| A | B |
|---|
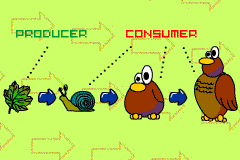 | Food Chain |
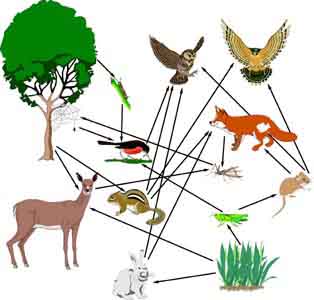 | Food Web |
| The energy contained in food is converted to free energy by the process of | cellular respiration |
| Heterotrophs are | consumers |
| Autotrophs are | producers |
| Abiotic Factors | air, soil, sun are examples of |
| Energy flow in an ecosystem can be described as ___ in which energy later leaves as heat | one-way |
| Where does most of the energy contained in producers end up? | Heat |
| Organisms store energy is the form of | chemical energy |
| All of the Earth's ecosystems together make up the | biosphere |
| Most of these organisms are microscopic | decomposers |
| These organisms are also called herbivores | primary consumers |
| These organisms are also called carnivores | secondary consumers |
| When a population reproduces rapidly, exceeds carrying capacity, and then declines in number it's called | a boom-and-bust cycle |
| Rhizobium bacteria live on the roots of legumes and carry out | nitrogen fixation |
| Chemical reactions in cells need activation energy unless the cells use | enzymes |
| Energy from food is converted to this molecule | 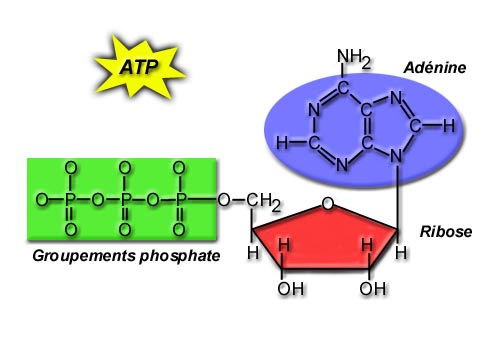 |
| The energy in an ATP molecule is released by breaking the bond between | phosphates |
| Reactions in which molecules are broken down (such as burning food) are | catabolic |
 | An example of mutualism, where both organisms benefit |