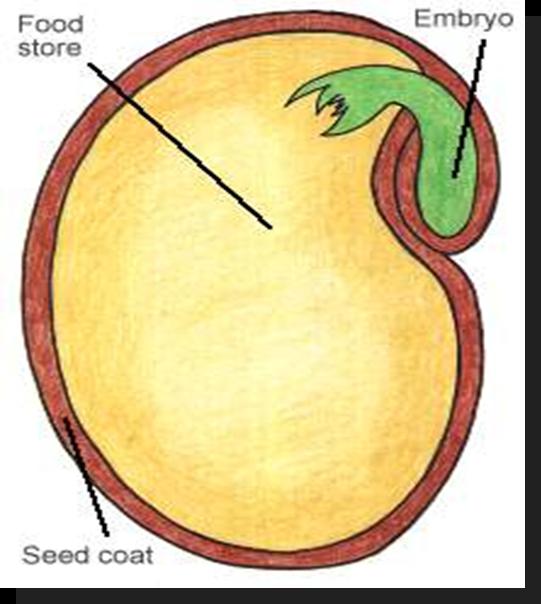 | Seed |
 | Germination |
| Characteristics of Seeds | Multi-cellular, Contain parent plants genetic information, hard, protective covering, contain a food supply, can survive harsh, dry condidtions |
| Female reproductive part of a flower | Pistil |
| The joining of the nuclei of a male and female reproductive cell is called.... | Fertilization |
| The reproductive parts of a flower | Stamen, and pistil |
| Male reproductive parts of a flower.. | Stamen- Filament, and anther |