| A | B |
|---|
| Hypothesis | A hypothesis is a tentative explanation of observed behaviors, (designed to guide experimentation,), can be supported or refuted through experimentation or more observation., 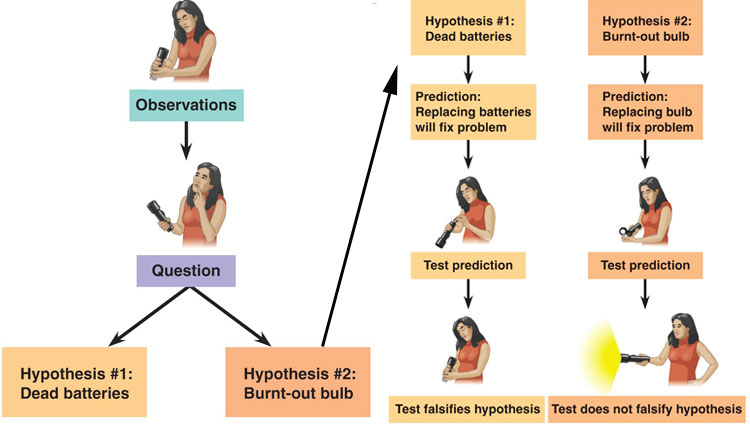 |
Inferences:,  | the process of making a conclusion from facts or hypothesis |
| Conclusion | a reasoned judgment,  |
| Theory | a plausible or scientifically acceptable general principle or body of principles offered to explain phenomena |
| Law | generalizes a body of observations |
Independent variable,  | determines the value of another variable (value is determined by the experimenter) |
Dependent variable,  | value is determined by the value of another variable (responds to changes in the independent variable) |
| Exterior | on the outside |
| Interior | on the inside,  |
Valid,  | reasonable or justifiable in the circumstances |
Toxic,  | deadly: causing serious harm or death |
Nauseous,  | suffering from the unsettling feeling in the stomach that accompanies the urge to vomit |
| Ventilation | the movement or circulation of fresh air,  |
| Function | an activity or role, job assigned to somebody or something |
Suppressed,  | to prevent something from happening, operating, or becoming apparent, or restrain something and limit its effects,  |
| Arid | characterized by a severe lack of available water,  |
| Conclusion | decision based on facts: a decision made or an opinion formed after considering the relevant facts or evidence,  |
Transformed,  | change something completely,  |
| Control | : this will be the part of our experiment that does not receive independent or has everything except the variable you are testing |
Circle Graph, 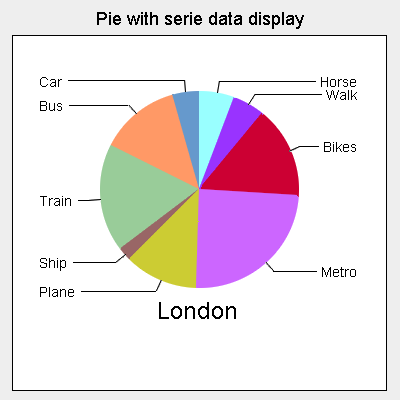 | Pie graphs are used to show how a whole is broken up into its parts. Note parts add up to 100%. |
Histograph or Bar graphs, 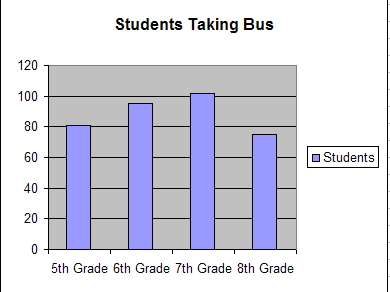 | are used to compare measurements taken from a number of objects or categories. (Demonstrates trend in data) |
Line Graph, 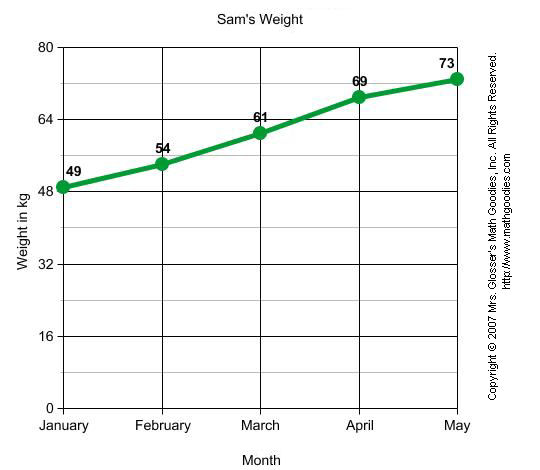 | Bar graphs are used to compare measurements taken from a number of objects or categories. |
| Phenomenon: | a fact or occurrence that can be observed |