| A | B |
|---|
| epithelial tissue | covers organs, forms inner lining of body cavities, lines hollow organs |
| basement membrane | base of epithelial cell or layer of cells; connects to underlying tissue |
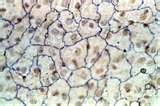 | simple squamous epithelium |
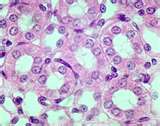 | simple cuboidal epithelium |
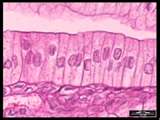 | simple columnar epithelium |
| pseudostratified columnar epithelium | 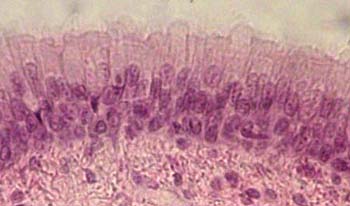 |
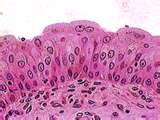 | stratified squamous epithelium |
| stratified cuboidal epithelium | 2-3 layers of cube-shaped cells |
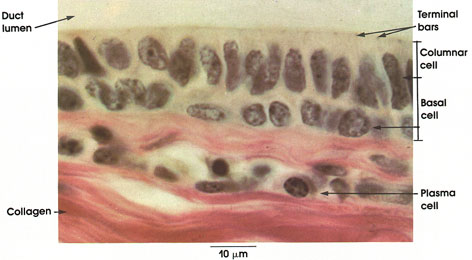 | stratified columnar epithelium |
| transitional epithelium | many layers of cube-shaped and elongated cells; change shape in response to tension |
| ligament | type of dense connective tissue; binds bone to bone |
| tendon | type of dense connective tissue; binds muscle to bone |
| loose connective tissue | beneath skin & epithelial cells, between muscles |
 | adipose tissue |
 | dense connective tissue |
| elastic connective tissue | connects parts of spinal column, in walls of arteries and airways |
 | hyaline cartilage |
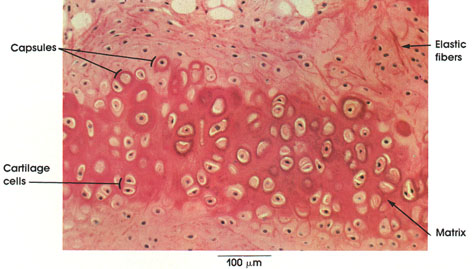 | elastic cartilage |
| fibrocartilage | between bony parts of spinal column, parts of pelvic girdle, knee |
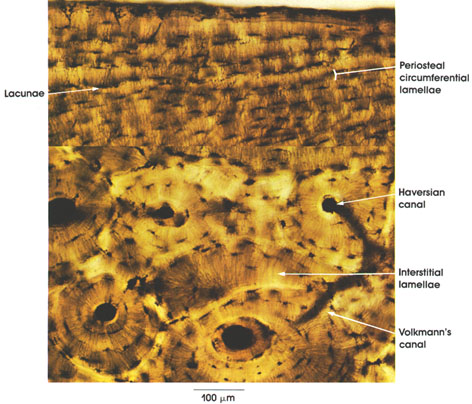 | bone |
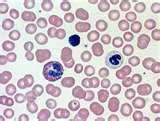 | blood |
| fibroblast | large star-shaped cell; secretes proteins that become fibers |
| macrophage | motile cell sometimes attached to fibers; clears foreign particles from tissue by phagocytosis |
| mast cell | large cell, usually located near blood vessel; releases substances that may help prevent clotting |
| collagenous fiber (white fiber) | thick, threadlike fiber of collagen w/ great tensile strength; holds structures together |
| elastic fiber (yellow fiber) | provides elastic quality to parts that stretch |
| reticular fiber | thin fiber of collagen |
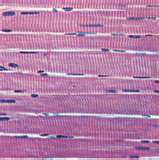 | skeletal muscle |
| cardiac muscle | involuntary, striated, branched muscle tissue |
 | smooth muscle |
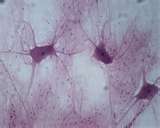 | neuron |
| neuroglial cells | supply nutrients to neurons by connecting them to blood vessels, bind nervous tissue together, phagocytosis |
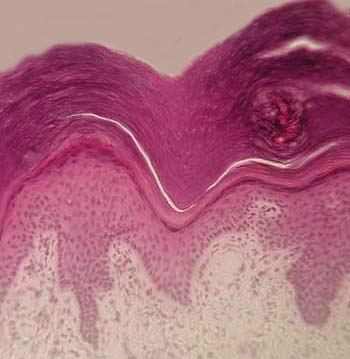 | Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelial |