| A | B |
|---|
| The leaflike structure of a seaweed that provides most of the surface area for photosynthesis is called the _____. | blade (Since seaweeds don't have a vascular system to transport nutrients, just about all parts of a seaweed conduct photosynthesis, not just the blade. For terrestrial plants with leaves, the flattened portion of a typical leaf is also called the blade.),  |
| The stemlike structure of a seaweed is called the _____. | stipe,  |
| A(n) _____ is a unicellular photosynthetic alga with a unique, glassy, cell wall containing silica. | diatom,  |
| _____ are short cellular appendages specialized for locomotion, formed from a core of nine outer doublet microtubules and two inner single microtubules ensheathed in an extension of the plasma membrane. | Cilia,  |
| An organism that is capable of both photosynthesis and heterotrophy is called a(n) _____. | mixotroph |
| A(n) _____ is a single mass of cytoplasm containing many diploid nuclei that forms during the life cycle of some slime molds. | plasmodium,  |
| A(n) ____ is an aquatic protist that secretes a hardened shell containing calcium carbonate and extends pseudopodia through pores in the shell. | foraminiferan (a.k.a. - foram): Notice the picture on the left of the calcium carbonate shell with the numerous pores where the pseudopods come out from the shell (see picture of threadlike pseudopods coming out from a live foram on the left). Foram skeletons make up a major part of the marine sediment as they sink to the bottom of the ocean.,  |
| Under the old five kingdom system, the ____ kingdom included all eukaryotic organisms that couldn't be classified as plants, animals, or fungi. Under the new three domain system, advances in molecular biology have made scientists realize that _____ should actually be broken down into several kingdoms with some possibly being placed back into the plant, animal or fungal kingdoms. Therefore, _____ is an informal term used to describe mostly unicellular organisms that are not plants, animals, or fungi. | protist (the answer for all of the blanks) |
| All ____ are parasites of animals. They spread through tiny infectious cells called sporozoites. Plamodium, the parasite that causes malaria, is an example. | apicomplexans |
| Diplomonads and parabasalids have modified ______. | mitochondria (Their mitochondria lack their own DNA, don't have electron transport systems, or enzymes that are normally needed for the citric acid cycle) |
| ______ is a type of diplomonad that causes severe diarrhea and is often picked up by drinking untreated water from rivers or lakes contaminated with feces containing the parasite in the dormant cyst stage. | Giardia (This is often the cause of sickness on camping trips when water is not filtered or boiled.) |
What type of protist is pictured below?,  | A diatom,  |
| A(n) ______ is a protist such as a water mold, white rust, or downy mildew, that acquires nutrition mainly as a decomposer or plant parasite. | oomycete |
| A type of protozoan that moves by means of cilia is called a(n) _____. | ciliate (The paramecium in the picture below is a classic example of a ciliate. If you look closely, you can make out the small hairlike cilia.),  |
The protozoan pictured below is a(n) ______.,  | paramecium,  |
| Protists that are animal-like in that they capture and consume food are called _______. | protozoans |
| The mutualistic collective formed by the symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic alga is called a(n) _____. | lichen (The picture below shows different species of lichens encrusted on a rock. Other types of lichens are found on the bark of trees. Instead of using a photosynthetic alga, some lichens use cyanobacteria for their photosynthetic part.), 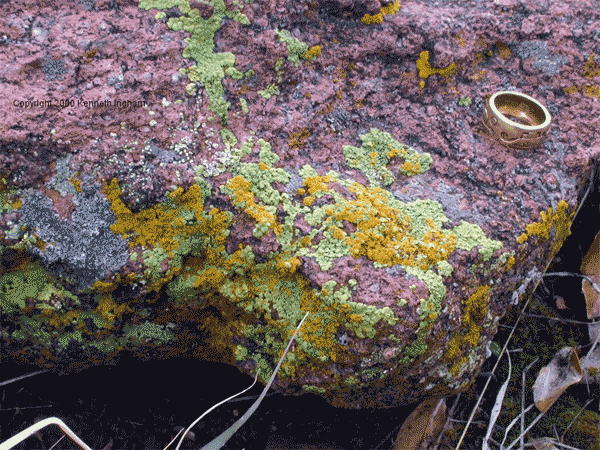 |
| A(n) ______ is a unicellular photosynthetic alga with two flagella situated in perpendicular grooves in cellulose plates covering the cell. | dinoflagellate (The alga that causes red tide is a dinoflagellate. Some dinoflagellates are bioluminscent which means that they can glow in the dark.),  |
| A(n) ______ is a protist, usually marine, with a shell generally made of silica and pseudopodia that radiate from the central body. | radiolarian,  |
| The process by which ciliates exchange haploid micronuclei is called _____. | conjugation (This is the same name given to the process in prokaryotes in which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another via a long pilus.) |
| A protist characterized by an anterior pocket, or chamber, from which one or two flagella emerge is called a(n) _____. | euglenid (The euglena pictured below is a classic example. Most euglenids are photosynthetic but can switch to a heterotrophic mode of food acquisition when light is unavailable.),  |
