| A | B |
|---|
| _____ is a method paleontologists use for determining the ages of rocks and fossils on a scale of absolute time, based on the half-life of radioactive isotopes. | Radiometric dating,  |
| The number of years it takes for 50% of an original sample of a radioactive isotope to decay is called the isotope's _____. | half-life,  |
| A(n) _______ is a collection of autonomously replicating cells of the same species. | colony (This Volvox in the picture below is considered to be a colony),  |
| The supercontinent formed near the end of the Paleozoic era when plate movements brought all the landmasses of Earth together is called ______. | Pangea, 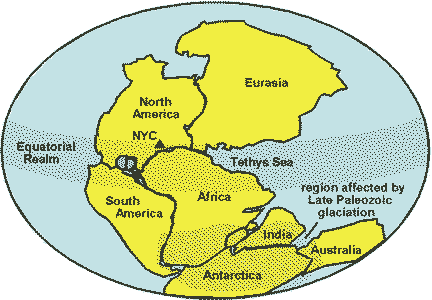 |
| What are the names of the three domains? | Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya |
| The model of the origin of eukaryotes that proposes that mitochondria, chloroplasts, and perhaps other cellular structures were formerly small prokaryotes that lived symbiotically inside larger cells. | endosymbiosis,  |
| Scientific data indicates that Earth formed about _____ years ago. | 4.6 billion |
| The first genetic material was probably ____ due to its ability to catalyze reactions including its own self replication. | RNA |
| ______ are similar fossils found in the same rock strata in different locations. They allow strata at one location to be correlated with strata at another location. | Index fossils,  |
| The earliest known fossils date back about _____ years ago. | 3.5 billion |
| Prokaryotes were the only life forms from about _____ to ______ years ago. | 3.5 billion to 2.1 billion |
| The first photosynthetic organisms were probably _______. | cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green bacteria) |
| Earth's early atmosphere was much different than today's atmosphere in that it lacked _____. | oxygen |
| The oldest fossils of unicellular eukaryotic organisms date back _____ years ago. | 2.1 billion |
| The oldest fossils of multicellular eukaryotic organisms date back _____ years ago. | 1.2 billion |