| A | B |
|---|
| Animals with two germ layers are ______. | diploblastic (The cnidarians and comb jellies are diploblastic) |
| Another word for "embryonic tissue layers" is "______ layers." | germ,  |
| Another description for "germ layers" is "_____________ layers." | embryonic tissue layers,  |
| A body cavity completely lined with mesoderm is called a(n) ______. | coelom,  |
| _________ is a type of embryonic development in deuterostomes, in which each cell produced by early cleavage divisions retains the capacity to develop into a complete embryo. | Indeterminate cleavage,  |
| Indeterminate cleavage is a type of embryonic development in ________, in which each cell produced by early cleavage divisions retains the capacity to develop into a complete embryo. | deuterostomes,  |
| The hollow ball of cells marking the end stage of cleavage during early embryonic development is called the _______. | blastula,  |
| Animals who develop their mouth before their anus are called ______. | protostomes (Means "mouth first"),  |
| Animals whose mouths develop from the blastopore are called _______. | protostomes,  |
| Animals who develop their anus before their mouth are called _____. | deuterostomes (means "mouth second"), 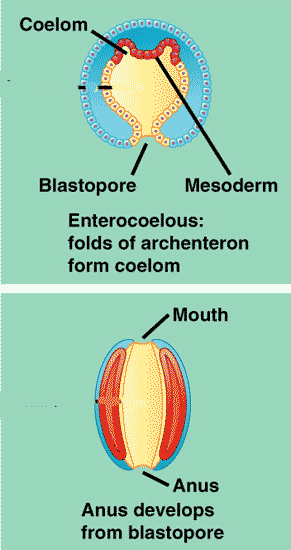 |
| Spiral cleavage of cells in early development is characteristic of _____. | protostomes,  |
| A(n) _______ is a free-living, sexually immature form in some animal life cycles that may differ from the adult in morphology, nutrition, and habitat. | larva,  |
| A proposed clade of animals that include the molting animals (arthropods and nematodes). | Ecdysozoans, 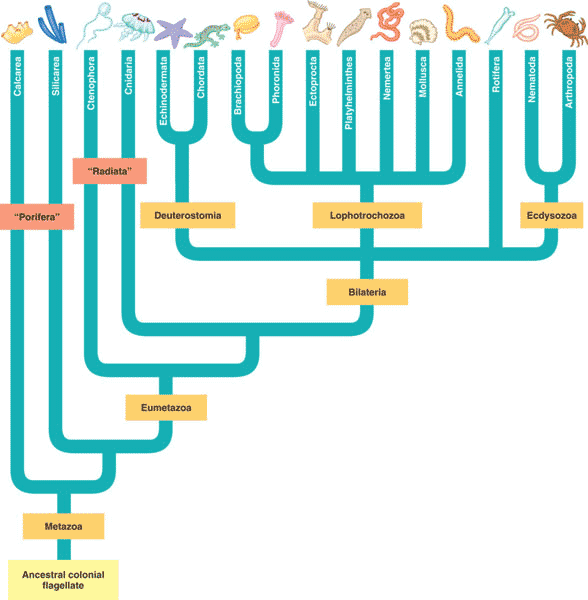 |
| The rear, or tail end, of a bilaterally symmetrical animal is called the _____ end. | posterior |
| A type of embryonic development in protostomes that rigidly casts the developmental fate of each embryonic cell very early. | determinate cleavage |
| The back side of a bilaterally symmetrical animal is the _____ side. | dorsal (think of the dorsal fin of a shark) |
| An animal whose body cavity is not completely lined by mesoderm is called a(n) _____. | pseudocoelomate ("pseudo" means "false"), 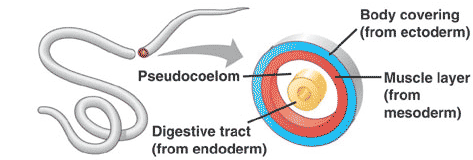 |
| An animal that possesses a true coelom (fluid filled body cavity lined by tissue completely derived from mesoderm) is called a(n) ______. | coelomate,  |
| Animals with three germ layers are ______. | triploblastic |
