| A | B |
|---|
| humanism | focus on wordly subjects and not just religious,  |
| Michelangelo | Renaissance- David, Sistine Chapel,  |
| Da Vinci | Renaissance- Mona Lisa, -mona-lisa.jpg) |
| Machiavelli | wrote The Prince- commentary of politics,  |
| Martin Luther | posted the 95 theses against indulgences,  |
| Henry VIII | his need for a divorce caused the English Reformation- formed the Church of England,  |
| Glorious Revolution | Wm and Mary had to sign Bill of rights- limited power of the monarchy |
| Peter the Great | absolute ruler of Russia- wanted to westernize,  |
| John Locke | Enlightenment thinker- natural rights such as life, property, liberty,  |
| Adam Smith | wrote Wealth of Nations- supported laissez-faire or gov't out of industry |
| Estate System | 1st: clery, 2nd: nobles, 3rd everyone else (largest class/least power), 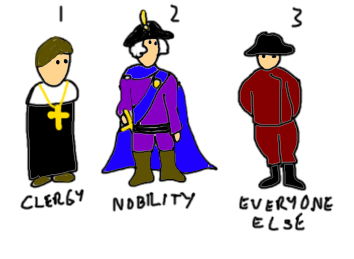 |
| France's debt problem | Supported Am Rev, lavish court of Louis XIV (Versailles),  |
| Ropespierre | Committee of Public Safety- Reign of Terror, 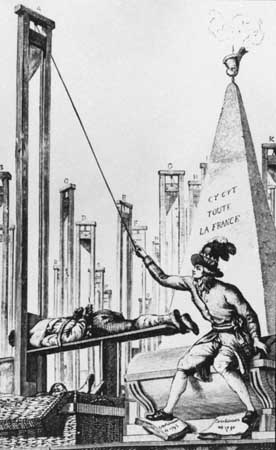 |
| Napoleon | took over as Emperor of France, land reforms, Napoleonic Code,  |
| Waterloo | Napoleon defeated for good |
| Congress of Vienna | to turn the clocks back to before Napoleon- redraw map of Europe |
| Industrial Revolution | began in Great Britain |
| textile industry | where the 1st factories were |
| problems of the Industrial Revolution | tenements, child labor |
| Middle Class | new class due to Industrial Revolution |
| Karl Marx | father of communism; class struggle between the haves (bourgeoisie) and have nots (proletariat) |
| Social Darwinism | the theory of natural selection applied to people- racist element |
