| A | B |
|---|
| Three-field system | A system of farming developed in medieval Europe in which farmpland was divided into three fields of equal size and each of these was planted with a winter crop, a spring crop and one field left unplanted., 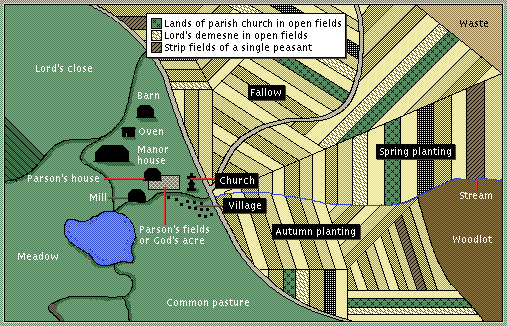 |
| fallow | The term for the field left unplanted in the three-field system. |
| Guild | An organization of individuals in the same business or occupation working to improve the economic and social conditions of its members. |
| Merchant guilds | Merchants banded together to control the number of goods being traded, to keep prices up and for security. |
| Craft guilds | Artisans and craftspeople who banded togather to set standards of quality, set wages and working conditions, and to create a system of educating new members. |
| Apprentice | A young person who was learning a trade or occupation. |
| Journeyman | A trained craftsman or merchant who worked for a master to earn a salary. |
| Master | A shop or business owner who worked with other owners to protect their trade. |
| Commercial Revolution | The expansion of trade and business that transformed European economies and changed life. |
| Fairs | Great international markets held in some medieval towns during certain seasons of the year. |
| Bills of exchange | Established exchange rates between different coinage systems. |
| Letters of credit | Written agreements between merchants for the deposit and delivery of large amounts of money. |
| Usury | Sin of lending money to another Christian for interest. |
| Burr | Term for the wall that surrounded a town. |
| Burghers | Those who lived within the protection of the wall. |
| Suburbs | Area below and outside the protection of the town wall. |
| Charter | A letter of permission from a king given to a town allowing it to govern itself and to make its own laws. |
| Liberal Arts | Education for a “Free Man," usually a churchman. |
| Trivium | "The Three Roads," grammar, rhetoric and logic. |
| Quadtivium | "The Four Roads," arithmetic, geometry, astronomy and music. |
| University | A group os scholars: teachers and students. |
| Bachelors | Students who had completed the trivium. |
| Masters | Students who had completed the Quadtrivium and had passed a disputation. |
| Scholasticism | Method of formal debate using reason, logic, and faith. |
| Plainsong | One-voiced music such as Gregorian Chants. |
| Polyphony | Polyphonic or many-voiced music. |
| Troubadours or Minnesingers | Traveling composers and musicians. |
| Vernacular | The everyday language of a people in a country or region. |
| fabliaux | Fables or "beast tales" in which animals act as humans. |
| Chansons de Geste | Romantic or heroic epics called "Songs of Deeds." |
| Courtly Love | Stories and acts of idealized romantic conduct which allowed noble women to have some control over their lives. |
| Morality Plays | Plays about how life should be lived. |
| Miracle Plays | Plays about the lives of saints. |
| Mystery Plays | Plays about events from the Bible. |
| Dante Alighieri | Italian poet (1265 - 1321) who wrote The Divine Comedy which describes his journey through Hell, Purgatory, and Paradise.,  |
| Geoffrey Chaucer | English author, poet, philosopher, bureaucrat, courtier and diplomat who wrote The Canterbury Tales (1386 - 1400).,  |
| Christine de Pisan | An Italian poet who spent much of her life in France. She wrote The Book of the Cities of Ladies in which she uses famous women from history and literature as building blocks for not only the walls and houses of the city, but also as building blocks for her defense of female rights. |
| Thomas Aquinas | Italian scholar who blended Greek philosophy and Christian doctrine by suggesting that rational thinking and the study of nature, like revelation, were valid ways to understand truths pertaining to God. |
| Summa Theologicae | Great book of Thomas Aquinas that combined Greek thought with Christian thought. |
| Ibn Sina or Avicenna | Persian Muslim scholar whose book The Cure interpreted Aristotle's philosophy for the scholastics. |