| True tissues (collections of specialized cells isolated from other tissues by membranes) evolved after sponges. Animals with true tissues are called _______ while sponges are called ______. | eumetazoans, parazoans., 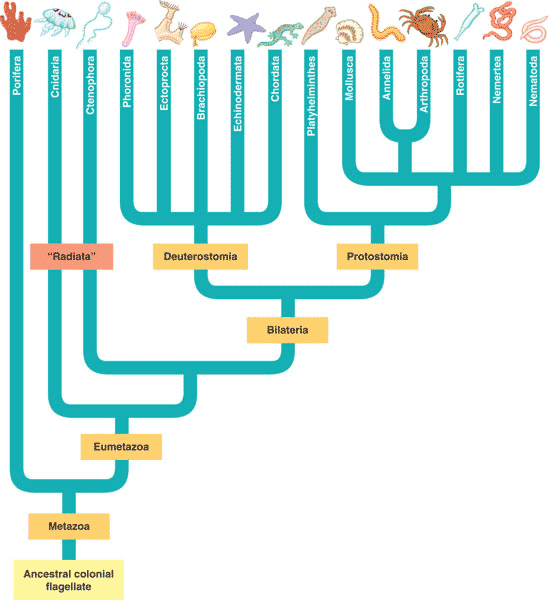 |
| The succession of rapid cell divisions without growth during early embryonic development that converts the zygote into a ball of cells. | cleavage,  |
| The earliest generally accepted animal fossils date back about ______ years ago. | 575 million |
| _______ symmetry is characterized by a body shaped like a pie or barrel, with many equal parts coming outwards from a center point, like the spokes of a wheel. | Radial, 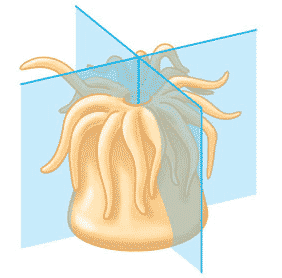 |
| _______ symmetry is characterized by a body form with a central longitudinal plane that divides the body into two equal but opposite halves. | Bilateral,  |
| The ______ is the opening of the archenteron in the gastrula that develops into the mouth in protostomes and the anus in deuterostomes. | blastopore,  |
| Another word for the archenteron is the _____. | digestive tract,  |
| Another word for the digestive tract is the _____. | archenteron,  |
| The primary germ layer of an early embryo that develops into the muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys and most of the circulatory system is called the _____. | mesoderm |
| The underside, or bottom, of a bilaterally symmetrical animal is called the _____ side. | ventral |
| The ____ is the primary germ layer of an early embryo that develops into the outer covering and the ______ system. | ectoderm, nervous system |
| The head end of a bilaterally symmetrical animal is called the ____ end. | anterior |
| Radial cleavage of cells in early development is characteristic of _____. | deuterostomes,  |
| The resurgence of development in an animal larva that transforms it into a sexually mature adult is called ______. | metamorphosis,  |
| An evolutionary trend toward the concentration of sensory equipment on the anterior end of the body plan is called _____. | cephalization ("Cephalo" means "head." This planarian represents one of the earliest types of animal to show cephalization.),  |
| A fluid-containing space between the digestive tract and the body wall is called the ______. | body cavity (its called a coelom if it is completely lined with mesoderm),  |
| The ____ is the primary germ layer of an early embryo that develops into the pancreas, lungs, liver, and the lining of the digestive tract. | endoderm |