| Bismarck | unified Germany through wars- "Blood and Iron" |
| Mazzini, Cavour, Garibaldi | unified Italy - use of nationalism and force |
| Ottoman Empire | sick man of Europe= nationalism tore apart |
| underlying causes of WWI | MAIN |
| Triple Alliance | Italy, Austria-Hungary, Germany |
| Triple Entente | France, Great Britain, Russia |
| event to spark WWI | assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand |
| Balkan Powder Keg | where WWI began |
| Central Power in WWI | Germany, AH, Ottoman Empire |
| Allies in WWI | Great Britain, France, Russia, later Italy |
| weapons in WWI | trench warfare, machine guns, deadlier |
| Economic impact of WWI | raised taxes, factories made war goods |
| Russia left WWI | hurt Allies- 2 front war; Civil War in Russia |
| US entered WWI | Lusitania, Zimmermann telegram, unrestricted submarine warfare |
| Wilson's 14 points | League of Nations, self-determination, safe for democracy |
| Treaty of Versailles | punished Germany severely |
Czar Nicholas II,  | last czar; resisted reform |
Lenin,  | brought to Russia by Germany; brought communism |
| March Revolution | Czar overthrown, provisional gov't |
| November Revolution | Lenin/Bolsheviks took over |
Russian Civil War, 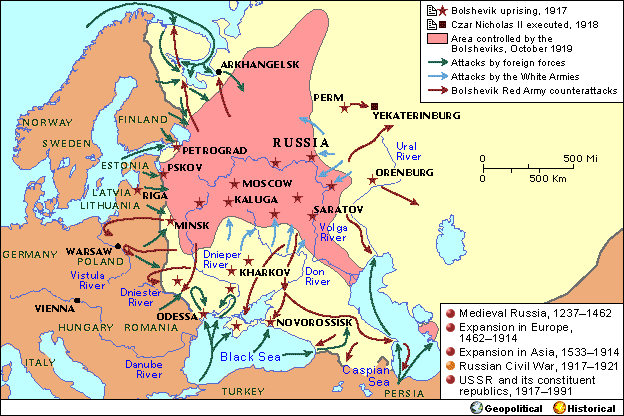 | Reds (Bolsheviks) vs Whites (loyal to Czar) |
| NEP | Lenin's economic plan- some capitalism so Russia could recover |
5 year plan,  | Stalin's economic plan- industrialize Russia |
| farms collectivized in Russia | resisited by farmers; many killed |
| Mussolini | fascist dictator of Italy,  |
| Weimar Republic | Germany after Versailles, inflation problems |
| Hitler | fascist leader of Germany,  |
| fascism | extreme nationalism, militarism, expansion, against Communism,  |
