| A | B |
|---|
| An organism that harnesses light energy to drive the synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide is called a(n) _____. | photoautotroph |
| Any organism that must consume organic molecules for a source of carbon is called a(n) _____. | heterotroph (The two types of heterotrophs are photoheterotrophs and chemoheterotrophs) |
| Any organism that can use inorganic carbon dioxide as its carbon source is called a(n) _____. | autotroph (The two types of autotrophs are photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs) |
| The assimilation of atmospheric nitrogen by certain prokaryotes into nitrogenous compounds that can be directly used by plants is called ____. | nitrogen fixation |
| The larger participant in a symbiotic relationship, serving as home and feeding ground to the symbiont is called the ____. | host |
| An organism that requires oxygen for cellular respiration and cannot live without it is called a(n) _____. | obligate aerobe |
| A staining method that distinguishes between two different kinds of bacterial cell walls is called the ____. | gram stain,  |
| The sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces is called the ____. | capsule,  |
| A thick-coated, resistant cell produced within a bacterial cell exposed to harsh conditions is called a(n) ____. | endospore, 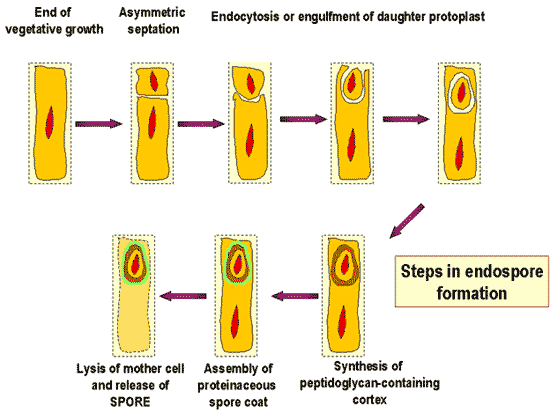 |
| Movement toward or away from a stimulus is called _____. | taxis |
| A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of a bacterial chromosome is called a(n) ____. | plasmid (plasmids are also found in some eukaryotes, such as yeast),  |
| An ecological relationship between organisms of two different species that live together in direct contact is called _____. | symbiosis |
| An organism that absorbs nutrients from the body fluids of living hosts would be classified as a(n) ____. | parasite |
| A long, hairlike prokaryotic appendage that functions in adherence or in the transfer of DNA during conjugation is called a(n) ____. | pilus (plural - pili),  |
| A bacterium that absorbs nutrients from nonliving organic materials such as corpses, fallen plant material, and the wastes of living organisms and converts them into inorganic forms would be classified as a(n) ____. | decomposer |
| A process that uses inorganic molecules other than oxygen to accept electrons at the downhill end of electron transport chains is called ____. | anaerobic respiration |
| A symbiotic relationship in which the symbiont benefits at the expense of the host is called ____. | parasitism |
| A symbiotic relationship in which both participants benefit is called ____. | mutualism |
| The smaller participant in a symbiotic relationship, living in or on the host is called the ____. | symbiont |
| A type of polymer in bacterial cell walls consisting of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides is called a(n) ____. | peptidoglycan |
| An organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but that switches to fermentation under anaerobic conditions, is called a(n) ____. | facultative anaerobe |
| The region in a prokaryotic cell consisting of a concentrated mass of DNA is called the _______. | nucleoid region,  |
| An organism that cannot use oxygen and is in fact poisoned by it is called a(n) _____. | obligate anaerobe |
| A symbiotic relationship in which the symbiont benefits but the host is neither helped nor harmed is called _____. | commensalism |
Prokaryotic cells lack _______, 
| a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles |
| Cells that have a nucleus and organelles are called ____ cells. | eukaryotic, 
|
| What are three different shapes that bacteria can be? | spheres (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), spiral |
| Bacteria that stain purple are known as _______ . | gram-positive bacteria,  |
| bacteria that don't stain purple are known as ______. | gram-negative bacteria,  |
| Mutualism, parasitism and commensalism are all types of ____. | symbiosis, 
|
| Some bacteria have a whip-like tail called a ____. | flagellum, 
|
| The structure just outside the cell membrane of a bacterium is called the ___. | cell wall,  |
| Which gas in the atmosphere do some bacteria capture and turn into fertilizer that plants can use? | nitrogen |
| Medicines that kill bacteria as well as other living microorganisms are known as ____. | antibiotics, 
|
| Specialized pili, called sex pili, link prokaryotes during ______, a process in which one cell transfers DNA to another cell. | conjugation, 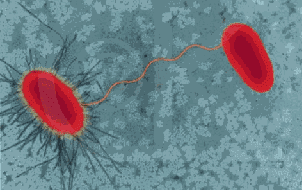 |
| What is the scientific name of the bacteria that reside in the intestines of mammals, including humans? | Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| What do you call the photosynthetic oxygen producing bacteria? | Cyanobacteria (A.k.a. - Blue-green bacteria) |