The protist pictured below is called a(n) _____.,  | euglena (a common freshwater alga),  |
| Photosynthetic protists are commonly called _____ and can be either unicellular or multicellular. | algae |
| A membranous sac formed by phagocytosis is called a(n) _____. | food vacuole,  |
| The tiny infectious apicomplexan cell that spreads disease is called the _____. | sporozoite |
| Algae and photosynthetic bacteria that drift passively in the pelagic zone of an aquatic environment are called ____. | phytoplankton |
The cross section shown below shows the typical "9+2" structure of eukaryotic _____ and _____.,  | cilia, flagella,  |
| A short cellular appendage specialized for locomotion, formed from a core of nine outer doublet microtubules and two inner single microtubules ensheathed in an extension of plasma membrane. | cilium (The plural is cilia. The key word here is short. Otherwise it could be a flagellum) |
| A type of protozoan characterized by great flexibility and the presence of pseudopodia is called a(n) _____. | Amoeba,  |
| _______ are cellular extensions of amoeboid type cells used in moving and feeding. | Pseudopodia,  |
| A protist that has modified mitochondria, two equal-sized nuclei, and multiple flagella is called a(n) ______. | diplomonad (Giardia intestinalis is a species classified as a diplomonad.) |
| The most common type of multicellular seaweeds, including kelp, are classified as _____ algae. | brown (The giant kelp in this kelp "forest" are brown aglae.),  |
| A(n) is a type of protist that has unicellular amoeboid cells and multicellular reproductive bodies in its life cycle. | cellular slime mold (Cellular slime molds are different from plasmodial slime mold in that the large aggregate retains cell membranes in between the cells that have come together. Also, only the zygote is diploid and there are no flagellated stages.),  |
| The term _____ refers to mostly microscopic organisms that drift passively or swim weakly near the surface of oceans, ponds, and lakes. | plankton (Some larger organisms such as multicellular floating seaweed, most jellyfish, and the Mola Mola fish are classified as plankton also. The fish is classified as plankton because it is not a strong enough swimmer to swim against ocean currents.) |
| The type of protists that are believed to have given rise to true plants are called _______. | green algae |
| A process in eukaryotic evolution in which a heterotrophic eukaryotic cell engulfed a photosynthetic eukaryotic cell, which survived in a symbiotic relationship inside the heterotrophic cell. | secondary endosymbiosis,  |
| A(n) ______ is a type of protist that contains a single, large mitochondrion that contains an organized mass of DNA called a _____. | kinetoplastid, kinetoplast,  |
| A seaweed's body is referred to as a ____ because it lacks "true" roots, stems, and leaves. | thallus,  |
Letter "A" in the picture below refers to the ____ of a seaweed.,  | blade,  |
Letter "B" in the picture below refers to the ____ of a seaweed.,  | float,  |
Letter "C" in the picture below refers to the ____ of a seaweed.,  | stipe,  |
Letter "D" in the picture below refers to the ____ of a seaweed.,  | holdfast,  |
| The ____ is the term that refers to the hardened shell of some protists, including forams and radiolarians, or the rigid endoskeleton of a sea urchin or sand dollar. | test,  |
| ______ are photosynthetic marine protists that contains the accessory pigment phycoerythrin. | Red algae |
| The rootlike structure that anchors seaweed is called the ______. | holdfast,  |
| Trichomonas vaginalis is a type of Parabasalid protist with modified mitochondria that is a common inhabitant of the _______. | human vagina (This flagellated protist can gain a foothold in the vagina when the normal pH is disturbed, allowing it to outcompete other favorable microbes that inhabit the vagina.) |
| Euglenozoans are unique in that they have a rod of unknown function in their _______. The two best known types of euglenozoans are kinetoplastids with their single large mitochondrion and the euglenids which include euglenas. | flagella,  |
| Kinetoplastids in the genus _______ cause African sleeping sickness and Chagas' disease. | Trypanosoma |
| The clade of protists called the alveolates are characterized by ________ just underneath the plasma membrane. This clade includes the dinoflagellates, the parasitic apicomplexans, and the ciliates. | membrane-bounded sacs |
| Algal blooms of certain types of dinoflagellates cause a phenomenon called ______ in which toxins produced by these algae cause massive fish kills. | red tide,  |