| appeasement | giving in to Hitler's demands, 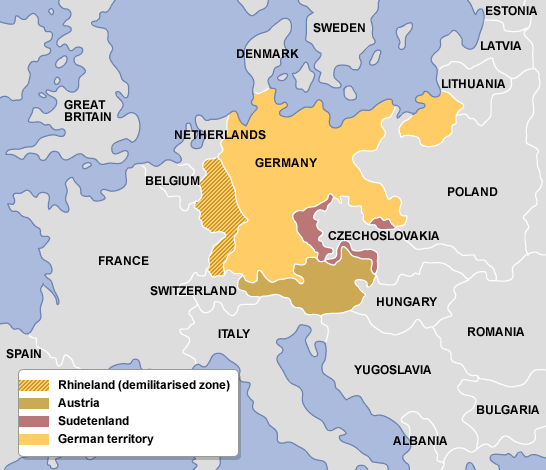 |
| Poland 1939 | Hitler's invasion started WWII,  |
| Battle of Britain | Germany's attempt to make Churchill (British Prime Minister) quit the war |
| Pearl Harbor | Dec 7, 1941; brought US into WWII,  |
| Holocaust/anti-semitism | Hitler's hatred of Jews; the final solution, 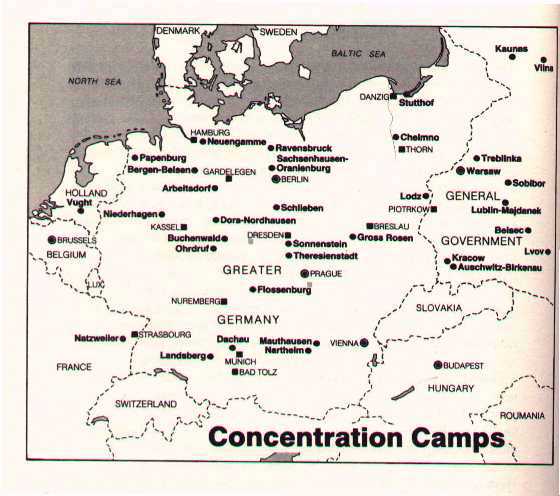 |
| D Day | allied invasion of Vichy, France, 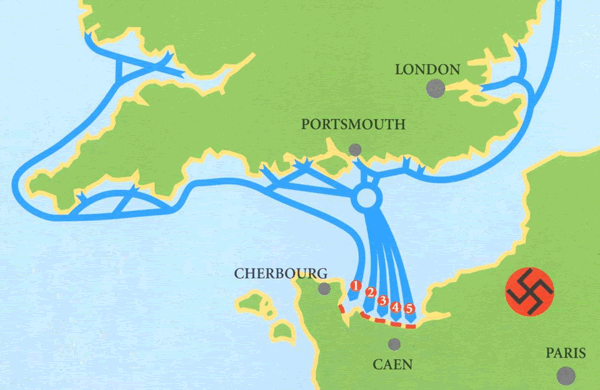 |
| Pacific Theatre of WWII | island hopping, battle of Midway turning point for Allies,  |
| President Truman | President at the end of WWII,  |
| Nuremberg Trials | to try Nazi war criminals for crimes against humanity,  |
| United Nations | to stop another war, modern League of Nations,  |
| Security Council | permanent nations can veto actions by the United Nations |
| Iron Curtain | how Churchill described the Soviet control of Eastern Europe,  |
| Cold War | conflicting ideas led to mistrust (Communism vs. Democracy),  |
| containment | stop the spread of communism- Truman Doctrine,  |
| Marshall Plan | US plan to rebuild Germany after WWII, 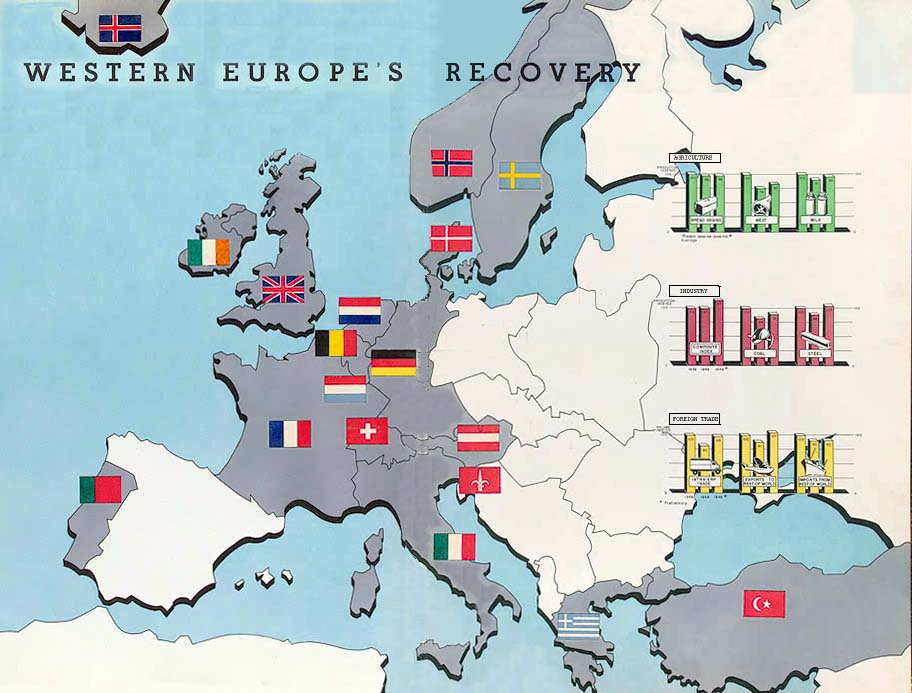 |
| satellite country | dependent states of the Soviet Union |
Warsaw Pact,  | USSR and satellites,  |
NATO,  | allies of Western Europe and US,  |
| Copernicus | Renaissance idea- sun centered model of universe |
| Montesquieu | Enlightenment idea= separation of powers |
| enclosure movement | from the Industrial Revolutio- idea of wealthy to fence off land |
| Great Depression | set the stage for fascism |
Maginot Line, 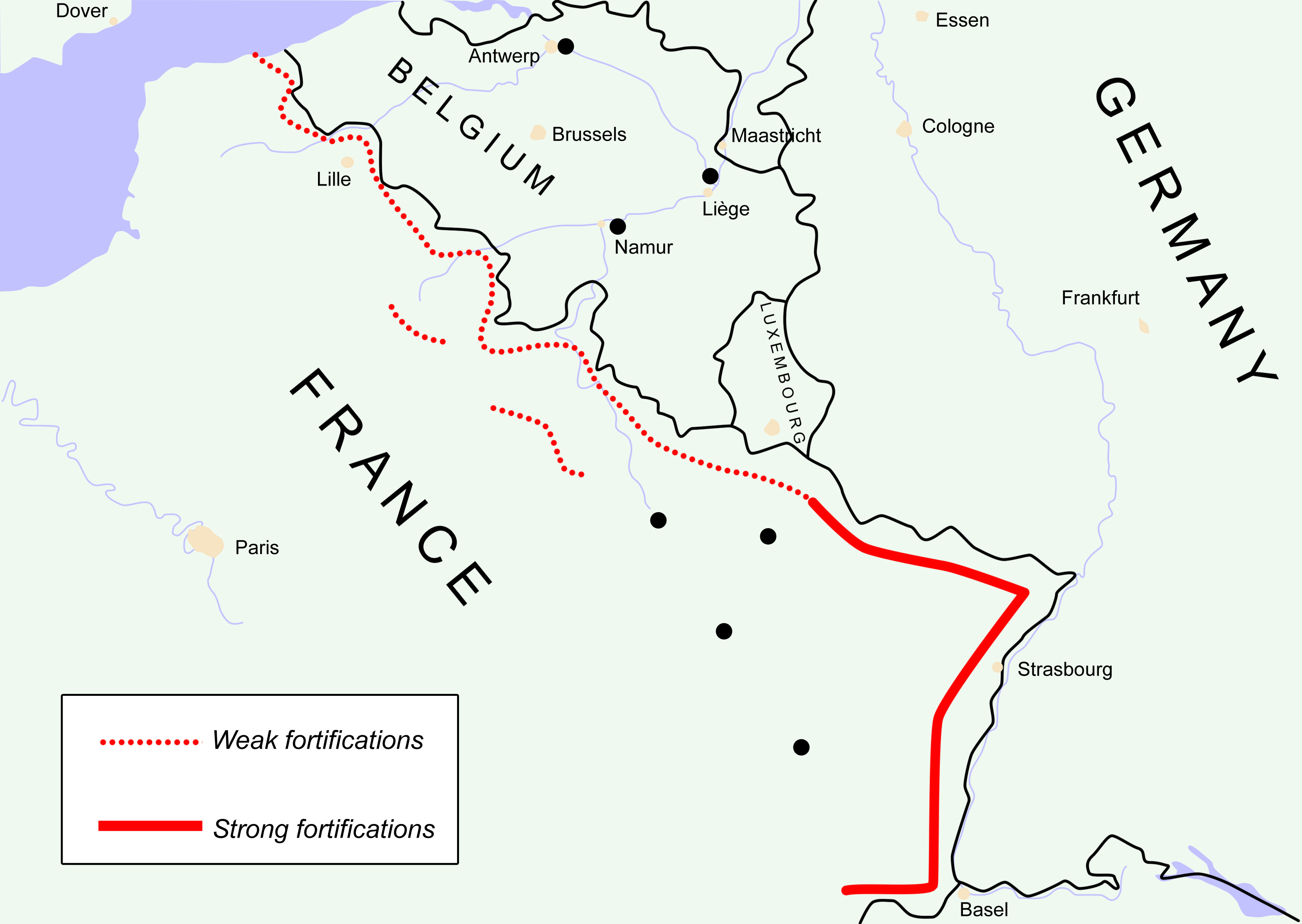 | fortification built by France to stop Germany from invading,  |