| Members of a group of animal phyla with protostome development that some systematists hypothesize form a clade, characterized by lophophore or trochophore larvae. | lophotrochozoans |
| A solid-bodied animal lacking a cavity between the gut and outer body cavity is called a(n) ______. | acoelomate, 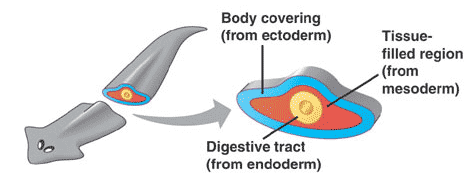 |
| The endoderm-lined cavity, formed during the gastrulation process, that develops into the digestive tract of an animal is called the _____. | archenteron,  |
| A burst of evolutionary origins when most of the major body plans of animals appeared in a relatively brief time period between 525 and 545 million years ago is called the _____. | Cambrian explosion |
| The formation of the gastrula from the blastula is called _____. | gastrulation,  |
| In embryonic development, infolding of the blastula marks the start of _____. | gastrulation,  |
What process is happening in "A"?, 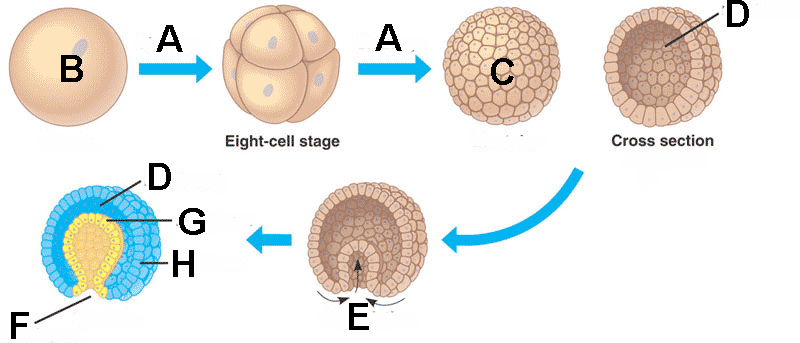 | cleavage,  |
What is "B" called?,  | the zygote,  |
What is "C" called?,  | the blastula,  |
What is "D" referring to?,  | the blastocoel (The root word "-coel" refers to "cavity. Think about coelom.),  |
What process is "E" referring to?,  | Gastrulation,  |
What is the opening that "F" refers to called?,  | the blastopore (This is the opening that develops into the mouth in protostomes and the anus in deuterostomes.),  |
Which germ layer is "G" pointing to?,  | endoderm,  |
Which germ layer is "H" pointing to?,  | ectoderm,  |
What is the last structure (labelled with the letters D, F, G, and H) called?,  | gastrula (an early stage in embryonic development),  |
What is the arrow labelled "1" pointing to?, 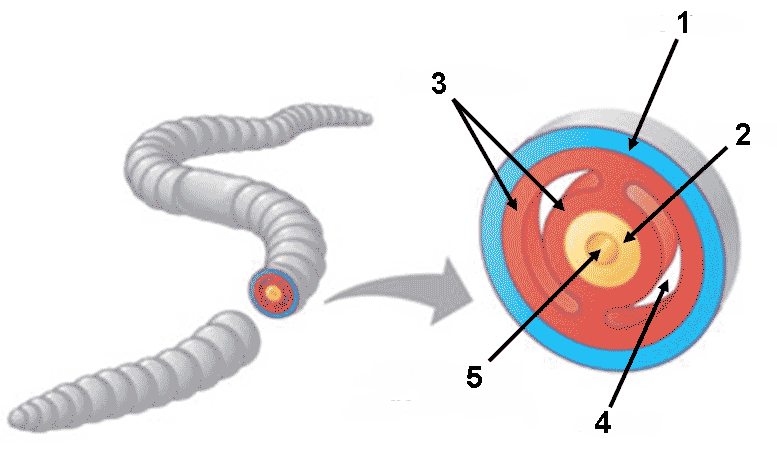 | ectoderm,  |
What is the arrow labelled "2" pointing to?,  |  |
What is the arrow labelled "3" pointing to?,  | mesoderm,  |
What is the arrow labelled "4" pointing to?,  | coelom (pronounced "see - lome"),  , , 
|
What is the arrow labelled "5" pointing to?,  | Archenteron (a.k.a. gut or digestive tract),  |
What type of symmetry does the organisms pictured below possess?, 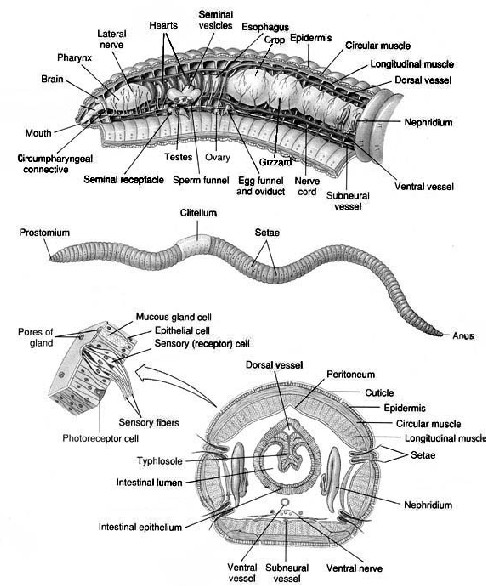 | bilateral (Notice the cross-section of the earthworm. The earthworm has a bilateral internal anatomy. It's external anatomy is also bilateral as the hairlike bristles are found only on the ventral side.),  |
What type of symmetry does the organisms pictured below possess?,  | radial (If you straightened out the legs of this brittle star, you could slice it like a pizza into 5 equal slices.),  |