| An explosive growth in the population of algae is known as a(n) ________. | algal bloom |
Red tide is caused by a neurotoxin released by a type of ________.,  | dinoflagellate,  |
___________ dinoflagellates glow in the water like fireflies when disturbed.,  | Bioluminescent (You can often see this at night if you are on a boat out at see looking out at the wake left by the boat's propeller.) |
| The common name for the chrysophytes is ________. | golden algae |
| Golden algae are also referred to as the _______. | chrysophytes |
| The common name for the phaeophytes is ________. | brown algae (The life cycle of a type of brown alga is shown below.),  |
| Brown algae are also referred to as the _______. | phaeophytes (The life cycle of a type of brown alga is shown below.),  |
| The largest and most complex of the algae are the _______. All are multicellular and most are marine. | brown algae (phaeophytes) -- Include the giant kelp which can grow as long as 60 meters.,  |
| The gel-forming substances in the cell walls of algae include ______ from brown algae, and _____ and _____ from red algae. They are used in many food products like pudding, ice cream and salad dressing as thickening agents. | algin, agar, carrageenan |
| In alternation of generation life cycles, the two generations are ______ if the sporophyte and gametophyte are structurally different from each other. | heteromorphic,  |
| In alternation of generation life cycles, the two generations are ______ if the sporophyte and gametophyte are structurally similar to each other (though they differ in chromosome number).. | isomorphic |
| One type of entamoeba is a parasite that causes _______ which causes people to get life-threatening diarrhea from drinking contaminated water. | amebic dysentery (This is the third leading cause of death due to parasites after malaria and schistosomiasis.) |
| The common name for the rhodophytes is ________. | red algae |
The _______ shown below is an example of a colonial organism, meaning that it is a colony of individual cells that work together.,  | Volvox,  |
| Red algae are also known as the _______. | rhodophytes |
| Green algae are divided into two main groups, the ______ and the _____. | chlorophytes, charophyceans |
The protist pictured below is a(n) _____.,  | amoeba,  |
What is "A" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | flagellum,  |
What is "B" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | eyespot (Along with the light detector, the eyespot helps the euglena stay near the surface so it can photosynthesize.),  |
What is "C" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | light detector (Along with the eyespot, the light detector helps the euglena stay near the surface so it can photosynthesize.),  |
What is "D" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | contractile vacuole (used to get rid of water that is continually entering the cell in the freshwater hypotonic environment),  |
What is "E" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | nucleus,  |
What is "F" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | chloroplast,  |
What is "A" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | cilia,  |
What is "B" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | food vacuoles,  |
What is "C" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | oral groove,  |
What is "D" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | gullet,  |
What is "E" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | micronucleus [Paramecium, like other ciliates, stores its genetic information in two types of nuclei. There is usually one large (macro) nucleus and one or more smaller (micro) nuclei in each cell. The macronucleus is polyploid, containing up to 800 copies of each gene, and is transcriptionally active. The micronucleus is diploid and holds the cell's germline DNA, genes which are exchanged during sexual reproduction.],  |
What is "F" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | macronucleus [Paramecium, like other ciliates, stores its genetic information in two types of nuclei. There is usually one large (macro) nucleus and one or more smaller (micro) nuclei in each cell. The macronucleus is polyploid, containing up to 800 copies of each gene, and is transcriptionally active. The micronucleus is diploid and holds the cell's germline DNA, genes which are exchanged during sexual reproduction.],  |
What is "G" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | contractile vacuole (Contracts to squeeze water out of the cell so that it doesn't explode due to being in the freshwater hypotonic environment.),  |